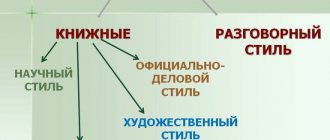
In each communication environment, it is customary to use certain means of expressive language, which are called text style.
In total, 5 styles are used in Russian writing:
- art;
- scientific;
- official business;
- journalistic;
- colloquial.
The scope of use of the conversational style is daily direct communication between people, various discussions on forums and blogs. People simply exchange views, thoughts and feelings, discuss everyday issues. Therefore, this style is often called household.
Briefly about speech styles
There are several of them. Each of them has its own purpose. The artistic style is characterized by emotional coloring and imagery. It is used by authors of prose and poetic works. Scientific speech is found in textbooks, dictionaries, reference books and encyclopedias. This style is also used in meetings, reports and formal conversations.
The author of an article written in a scientific style sets himself the goal of accurately conveying knowledge and information, and therefore uses a large number of terms. All this allows you to clearly express thoughts, which is not always possible to achieve using spoken language.
In colloquial speech there may be words that are not found in reference books. Moreover, approximately 75% of units of the Russian literary language are used by people in any style of speech. For example, words such as I walked, forest, watch, earth, sun, long ago, yesterday. They are called commonly used.
Words such as rectangle, pronoun, multiplication, fractions, set are classified as scientific terms. But about 20% of words in the Russian literary language are used only in colloquial speech. Thus, “electric train” does not appear in the railway directory. Here this word replaces the term “electric train”. What are the features of spoken language?
It is implemented mainly orally. This is precisely what distinguishes spoken language from written language. In the book style, literary norms are strictly observed at all language levels. Among the styles of speech, as already mentioned, there are scientific, journalistic, and official business. All of them have a more general name, namely book. Sometimes artistic style is distinguished as a functional style. However, this point of view raises objections among many linguists. More on the art style below.
Introduction.
People have been named in various ways: homo sapiens (reasonable man), homo fiber (producing man), and homo ludens (playing man). It seems that with no less justification he can be called hom communicans - a person communicating.
Russian thinker Pyotr Chaadaev (1794-1856) wittily remarked: “Deprived of communication with other creatures, we would pluck grass rather than reflect on our nature.” And he was right, since the natural way of a person’s existence is his connection with other people, and a person himself becomes a person only in communication.
The need for communication, according to psychologists, is one of the basic (basic) human needs. The importance of communication as a basic need is determined by the fact that “it dictates the behavior of people with no less power than, for example, the so-called vital (life) needs.” Communication is a necessary condition for the normal development of a person as a member of society and as an individual, a condition for his spiritual and physical health. Although human communication has always been the basis of people’s social existence, it became a direct object of psychological and socio-psychological analysis in the 20th century.
In psychology, communication is defined as the interaction of two or more people, consisting in the exchange of information between them of a cognitive or affective-evaluative (i.e., emotional-evaluative) nature.
Language is the most important means of human communication and an instrument of artistic creativity. The Russian literary language has spoken and written forms of expression. Written speech more strictly follows the rules of word formation and word usage established by normative grammar. Conversational speech is much freer in this regard. There is also a difference in the selection of some linguistic means. When talking with interlocutors, intonation and gestures often free us from the need to use complex and complete sentences and allow us to use rich, emotional words and expressions. We speak differently than we write, and if you record spoken language, it will look so unusual that you will involuntarily want to amend it in accordance with the norms of written speech. However, this should not be done, because colloquial speech is subject to its own norms and what is not justified in book speech is quite appropriate in casual conversation. Spoken speech forms a system that has its own characteristics at all tiers of the language structure: in phonetics (pronunciation, intonation), vocabulary, phraseology, word formation, morphology, syntax.
The role of communication in human life is enormous. Only after the emergence of verbal communications in primitive society was humanity able to move to a new level of development and continue to develop. Communication is characteristic of all higher living beings, but at the human level it takes on the most perfect forms, becomes conscious and mediated, i.e. speech. There is not even the shortest period of time in a person’s life when he is outside this process of life activity, outside interaction with other objects of society. Consideration of the communicative aspect of human life is not only interesting, but also valuable in the light of improving the mutual understanding of individuals in society. In modern life, people make purchases, make deals, and share information every day. The ability to behave with people during a conversation is one of the most important factors determining the chances of achieving success. A person’s success in his business, even in the technical field, depends only fifteen percent on his professional knowledge and eighty-five percent on his ability to communicate with the people with whom he works.
There is nothing simpler, and at the same time more complex, than the process of human communication. It is the source of our joys and sorrows, hopes and successes. There are no professions that do not require communication. The problem of communication - one of the most important and complex in psychology - is considered in various aspects. This:
- a person in the world of communications, in the process, conditions of implementing different forms of life, means of achieving different goals and satisfying different needs;
— structure, types and functions of communication.
Communication is an art and science where not only natural abilities are important, but also education. The effectiveness of work and success in achieving goals largely depends on the level of development of communication abilities.
Communication is a broad, multifaceted concept. A person reading a book communicates with the writer, and the writer communicates with the reader. A person is watching a play, giving a lecture, talking on the phone, talking to a friend - all this is communication. With all the differences in the understanding of the word “communication”, it is necessary to highlight the exchange between people of certain results of their mental activity - acquired information, thoughts, judgments, assessments, feelings. Usually, communication is included in the practical interaction of people: joint work, learning, collective play, etc.
Spontaneity
Conversational speech falls into the category of unprepared speech. It is spontaneous, involuntary. It is created simultaneously with the thought process. That is why its laws differ significantly from the laws of the journalistic style. But they still exist, and even in everyday communication one should remember the norms of the literary language.
Examples of conversational style texts are found in speeches by public and political figures. Some of them have gained fame among the people as the authors of unique sayings and aphorisms. “We wanted the best, it turned out as always,” this phrase became famous. However, it is worth saying that its creator made a gross stylistic mistake. Oratory speech should consist exclusively of elements of journalistic style. The incompleteness of the phrase and emotionality are unacceptable for it.
Differences between colloquialism, slang and jargon
Colloquial speech is similar to slang and jargon, as they are two other ways of informal communication.
The difference is that slang words are used by certain social groups, such as teenagers, while colloquial expressions can usually be understood across age and socioeconomic barriers if all speakers are in the same geographic region.
Colloquial vocabulary may contain elements of jargon, but this is not always the case.
Like slang, jargon is used only by certain groups, but it often refers to words used in a particular profession. For example, the way lawyers speak is so specific to their profession that it is often called "legal."
Other professions that rely on the exchange of complex information also use jargon, such as scientists, doctors, and businessmen.
Functions of spoken language:
- transfer of information;
- communication;
- narration;
- artistic coloring of the text;
- stylistic turns.
Trends in the development of conversational style of speech show a high rate of integration of slang and phraseological units, and pragmatics and stylistics of everyday speech are gaining popularity in all types of information sources. The simpler the better.
Expressiveness
Using everyday conversational speech, people easily share information, thoughts, feelings with loved ones and acquaintances. It is not applicable in every situation. One of the main features of the conversational style of speech is emotionality. It is appropriate in any informal setting.
In everyday communication, people constantly express their feelings, preferences, preferences or, on the contrary, indignation, irritation, hostility. In the examples of conversational style texts there is an emotionality that is not found in journalism.
Without expressiveness it is impossible to create advertising slogans. The main task of a marketer is to instill confidence in consumers, and this can be done by using texts created in the language spoken by potential buyers. An example of a conversational text: “Fly with Aeroflot planes!” If this phrase is put into a journalistic style, it will turn out to be “Take advantage of it!” The second option is more difficult to perceive and hardly evokes positive emotions.
Scheme for performing text parsing point by point
To carry out a stylistic analysis of any text, the following algorithm is used:
- Determine whether there is a main function, what speech tasks there are in the end. Availability of additional functions.
- Highlight the characteristic features.
- By what means can these features be created?
- What genre or scope of application.
- Determine which of these features are inherent in speech: emotionality, imagery, ease, accuracy, vagueness, subjectivity.
- Specifics of speech: phraseology, vocabulary, grammar. (Perhaps give an example passage.)
- Conclusion.
Jargons and dialectisms
Spoken speech is not codified, but it has norms and laws. Certain taboos exist for her too. For example, contrary to generally accepted opinion, profanity should not be present not only in journalistic, but also in colloquial speech. In the dialogue of educated people there is no place for jargon and rude vernacular, unless, of course, these linguistic elements carry a certain emotional connotation. There should be no dialectisms in colloquial speech - signs of lack of proficiency in the orthoepic norms of the Russian language. Although in some cases they are also irreplaceable.
Examples of conversational style of speech are present in prose. In order to be convinced of this, you just have to open any book by Bunin, Kuprin, Tolstoy, Turgenev, Dostoevsky or any other Russian writer. Creating a portrait of the characters, the author endows them with characteristic features that manifest themselves best in the dialogues. In this case, colloquial speech may include both jargon and dialectisms.
The norms of the literary language do not include vernacular language. But they are also often found in everyday speech. Example: “I came from Moscow.” It is worth knowing that the incorrect use of verbs is outside the norms and conversational style.
List of used literature:
1. Psychology and ethics of business communication. Ed. Lavrinenko V.N. 4th ed., revised. and additional - M.: Unity-Dana, 2005. - 415 p.
2. Business communication: Chernysheva L.I. Publisher: Unity-Dana, 2011. – 414s.
3. Business communication - Titova L.G. — Textbook, 2006. – 271s.
4. Borozdina G.V. Psychology of business communication: Textbook.— M.: INFRA-M, 2006. — 224 p.
5. Vvedenskaya L.A., Pavlova L.G., Kashaeva E.Yu. Russian language
and speech culture. – M.: Phoenix, 2011. – 511s.
Attention!
If you need help writing a paper, we recommend turning to professionals. More than 70,000 authors are ready to help you right now. Free adjustments and improvements. Find out the cost of your work
Free estimate
0
Size: 26.64K
Downloads: 146
06/01/13 at 11:30 Author: Svetlana_Skots
Liked? Click on the button below. It's not difficult for you
, and we
are pleased
).
To download test papers for free at maximum speed, register or log in to the site.
Important! All submitted Tests for free downloading are intended for drawing up a plan or basis for your own scientific works.
Friends! You have a unique opportunity to help students just like you! If our site helped you find the job you need, then you certainly understand how the job you add can make the work of others easier.
Add a job
If the Test work, in your opinion, is of poor quality, or you have already seen this work, please let us know.
Art style
Writers use a variety of linguistic means to the maximum extent. Artistic style is not a system of homogeneous linguistic phenomena. He is devoid of stylistic closure. Its specificity depends on the individual style of a particular author. And, as already mentioned, examples of conversational style texts are present on the pages of works of fiction. Below is one of them.
Reading Mikhail Bulgakov’s famous novel “The Master and Margarita,” you can already come across many examples of conversational style texts in the first chapter. Elements of everyday language are present in the dialogues. One of the characters says the phrase “You, professor, have come up with something awkward. It may be smart, but it’s painfully incomprehensible.” If you “translate” this phrase into journalistic language, you get: “Professor, your point of view deserves attention, but raises some doubts.” Would Bulgakov's novel have gained the interest of millions of readers if the characters had expressed their thoughts so dryly and formally?
Such elements of language as jargon and dialectisms have already been mentioned above. In another work by Bulgakov, namely in the story “Heart of a Dog”, the main character - Poligraf Poligrafovich - actively uses profanity in communication with the professor and other characters.
We will not give examples of texts in a colloquial style of speech with an abundance of obscene expressions, which the author included in the work in order to emphasize Sharikov’s lack of education and rudeness. But let us remember one of the phrases uttered by Professor Preobrazhensky, a hero in whose speech, unlike the speech of Poligraf Poligrafovich, there are no syntactic, spelling and other errors.
“If, instead of operating, I start singing in chorus in my apartment, devastation will come,” said Philip Philipovich in a dialogue with his assistant. What is the importance of colloquial speech in fiction? It is impossible to overestimate her role in prose. Being in a state of emotional excitement, the professor, an extremely educated person, makes a semantic mistake (singing in chorus) intentionally, thereby giving the speech a certain irony, without which he would not be able to express his indignation and indignation so clearly.
There are two forms of oral speech: written and oral. We looked at the first one above. Every person uses spoken language every day. It is worth talking in more detail about other features of this important layer of language.
Example of stylistic analysis
Text for parsing:
Tube amplifiers. Compared to transistor ULFs, the incoming resistance of the output tube stage is high - up to several tens of ohms, so the purity and quality of the sound depends on the assembly and quality of the output stage tubes and on the quality of the output transformer, which acts as a matching one.
Example of stylistic analysis:
- The purpose of all the above text is a message.
- The message is in the form of a concept or definition (a feature of tube amplifiers). Most likely this passage is from a textbook or encyclopedia.
- In this way, we can determine the scope of application of this passage - these are lines of a scientific nature, but not of a business nature.
- This passage is accompanied by the following characteristic features: dispassion, objectivity, clarity, accuracy, lack of imagery.
- These features are formed using the following means: the lines are in the nature of scientific terminology, which consist of individual phrases of a terminological nature (resistance of the output tube stage, etc.). The content of the passage does not have emotional vocabulary. Grammatical features: word order in sentences is direct.
- The syntax of the passage confirms that the lines of text are in scientific style.
Diminutive forms and metaphors
In modern colloquial speech there are a large number of zoomorphic metaphors. Bunny, kitty, bird, cat, mouse - all these are words that are not found in scientific articles. A person uses the name of animals in relation to his interlocutor mainly in diminutive forms, and he does this in order to express his favor and sympathy.
But other words are also found in colloquial speech. For example: goat, donkey, ram, snake, viper. If these nouns are used as zoomorphic metaphors, then they have a pronounced negative character. It is worth saying that in colloquial speech there are much more words of negative evaluation than positive ones.
Phonetic features
This category includes features of the pronunciation of spoken language. The most striking of them are the following:
- "abbreviation" of words. Sounds may not be pronounced clearly, and some may be swallowed. Sometimes entire syllables are dropped from words. For example: “zdastye”, “goodbye”, “Ann Sergevna”;
- “stretching” vowels, which helps express an assessment or attitude towards the situation being described. For example, “The bread is so-a-a-a-a-a-a-a-a-a-a!”;
- use of local or regional pronunciations.
Abbreviations
First names and patronymics are used in a truncated form. For example, San Sanych instead of Alexander Alexandrovich. In linguistics, this phenomenon is called prosyopesis. In addition, in everyday speech, “dad” and “mam” are more often used than the words “mom” and “dad”, “mother” and “father”.
In conversation, people actively use aposiopesis, that is, intentionally breaking off a phrase. For example: “But if you’re not home by two, then...” Sometimes authors of literary and journalistic texts also resort to this linguistic device (“If serious changes do not occur in the economy, then...”). But first of all, aposiopesis is characteristic of colloquial speech.
Verb
If you look at one of the examples of conversational texts, you will find that verbs appear more often than nouns or adjectives. In everyday communication, people for some reason prefer words that denote actions.
According to statistics, only 15% of the total number of nouns are used in colloquial speech. As for verbs, preference is given to the present tense in cases where it would be more correct to use the future. For example: “Tomorrow we are flying to Crimea.”
Scientific style of writing text
To determine this style in a text, you need to know its signs and features. Such features are the use of terms, scientific definitions, foreign expressions and words, a large number of neuter nouns (property, attitude), as well as the lack of emotional connotation. The style is also characterized by the logical expression of thought, which promotes a logical connection between sentences and their individual parts. Scientific text, as a rule, often has complex narrative sentences with a considerable number of adverbial and participial phrases.
This may be useful: Derivative analysis of words online.
Other features of spoken language
In everyday speech there are words that, it would seem, in themselves no longer mean anything: thing, thing. For example: “I want to tell you one very important thing.” In addition, colloquial speech is rich in particles: well, even, already, and so on. They are not filler words unless they occur too often. The presence of particles is one of the features of everyday speech.
The conversational style is a full-fledged functional style of language, but it lives according to slightly different laws than the written one. When communicating freely, a person creates statements spontaneously, and therefore they do not always sound perfect. However, even colloquial speech should be monitored so that phrases such as “We wanted the best, but it turned out as always” do not appear.