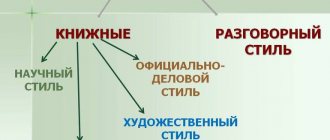
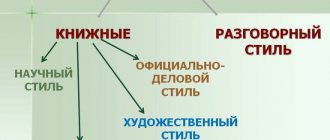
The journalistic style of speech is a unique way of influencing huge masses of people. It is texts of this type that can be traced in various newspaper articles, magazines, and other sources that express the main social problems.
Substyles of journalistic style:
- newspaper and journalistic;
- television journalist;
- radio journalistic;
- direct contact with the audience.
Signs of journalistic style
You can understand that this is the style of speech in question by the following features:
- The validity and validity of statements that are used in speech. That is, the author of the text does not intend to distort reality in any way, but, on the contrary, strives to show the real sides of social life.
- Sentences in the text must be logically connected. People to whom the text is addressed in a journalistic style must clearly understand the problem of the text, its meaning and main idea in order to draw the right conclusions for themselves.
- Using a large number of questions and exclamations to decorate speech during a speech. Such articles are the most motivating and attract society.
- The text is filled with emotions and the author’s evaluative suggestions regarding the problem of speech. Speech is capable of influencing a huge class of people, therefore the text must be for the people. This is what distinguishes the journalistic style of speech from such styles as scientific, business or artistic. It uses colloquial language tools that are understandable to everyone.
- The presence of a socio-political set of words (citizens, democracy).
- Various slangs and short but expressive sentences are used here.
- Frequent use of proper names.
Tasks of analytical genres of journalism
The main objectives of analytical genres of journalism are:
- communication of information;
- its analysis and research;
- justification and commentary on current events, phenomena and facts.
The texts of the analytical genres of journalism contain the author’s reasoning, argumentation, analysis of the event, personal conclusions and assessment of what is happening.
As in the information genres of journalism, the starting point and main element of any analytical genre is a certain fact or event. Events mean those processes that occur in society every day and even every second, and cause certain changes and changes.
Functions
This style of speech performs the following functions:
- Notification
— this function is aimed at transmitting information to a huge audience and, moreover, in a fairly quick period of time.
- Influential
— this function solves the problem of people’s interest in solving the problem being described, that is, the journalistic style of speech is aimed at attracting an audience.
- Conscription
— people should not only be interested in the problem, but should be eager to solve it and take some action.
Analytical report
A report is a chronologically sequential, detailed account of an event. The central element in this case is the description or analysis of people's activities.
Examples: a report on military operations, a report on the results of a meeting, a conference, a government or judicial meeting, a communiqué report on international negotiations.
The report can include not only people’s opinions and judgments on a particular issue, but also their discussions, disputes, remarks, as well as comments from the author himself.
The report relates to both informational and analytical genres of journalism. It all depends on what task the journalist faces. If it is necessary to conduct an author’s analysis of some event, for example, with comments and personal opinion, then we are dealing with an analytical report.
But, if a journalist needs to inform the public about an event, briefly report what happened, and describe the development of the action in strict sequence, then the author is faced with the task of writing an information report.
Scope of application
If the goal of this style of speech is to convey a public problem to the audience, then it is used where there will be the most readers/listeners/subscribers:
- newspapers magazines;
- radio journalism, television journalism;
- speeches by political parties, rallies, calls for strikes, etc.
Analytical genres of journalism: review
Review is a critical review that contains an assessment and brief analysis of a work of fiction, science, art, journalism, etc.
The subject of the review is not just facts, but various information phenomena - performances, books, games, brochures, scientific works, films, television shows.
Examples: book review (examples of reviews are on the Literary Gazette website lgz.ru), review of a play, movie, TV show, game.
Since a review is an analytical genre, its main task is not just to inform about an event or object, but to present this event: analysis, assessment of what is happening, argumentation, personal conclusions and reasoning. But at the same time, a review should not be considered as a means for solving some global social problems. This is done in various studies, literary critical articles or reviews.
Basically, the author of the review (reviewer) studies one or two works and gives them an assessment, often a critical one.
Types of reviews
Depending on the number of works analyzed, two types of reviews are distinguished:
- Mono review. The subject of a mono-review is one work, which the author can compare with other works known to the public. The scope of this review is small.
- Poly review. The subject of a polyreview is two or more works, which, most often, the author compares with each other or with other new or little-known works. This review is impressive in length.
Depending on the topic, reviews can be:
- literary;
- theatrical;
- musical;
- film reviews;
- review of scientific work;
- reviews of advertising clips;
- reviews of animated films;
- game reviews, etc.
Depending on the volume there are:
- Mini-reviews. This is a small review (1-1.5 pages of printed text), in which the reviewer briefly, concisely and without unnecessary digressions gives a reasoned assessment of the work. Mini-reviews are in great demand.
- Grand reviews. This is a large-scale review, in which the topic is thoroughly explored, an in-depth analysis is presented and a comprehensive assessment of the work is given. Grand reviews are usually written by expert critics.
Example of a literary review
Review of E. Remarque’s book “All Quiet on the Western Front”:
"The Other Side of War"
Erich Maria Remarque. - “No change on the Western Front.” Authorized translation from German by Sergei Myatezhny and Peter Cherevin, ed. Abram Efros. Publishing house "Federation". Moscow. 1929 pp. 298. Ts. 1 rub. 40 k.
Among works of art dedicated to the imperialist war, the book by Erich Maria Remarque will occupy a prominent place.
This is not at all because he reports in his conclusions and observations something new, unknown to us. On the contrary, the significance of his narrative lies in the extreme nakedness of well-known facts, in the ability to deprive the war of those heroic illusions from which even Tolstoy was not freed. Already the basic artistic technique ensured the artist the right to our trust: the book was written from the point of view of an ordinary soldier... At the age of eighteen, he volunteered for the war from the last class of the gymnasium and stayed at the front almost until its graduation. A month before November 9, 1918, he died on a day when there was such a calm that the entire report was limited to one remark: “No change on the Western Front.” Hence the title of the book, emphasizing the tragedy of a lonely, lost soldier, keeping his notes...
...All of life in this book comes down to a few elementary experiences that reduce a person to the level of an animal. But the light of reason, illuminating his strange and terrible vegetation, is artistically shaped in the laws of merciless realism. Remarque is strong precisely because he avoids reasoning or unnecessary humanitarian pathetics - he writes down only the facts, and they make a stunning impression thanks to his businesslike, precise style. The composition of the book reveals a great artist in the same way. In a relatively small number of pages, Remarque managed to show the front, the rear, a military hospital, prisoners, and opponents.
...The book clearly shows the simple and peaceful average German, for whom the war was the same misfortune as for everyone else.
K. Locks 1929, No. 21 lgz.ru
Lexical features
Some lexical features of the style can be noted:
- the predominance of colloquial and socio-political vocabulary;
- use of particles and interjections;
- words are colored emotionally, expressively;
- the use of excessive exaggeration - hyperbole.
Analytical genres of journalism: article
An article is a genre of journalism that expresses the author’s reasoned point of view on social processes, on various current events or phenomena.
After reading the analytical article, the reader receives the information he needs and then independently reflects on the questions that interest him.
The subject of the article is not the event, processes or phenomena itself, but the consequences that they cause.
Example: a general research article on the political development of the country, a practical-analytical article on rising food prices, a polemical article (dispute) on teaching the fundamentals of Orthodox culture.
Morphological features
Morphological features include:
- frequent use of synecdoche - the plural is replaced by the singular or vice versa (fathers, grandfathers, Russian, French
);
- frequent use of imperative verbs (look, think
);
- use of all forms of adjectives (regular, comparative and superlative).
Syntactic features
The following apply:
- The use of various figurative and expressive means of language, expressive sentences and tropes to decorate speech (for example: epithets, rhetorical questions, appeals, parcellation, exclamation, gradation, etc.).
- Attractive text title.
- Expressiveness of short sentences.
- Direct speech.
- Separate structures.
Conclusion
In conclusion of the above, I would like to once again emphasize the importance of journalism for modern people. Thanks to her, you feel the spirit of the time, you are always at the center of events, you feel involved in what is happening in the country, the world, and you are formed as a person. In addition, by listening to news, reports, interviews, reading articles, essays in periodicals, on a subconscious level you assimilate the linguistic means of expressiveness of the journalistic style, which helps to increase the level of speech culture.
Linguistic means of journalistic style
Among them:
- epithets
, expressed by evaluative and emotional feelings;
- comparison
using the words
“as”, “as if”
; - metaphor
– transfer of characteristics and properties from one object to another;
- metonymy
- replacing one concept with another.
For example: “Russia is rejoicing”
(that is, the population of the country, Russians); - hyperbola
;
- irony
;
- paraphrase
– avoiding repetition.
For example: “our little brothers”
(animals).
Analytical correspondence
Analytical correspondence is a message that contains information about an event or phenomenon (usually one significant fact).
Analytical correspondence may include fragments of a “live” report or a retelling of what is happening, but such a message must include clarification of the causes of the event/phenomenon, determination of its value and significance for society, and prediction of its further development.
The primary source of such a message is always the author of the publication (correspondent).
An example of analytical correspondence is the description of a rather unusual event - the rescue of a person struck by lightning. The main part of the publication is devoted to this event. In describing it, the journalist uses information received from the victim herself, her parents, her rescuers, and other people. The matter is not limited to the description of the event itself. The author carries out a cause-and-effect analysis of what happened, looking for an answer to the questions that torment Dalia Ralene, her parents, and their friends: why did lightning strike this particular woman? Why did she still end up alive?