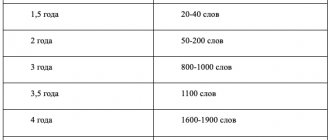
A child’s speech at 1 year of age depends on how the preparatory work for its development was carried out from birth to one year. Humming, babbling and pronouncing the first words prepared the articulatory apparatus for more complex work; the baby's acquaintance with the objects of his immediate environment enriched his passive vocabulary.
At the age of one year, the baby already knows the meanings of many words, the active dictionary contains 10–25 words, and he begins to use speech as a means of communication. He can pronounce words correctly (mama, lalya, baba), babble (pa, ma, bah), partially reproduce the forms of words (“kach” - swing, “zya” - impossible), and imitate the voices of animals and the sounds around him (mu -mu, boo-boo, pee-pee, beep).
At this stage, it is already possible to determine whether there are speech problems. Unlike specialists, it can be difficult for parents to see them, but below we will tell you what signs you can use to independently identify speech problems in your baby.
Physical development of a child at 12 months
By the age of one year, monthly weight gain most often does not exceed 300–350 grams. An unspoken rule is popular among experienced mothers and experienced pediatricians: by 12 months, the baby should triple its birth weight. Indeed, an important indicator for assessing physical development is initial body weight.
The body length of babies also depends on the data at birth and ranges from 70 to 80 centimeters.
You can compare a baby’s weight and height with average values using the standards tables of the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
What can a one-year-old child do?
Children show significant progress in development every year - they sit confidently, crawl, and stand independently. However, now the baby spends all his energy on mastering walking. It is at this time that parents most often watch their baby’s first steps! Some of the children do them very timidly along the support, some - holding on to their mother, and some confidently run towards adventure. Advice: Doctors do not recommend “stimulating” walking by holding a child’s hands until he decides to do it himself. Such actions violate the algorithm for starting walking laid down by nature, and this is fraught with postural disorders in the future. By the way, note: the WHO “window” of achievement for the six main skills of motor development allows a child to master independent walking up to 1 year 4 months.
Also an important milestone in the development of a 1-year-old child is the pointing gesture - the baby points his finger at the desired object. Thus, he draws both his own and others’ attention to a specific object. This is an important indicator of mental development; a number of authors call it a predictor of the appearance of the first words. Normally, the pointing gesture can be formed up to 1 year 6 months.
Self-diagnosis of speech delay
Without being specialists, parents are unlikely to be able to independently determine the cause of the speech defect. They only have access to simple diagnostics. Parents can determine:
- Is the baby's hearing impaired?
- What is the state of the child’s gross and fine motor skills?
- whether the mobility of his articulation organs is preserved,
- to what extent he understands the speech addressed to him.
Hearing test
Hearing impairment is a significant cause of delayed speech development. Without hearing the correct pronunciation of words, the baby will not be able to pronounce them. You can suspect such a pathology if the following symptoms appear over the course of a year:
- the baby does not respond to quiet sounds that are heard outside his field of vision;
- it does not turn towards the source of the sound;
- the child does not show interest in music, the sounds of operating household appliances, electronics;
- the baby does not understand when he is addressed;
- he does not imitate onomatopoeia, there is no babble or simple words in his speech;
- the child does not use his voice to attract the attention of adults.
If you have doubts, you can check your baby’s hearing yourself. To do this, you need an adult assistant and a separate room, protected from extraneous noise. The baby should be invited to play with sounding toys with his mother. Next, the adult uses them to make sounds behind the baby’s back at a distance of at least 6 meters, so that he does not see the source of the noise. If there is no reaction, the distance is reduced by one meter, getting closer to the child with each stage.
You can start the examination by whispering behind the baby’s back, depicting an unusual combination of sounds that should attract the child’s attention. Then these sounds or the baby’s name are repeated in a voice at normal volume. The same procedure is carried out a few days later. If you suspect absence or decreased hearing, you should show the child to an otolaryngologist.
Diagnostics of fine and gross motor skills
It is not for nothing that such great importance is attached to the examination of motor skills. The areas of the brain responsible for the development of speech and fine motor skills of the child are located next to each other. There are no problems with fine motor skills, which means that the mechanisms of speech emergence are preserved, and, most likely, the problem does not lie in the field of neuropathology. Uncertain and uncoordinated movements, inability to make precise movements with the hand and fingers - you need a consultation with a neurologist and a thorough diagnosis.
Indicators of the development of general motor skills by the end of the child’s second year of life:
- He can run;
- climbs stairs well, stepping on each step in turn with one foot;
- jumps up low or jumps over a very low obstacle;
- kicks the ball;
- steps over objects;
- marches, although not too deftly;
- may back away.
Achievements in the development of fine motor skills in a two-year-old child:
- tries to stop the ball rolling towards him;
- he can stack from 4 to 6 cubes on top of each other (“building a tower”);
- the child draws vertical lines or simply “doodles,” although he often holds the pencil or felt-tip pen incorrectly;
- he has a well-developed “tweezer grip,” when the baby takes very small parts of toys or pieces of food with two fingers;
- he strings the rings of the pyramid onto the pin of the stand;
- tears small pieces from a sheet of paper or a piece of plasticine.
To determine the level of development of motor skills, there is no need to organize a special examination; it is enough to carefully observe the child’s movements while awake.
Diagnostics of articulation organs
Anomalies in the structure of the speech organs and impaired mobility can affect the ability to pronounce certain groups of sounds. To detect pathology, it is enough to check the structure of the tongue, jaws, lips, and palate.
Possible problems:
- progeny - the lower jaw is pushed far forward relative to the upper jaw;
- prognathia – the upper jaw protrudes forward;
- open bite - a gap is visible between the closed teeth;
- high and narrow palate (“Gothic”);
- shortened frenulum of the tongue, it is difficult for the baby to lift the tongue upward, it begins to bifurcate in the child like a snake;
- massive or very small tongue.
In addition to these defects, parents may notice increased salivation, tongue trembling, limp lips, and a constantly slightly open mouth. If you have such symptoms, you should immediately contact a specialist. Failure to carry out timely corrective measures can lead to the development of mental retardation and even mental retardation.
Testing speech understanding
To make sure that the child understands the speech addressed to him, he is asked to complete several tasks in a playful way:
- offer to choose one toy from several laid out in front of the baby;
- understands and selects red, yellow, blue and green objects;
- assemble a matryoshka or pyramid
- ask to show things that he uses in everyday life: a spoon, a cup, a chair, slippers;
- offer to show yourself or the doll body parts;
- ask to find an object or action in the picture (they can be cut out from unnecessary magazines and pasted on cardboard);
- offer to fulfill a simple request: bring a book, come closer, give a toy.
The absence of defects in the organs of articulation and understanding of the speech of others with underdevelopment of speech skills may indicate a tempo delay in speech or general underdevelopment of speech. Stimulating classes with a specialist, started as early as possible, will help overcome the gap with peers.
Features of speech and mental development of a 1 year old child
By 12 months, children normally develop their first words that are easy to pronounce: “mama”, “baba”, “bang” - they are also called babbling words. However, now each word has a specific, one and only meaning. A baby's vocabulary is approximately 5–10 words. Speech has an emotional connotation. In addition, active attempts to repeat words after adults continue.
At one year of age, most children actively use simple gestures in everyday life, such as “bye-bye,” nodding their head in agreement and waving their head in denial. Even one-year-old children tend to copy the movements of adults.
How to develop a child at 12 months? With the help of the simplest games and tasks. For example, at this age, many children already have their favorite toys: try to teach your child to clean up after themselves, because putting and taking objects out of a box is one of the favorite activities at this age. Also, many children can show objects in the picture that they are asked about (for example, “Show me the cat”) and easily find hidden things.
Communication skills of a child per year
Due to the next separation crisis, one-year-old children can actively express their dissatisfaction when mom or dad leave, for example, for work. And yes, by this age the baby has already formed his own circle of people with whom he is calm and comfortable. Therefore, an absolutely adequate reaction is embarrassment and nervousness in the presence of strangers.
By the age of one year, some children already develop an interest in other kids, so walks on playgrounds become more and more entertaining.
Introduction
Nowadays, the development of speech in children at an early age is one of the most important and main problems, since not all children develop speech according to established standards. This problem is considered most deeply by Gribova O.E. “What to do if your child does not speak / A book for those who are interested” [3] and Tkachenko T.A. “If a preschooler speaks poorly” [13].
Purpose of the work: to study the stages of development and methods of speech formation in young children.
Object of study: preschool children.
Subject of research: stages of speech development and methods of its formation.
Research methods:
- Research theoretical material on the topic of speech development in young children.
- Formation of a methodological piggy bank for speech development.
Nutrition for a one-year-old baby
At 12 months, as a rule, a child’s diet includes, in addition to breast milk (or its substitute), an extensive range of complementary foods: per year, a child can eat almost everything that his parents eat. After a year, you can already allow your child to try foods that WHO experts and the Union of Pediatricians of Russia do not recommend: honey, fruit juices (yes, due to the high content of natural sugar, this drink is not intended for younger children), nuts and whole cow's milk. milk. The basis of the diet is “adult” food (3-5 times a day), breast milk and its substitutes - at the request of the child.
Two to three years of mastering the grammar of the language
The number of words in the child’s phrases has increased and continues to increase. The sentence is built according to a linear principle: a key word and non-main words. Words in a sentence acquire a grammatical connection.
During this period, the child begins to master changing words by numbers, genders, and cases. But some grammatical categories are difficult for him. Such “difficulties” include the declension of nouns by case, and sometimes the use of the correct gender. For example, a two and a half year old boy can say “I went”, “I did”, and this is the age norm. The most important thing is that during this period the child’s speech becomes understandable regardless of the situation in which it is spoken.
The child begins to think verbally, that is, not only in images, but also in words. Inner speech appears. At three years old, the child begins to master the system of his native language.
Baby's daily routine at 12 months
The routine of a one-year-old child becomes predictable: any mother can easily answer when her child wakes up, when he eats, and when he plays.
The baby's waking time increases to 3-4 hours, daytime sleeps remain at 2. The number of night awakenings for feedings is noticeably reduced (sometimes there are none at all).
At one year old, some parents may note that it is difficult to get their one-year-old to sleep at night. This may be due to the child's increased physical activity, as a result of which the baby becomes overexcited before bedtime. Advice: 30 minutes before bedtime, dim the lights in the house, offer your child quiet games, and stop using gadgets and watching cartoons. Give preference to reading books, a relaxing massage or tactile contact (“cuddling”). This will calm the child and help him fall asleep easier.
It is extremely interesting to observe the development of a child at 1 year old! He becomes independent, inquisitive, mischievous. The task of loving parents is to be there and help taste, fall and rise, make mistakes, smile, be naughty, play and enjoy childhood!
Sources
- Wu Y., Li G., Zheng Y. . // Lin Chung Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi - 2022 - Vol35 - N4 - p.341-345; PMID:33794634
- Voitenkov VB., Komantsev VN., Klimkin AV., Ekusheva EV., Skripchenko NV., Bedova MA. // Adv Gerontol - 2022 - Vol33 - N5 - p.1002-1006; PMID:33550760
- Liu X., Zhong R., Kusuma L., Li N., Tang W. Determining social power: Do Chinese preschoolers integrate verbal and nonverbal cues? // J Exp Child Psychol - 2022 - Vol204 - NNULL - p.104943; PMID:33360276
- Ganc M., Kobosko J., Jedrzejczak WW., Kochański B., Skarzynski H. Psychomotor development of 4-year-old deaf children with cochlear implants: Three case studies. // Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol - 2022 - Vol141 - NNULL - p.110570; PMID:33348125
- Fordington S., Brown T.H. An evaluation of the Hear Glue Ear mobile application for children aged 2-8 years old with otitis media with effusion. // Digit Health - 2022 - Vol6 - NNULL - p.2055207620966163; PMID:33194218
- Jasińska KK., Shuai L., Lau ANL., Frost S., Landi N., Pugh KR. Functional connectivity in the developing language network in 4-year-old children predicts future reading ability. // Dev Sci - 2021 - Vol24 - N2 - p.e13041; PMID:33032375
- Tan LT., Nathan AM., Jayanath S., Eg KP., Thavagnanam S., Lum LCS., Gan CS., de Bruyne JA. Health-related quality of life and developmental outcome of children on home mechanical ventilation in a developing country: A cross-sectional study. // Pediatr Pulmonol - 2022 - Vol55 - N12 - p.3477-3486; PMID:33002341
- Vilela N., Sanches SGG., Carvallo RMM. Development of auditory perception in preschool children. // Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol - 2022 - Vol129 - NNULL - p.109777; PMID:31756662
- Wang J., Joanisse MF., Booth JR. Neural representations of phonology in temporal cortex scaffold longitudinal reading gains in 5- to 7-year-old children. // Neuroimage - 2022 - Vol207 - NNULL - p.116359; PMID:31733372
- Wu Y., Li G., Ma Y., Zheng Y. . // Lin Chung Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi - 2022 - Vol33 - N10 - p.918-922; PMID:31623034