Scientific Style: Freepick Did your teacher or supervisor send your report back for revision because of the presentation style? Abstracts and term papers, graduation projects - all this is written by schoolchildren and students using a scientific style. Examples from articles, monographs, textbooks and manuals will help you understand how a scientific style text differs from a regular one and how to create it.
Historical excursion
In Ancient Greece, the privileged class used special terminology that ordinary people did not understand. It was to this time that experts attribute the appearance of the first signs of the scientific style. All terms were called only in Latin, but over time, scientists began to translate details into other languages.
Narrow-profile areas of activity began to expand. Initially, the scientific style of speech differed little from the artistic one, but over time, characteristic features began to appear and the style became clear and concise.
As an example, we can recall Descartes’ negative review of Galileo’s works. The French philosopher and mathematician believed that the Italian physicist tended to use a large number of artistic devices in the text. Kepler also held a similar opinion. For a long time, the standard of style was the work of Isaac Newton. Everyone tried to imitate him in their works.
In the Russian state, a style for scientific work began to take shape only at the beginning of the 18th century. Mikhail Lomonosov especially helped in its development, who developed certain characteristics of the style.
The formation process was finally completed in the 19th century and was associated with the activities of major scientists. Today, the style of scientific works has a number of features that make it easy to distinguish it from other styles of the Russian language:
- Logicality - all parts of the text have a strict sequence and end with a conclusion. Sentences are linked by repeating nouns and demonstrative pronouns. Adverbs, conjunctions, and introductory words also indicate consistent presentation.
- Precision - all words are used only in the literal sense. Terminology is widely used. Key phrases may be repeated many times.
- Objectivity - describes the results of experiments and the patterns that were identified.
- Generalization - when writing a text, the author uses abstract concepts that are almost impossible to imagine, feel, or understand.
If necessary, the text is illustrated with graphs, diagrams, diagrams. You can apply formulas, calculations, and make tables. The author’s task is to fully disclose the topic.
Style Features
It is unusual for scientific texts to use exclamatory sentences and express subjective opinions. The use of emotionally charged words, false facts, and insults is not allowed.
Genres of scientific style - monograph, article, review, textbook, report at a scientific conference, etc. All these genres can be combined into one group - primary, i.e. texts that were created by the author for the first time. Based on scientific works, secondary texts are created - abstract, report, synopsis and others.
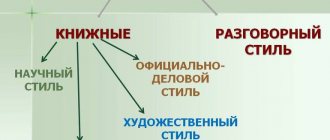
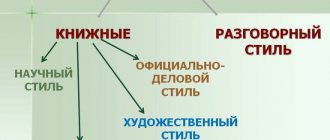
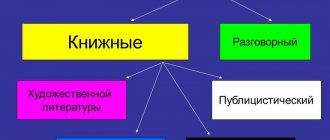
There are several substyles of scientific style:
- Properly scientific - focused on scientists. Used for writing dissertations, articles, reports, etc.
- Scientific and educational - for students of schools and other educational institutions. The material should be presented clearly and presented according to the principle “from simple to complex.” Used for writing textbooks and other manuals.
- Popular science - for ordinary people. Much information is presented in a general form accessible to everyone. The author makes significant simplifications of the information, gives definitions of terms, which are accompanied by simple examples. Used to write children's encyclopedias, popular science books, etc.
- Scientific and technical - aimed at technical specialists. It is used to describe skills and abilities that have been acquired through practical means. Accompanied by background information in the form of statistics and other characteristics.
The style has several functions. The first is a description of the world as an object of knowledge, the second is a presentation of data that was obtained through research, the third is the impact on the reader. The text should encourage interest in scientific information and achievements.
Sometimes this style is confused with a business style, which has its own characteristics. It involves a brief summary of the material and is intended for the preparation of various documents. Scientific publications imply the presence of not only information, but also facts that prove it.
Journalistic texts
The task of this functional style of literary language is not only to convey information to the reader or listener, but also to have a certain psychological impact on him and to arouse public interest . It is divided into five substyles:
- newspaper and journalistic - informational articles, notes and reports, interviews;
- propaganda - leaflets, posters, appeals;
- political-ideological - official substyle used in party resolutions;
- mass political - used at rallies, public speeches and other public events of a similar nature.
In the classification table, the journalistic style occupies an intermediate place between official and artistic everyday styles. From the former he adopted standardization and rigor, from the latter - expressiveness and emotionality. Other features of this style:
- information saturation;
- simplicity and accessibility of presentation, targeting the general public;
- elements of appeal, declarativeness;
- a combination of imagery and brevity in the expression of thoughts;
- constant use of emotional amplifiers;
- commitment to a certain position or idea, value judgments;
- motivational words and phrases;
- the presence of speech cliches characteristic of business and newspaper language;
- use of socio-political terminology, including labels (pseudo-democrats, fascists);
- first person presentation;
- addressing the reader directly;
- use of rhetorical questions and exclamatory sentences;
- reverse order of parts of speech in sentences;
- minimal use of negative words;
- an attempt to play on the reader’s feelings, an attempt to hurt his emotions.
Journalistic texts must interact with the reader and motivate him to action. Therefore, all information posted must be understandable and accessible to a wide audience.
Choosing the right speaking style is important to convey information completely and accurately to readers. The use of syntactic and morphological structures, intonation, speech stamps, artistic means and other language tools is necessary to fulfill the main task of the text.
Linguistic characteristics
Each style can have its main characteristic features - lexical, morphological, syntactic. The linguistic features of the scientific style include the use of certain vocabulary.
Its distinctive features:
- words are used only in the literal sense;
- artistic means of expression are not used - metaphors, hyperboles, epithets, etc.;
- abstract sentences and terminology are used.
Three groups of words can be used in the text - those with stylistic neutrality, general scientific and highly specialized. The use of terms depends on the substyle and audience. For example, in popular science books it is undesirable to use a large number of special words and a simplified presentation of information is allowed.
Features of morphology:
- a small number of first and second person singular verbs;
- a large number of present tense verbs and verbal nouns;
- adjectives are rarely used.
Syntactic features make it possible to distinguish the scientific style from others. This group may include such features as the use of special phrases, for example, according to experience or according to Newton. “Next” is often used as an introductory word. To logically link sentences use:
- "corresponding";
- "famous";
- “given”, etc.
A large number of complex sentences of complex type are used. With their help, generalizations are made or certain phenomena are described. Conjunctions are used to logically connect sentences.
The text necessarily uses references to the works of other scientists, especially if the author wants to show different points of view on one problem. Sentences include participles and gerunds.
Conversational or everyday
The most common style in modern society. It is used in household, informal-professional, household and other areas. Most often used orally. It develops very quickly and is filled with new speech features. Over time, the distinctive features of colloquial speech move into other styles, enriching them with new linguistic means: words, meanings, lexical constructions.
The main genres of everyday style: personal diary, informal note, personal letter, friendly dialogue or correspondence between two or more people. Its features:
- bright emotional coloring, expressiveness, a large number of interrogative and exclamatory sentences;
- frequent use of interjections, particles, conjunctions, introductory constructions and other words and phrases that do not carry actual meaning;
- permissibility of repetition of words and sounds;
- short, simple sentences;
- incomplete, unfinished phrases, the meaning of which can be understood from the context of the speech situation;
- ease, simplicity, familiarity of presentation;
- the use of abbreviated condensate words (oncoming lane - oncoming lane) and doublet words (city dweller meaning citizen, wolf instead of she-wolf);
- constant use of humor, irony, sarcasm, proverbs, sayings;
- imagery, inclusion of value judgments and personal opinions of the speaker;
- the predominance of verbs and pronouns in speech, the relatively rare use of nouns;
- lack of preparation, improvisation, lack of strict logic and presentation plan;
- free word order in sentences;
- use of diminutive suffixes.
One of the main features of conversational style is the importance of not only the content of the text, but also extra-speech factors such as intonation, facial expressions, gestures, and body language. Their correct understanding is necessary for the correct perception of information in everyday conversation. Knowledge of the speech etiquette of a particular area or community is also key in perceiving the message.
Oral speech
The scientific style of speech is used not only for writing papers. It is widely used in oral speech. It is used when speaking at conferences, symposiums, and seminars. In this case, the style retains its main features - accuracy, logic, objectivity and abstraction.
In oral speech, several genres are distinguished. When monologuing, a person does not take into account the reaction of another person. Varieties of monologue - report, message, defense of coursework or final qualifying work.
Oral speech can also be presented in the form of dialogue. For example, the scientific community may have a discussion. In this case, a discussion of some controversial topic occurs. It should not be confused with scientific conversation. This type is characterized by a calm discussion of the message being listened to. People can exchange opinions and add information.
There are two more types of oral speech - lectures. Training lectures are held to ensure that students have knowledge in the professional field. There are also popular lectures that are focused on obtaining information. They are carried out sporadically and presented in a simplified form.
There are different speech styles in the Russian language. Each of them performs its own tasks and is used in certain conditions. Scientific is found in dissertations, reports, specialized books and other works. When using this style, it is important to adhere to the above rules.