The most important feature of a person is his ability to pronounce sounds, which is facilitated by the structure of the speech apparatus. It is necessary so that people can exchange thoughts and communicate with each other. This is a very complex mechanism, the successful functioning of which requires the coordinated work of each component. The structure is represented by two sections: central (the human brain) and peripheral or executive.
Definition and purpose
In science, the speech apparatus is usually understood as a set of human organs intended for the formation of speech. The central section, represented by the brain and individual formations of the central nervous system, performs a regulatory function. Main destination:
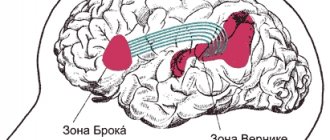
- To form oral speech, the frontal gyrus of Broca's area is necessary, which forms the motor area.
- People perceive the speech of their interlocutor thanks to the speech-auditory area, which includes the temporal gyrus of Wernicke's center.
- The parietal lobe is responsible for understanding.
- The assimilation of words during the perception of written speech (when reading or writing) occurs thanks to the visual zone located in the occipital lobe.
In addition, the diagram of the human speech apparatus includes the peripheral or executive department, which consists of nerves, bones and muscles.
The concept of the speech system and its components. Sound side of speech
Subject, object, purpose and objectives of speech therapy. Connections between speech therapy and other sciences
Speech therapy – (speech training/speech training) is the science of speech development disorders, their overcoming and prevention by means of special training and education.
The object of speech therapy is (a person (speech pathologist) with a speech disorder) is a state of speech and non-speech processes and functions in persons with various speech disorders.
The subject of speech therapy is speech disorders, the process of training and education of persons with speech disorders.
The goal of speech therapy is to develop a system for overcoming and preventing speech disorders, as well as the study, training and education of people with speech disorders.
Objectives of speech therapy:
1. Theoretical:
— study the etiology, pathogenesis (mechanism), structure and symptoms of speech disorders;
— identify individual characteristics of speech development (speech ontogenesis) in various disorders;
- characterize the mutual influence of speech and a person’s personality (logopsychology or psychologists of persons with speech disorders);
— to study the features of speech formation in children with various developmental disabilities (intelligence, hearing, vision, musculoskeletal system);
— develop examination methods and techniques for eliminating speech disorders in children and adults.
2. Practical:
— development of methods for overcoming speech disorders in persons with various developmental disabilities;
— to provide a scientific basis for the organization of speech therapy assistance in Russia.
Speech therapy is associated with many sciences. Traditionally, speech therapy connections are divided into intrasystem and intersystem.
1. Intrasystem communications include
a) pedagogical block: pedagogy (methods, techniques of teaching and upbringing), special pedagogy, methods of preschool education and methods of speech development (preschoolers), methods of teaching the Russian language (schoolchildren), speech therapy rhythms
b) psychological block: psychology, special psychology, psychodiagnostics, pathopsychology (persons with developmental pathologies - schizophrenics), neuropsychology (higher mental functions), psycholinguistics*
2. Intersystem connections include:
a) medical and biological block: pediatrics, genetics, neurophysiology and internal medicine, neuropathology (we do not have the right to make a diagnosis without a conclusion), otorhinolaryngology, psychopathology.
b) linguistic block: phonetics, lexicology, morphology, syntax, psycholinguistics.
*from psycholinguistics, a speech therapist especially needs theories of the origin and perception of speech utterances
The concept of the speech system and its components. Sound side of speech
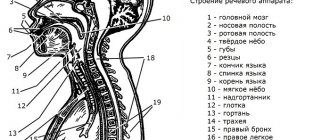
Features of the executive department
It includes three major structural divisions. The first is the respiratory section. Its activity, which is a sequence of inputs, exhalations and pauses between them, is regulated by the central nervous system. The main working “tool” is the diaphragm, which expands and contracts, due to which the lungs change volume and produce inhalations and exhalations. In this case, an air stream is formed, which is important for the formation of the voice; the clarity of the pronunciation of speech sounds depends on its intensity. In addition, the respiratory department includes:
The functions of the air stream are voice-forming and articulatory. The sound is formed when you exhale, and the inhalation when speaking becomes deeper and shorter. The number of respiratory movements performed during speech is much greater than directly during physiological breathing. The volume of air inhaled and exhaled during conversations is three times greater than during normal inhalations and exhalations.
Voice education
In the structure and functioning of the speech apparatus, the vocal section plays the most important role; it is responsible for the formation of the voice and its characteristics - timbre, strength, pitch. It includes the larynx and vocal cords, which, vibrating under the influence of an air stream, produce sounds.
The larynx is a tube consisting of soft tissues and cartilage; in its upper part it passes into the pharynx, in the lower part into the trachea. In the place where the larynx connects to the pharynx, the epiglottis is located, which serves as a kind of valve when swallowing: by descending, it prevents pieces of food and saliva from entering it. Organ Features:
The power of the air environment determines the strength of the sound, and the pitch and timbre of the voice depend on the size of the ligaments, their elasticity and degree of tension.
In addition, resonators, which include the pharynx, oral and nasal cavities, also influence the specificity. They change their volume, that is, they resonate, due to which the sounds acquire strength and overtone coloring.
Making sounds
The articulatory department, which includes the tongue and lips, jaws, alveoli, and palate (hard and soft), is responsible for this important process. In science there is a classification of them into active (moving) and passive (stationary). The first group includes the tongue, lips, soft palate and lower jaw; all others belong to the passive category. The profile of the articulatory apparatus will help you visualize what they look like.
The most important organ of the speech apparatus is the tongue, which takes part in the formation of almost all speech sounds with the exception of labial ones. During articulation, the organs move closer to each other, and closures or slits are formed, which causes the formation of a voice.
The extension tube contains resonators, which are responsible for the clarity and volume of speech. This tube has a specific structure that allows it to change shape and volume. It has two main functions - a noise vibrator and a resonator. The first can be performed by the vocal cords, the gaps between the lips, as well as between the tongue and the hard palate, the tongue and lips, the tongue and alveoli, lips and teeth. Features of the formation of various sounds:
These are the basic structural components of speech and language.
Stages of speech formation
The respiratory section of the vocal apparatus is responsible for supplying air, the vocal apparatus forms the voice, and the function of the articulatory apparatus is to create the resonance necessary for distinct sound and volume. Pronouncing a word consists of several stages. First, commands are selected in the cerebral cortex, that is, a specific articulatory program is formed. Subsequent stages:
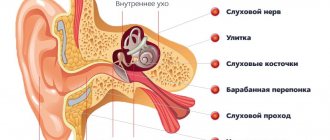
The pathways form the conduction section. Nerve pathways are divided into two types: centrifugal (transmit information from the central nervous system to the muscles, ligaments and tendons) and centripetal (information moves in the opposite direction - from the muscles, tendons and ligaments to the central nervous system). In the second case, the paths are also called sensitive.
Implementation of speech function
Two centers are responsible for the sound of speech: sensory and motor speech. The first helps to perceive phonemes and distinguish them from each other, while the second is necessary for reproducing sounds, words and sentences. In psychology, it is customary to distinguish two types of speech:
- impressive, that is, understanding someone else’s oral and written speech;
- expressive, pronounced out loud with a certain intonation, rhythm, tempo.
It is interesting that a healthy infant in the first year of his life can reproduce up to 75 shortest sounds, that is, at the physiological level he is capable of learning any language in the world. In the future, everything depends on what language is spoken in his family.
To learn to speak competently, every person must understand what subsystems there are in the Russian language. These include:
Speech sounds in Russian are divided into consonants (they are noises) and vowels (tones). The former are divided into voiceless and voiced, hard and soft, and the latter into stressed and unstressed. These signs are usually called semantically distinctive. There are 42 phonemes in the Russian language, of which 36 are consonants and 6 are vowels.
Components of speech in speech therapy
The main components of speech in speech therapy include:
- Sound composition of speech . The study of the sound composition of speech is carried out by such sciences as phonetics, grammar and vocabulary. The sounds that a person makes as part of communication are very important, since depending on the pronunciation, the correctness of the sounds and their sound, people can communicate and perceive information correctly. If one sound component is disrupted, then often we cannot understand what our interlocutor wants to say. For example, a child says “lypa” instead of the word “fish,” that is, he cannot reproduce voiced consonants and pronounce the letter “r.” In this regard, the word sounds incorrect and the other person will not be able to understand the essence of the sentence or phrase said by the child, as a result of which the essence of communication is lost or it becomes impossible;
- Vocabulary composition of speech . Speech consists of words that are generally accepted in society and have the same meaning, regardless of the phrase in which it is used. Therefore, all people can communicate using words that are in dictionaries. Each word sounds correctly and has stress on a specific syllable. If you don’t know the right words or interpret them incorrectly, then communication will become either completely impossible or one-sided. For example, a child uses words in his vocabulary that are not known to others, usually made up words that only he or he and his friends understand. In this case, the vocabulary of the child’s speech does not correspond to generally accepted vocabulary standards, so communication will raise many questions from other people;
- The grammatical composition of speech . Grammar is a set of letters, syllables, that form words. The correct arrangement of syllables in words, phrases, as well as the correct formation of sentences is the main component of speech. If, for example, a child confuses syllables in words, changes them in places, without understanding the meaning of the word, then it will be difficult to understand the child. This speech defect is also eliminated by a speech therapist.
The components of speech are important elements of communication in general. If at least one speech component is impaired, the meaning of all communication is lost, it becomes difficult and raises many questions.
Possible problems
The structure of the voice apparatus, as well as the functional features of each of its departments, will help you work out what problems may arise. In speech therapy, it is customary to distinguish several types of disorders:
In addition, children may experience delayed speech development (SDD), the essence of which is the inability to pronounce certain sounds, the inability to express emotions, and lack of control over intonation. Also included in the developmental developmental disorder are underdeveloped vocabulary, the absence of phrasal speech in 2-year-olds, and the absence of coherent speech in 3-year-olds. These defects should be eliminated as soon as possible by contacting speech therapists, otherwise they may cause the child to be unable to learn to write and read normally.
The vocal apparatus is the most important part of the human body; it helps people communicate with each other and find their place in society. For this reason, any problem detected in early childhood must be addressed immediately.
Previous
Anatomy Digestive process physiology of the human digestive system, functions of the gastrointestinal tract, sequence of processes, significance for the body
Next
AnatomyBlood pressure definition, types, optimal indicators for humans, causes and signs of high and low blood pressure, units of measurement
Environment as a factor in speech development
The environment itself is also an important factor. Children learn a special variety of language (dialect) that is spoken by almost all the people around them.
However, children do not learn only by imitating others. We know that children work on language rules on their own because they use forms that adults never use, such as “I went there before” or “I see your feet.” Children learn common forms over time, step by step, as they themselves recognize exceptions to the rules of syntax.
Just like walking, learning to speak takes time to develop and practice in everyday situations. Constant correction of children's speech is usually unproductive.