A conversational style of speech is on the agenda. If you take and record our everyday conversation, you will most likely get a pun, or, better said, nothing good will come out of this idea at all. Those norms that are applicable for book speech may be completely unsuitable for colloquial speech.
In this article you will learn what a conversational style of speech is, what function it performs, read about the characteristic features, features and genres of a conversational style, and also find examples of this functional style of speech.
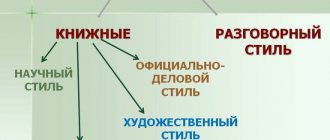
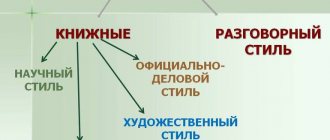
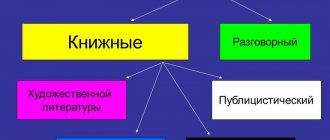
What is a conversational style of speech, its main function and scope of application
Conversational style of speech is a functional style, the main task of which is the direct transmission of information in an informal setting, most often in oral form (exceptions may be diary entries, notes, personal letters).
Thus, the main function of the conversational style is the communication function, which provides everyday, everyday connections between people.
The scope of application of this style is everyday relationships: in the family, among friends and acquaintances, communication with colleagues, in a store, on the street and in any other informal and informal setting.
In addition, the colloquial style of speech is found in artistic and journalistic styles for the purpose of reliable and realistic transmission, for example, a report from the scene of an event or to create the necessary atmosphere, character and appearance of a literary hero.
Read the articles:
- “Features, features, genres and examples of scientific style of speech.”
- “Features, characteristics, genres and examples of texts of official business style of speech.”
To design presentations, printed materials, publications, create logos, business cards or infographics, I recommend using the Canva program. This is a very simple and convenient all-in-one visual editor. With thousands of professional templates, images, and other quality elements, you'll get a great starting point to bring your best ideas to life.
Journalistic style
What are speech styles? These are its functional varieties that are used in one or another area of life:
- journalistic - media style;
- artistic - literature;
- business style is the language of documentation;
- colloquial is used in everyday life;
- scientific - in professional literature.
The scope of application is not the only thing that distinguishes the five existing styles from each other.
How to determine speech styles? Evaluate the text based on several criteria:
- his goal is what idea he wants to convey;
- vocabulary and genre;
- form - oral or written.
What are the features of journalistic style? It is used in media and public speaking. His goals:
- convince the reader (listener) of something;
- convey information;
- evoke an emotion;
- make you think.
Expressive, harsh expressions, value judgments and wordplay are acceptable here:
For the first time in his life and career, the director, who already has a cult status and an army of fans, was awarded a truly significant award.
By the way, “The Shape of Water” was only his second film competing at the festival, and the previous one, “Pan’s Labyrinth,” remained unnominated at Cannes. From outsiders - too strange for Hollywood, too pop for festivals - del Toro suddenly stepped into the favourites. Perhaps because he made his best film, for the first time finding the ideal balance of genre and authorship, universal and personal (Anton Dolin’s review of the film “The Shape of Water”).
Journalistic style of speech: Unsplash
Characteristics and features of conversational style
The characteristic features include :
- Oral form of speech.
- Informality and ease.
- Emotionality (in the form of a live reaction to people’s words and actions).
- Specificity.
- Simplicity and ordinariness of content.
- Use of colloquial vocabulary with a colloquial flavor.
In addition to the above characteristics, the conversational style of speech has a number of features and distinctive features :
- Most often it is implemented in the form of dialogue.
- Language material is not pre-selected.
- Facial expressions, gestures, and the surrounding environment are of great importance.
- Words are used in a figurative sense, there are incomplete sentences, addresses, interjections and particles, repetitions of words.
- The use of emotional words and expressions (nightmare, horror, victory, this is wonderful, etc.).
- Disorganized and fragmented speech (“A kilogram of apples, please.”).
- Intonation plays a special role: raising or lowering the tone, stretching vowels, pauses, changing the tempo of speech.
- Colloquial style vocabulary consists of common words (work, read, book, metro) and colloquial words (potato, giggle, butuz, scribble, hype).
- There are slang words (to fill up a place), colloquial words (dreary, sleepy, crazy) and slang words (teacher), professionalisms (non-cash, cash, turn on the meter), dialecticisms (pitching - duck, kuren - hut).
- Terminological, abstract vocabulary, as well as book words are almost not used.
- Law of economy of speech means. Very often, instead of two words, one is used: condensed milk - condensed milk, sick leave - sick leave; stable combinations are simplified: maternity leave - maternity leave.
- The conversational style is rich in phraseological units: sewn with white thread, touch a nerve, just a stone's throw away.
- To enhance emotionality, doubling of words is used, sometimes with exaggeration: big-very big, black-black water, quiet-quiet.
- Lots of pronouns (I, you, we) and verbs.
- Participles and gerunds almost never occur.
Scientific style
What features are inherent in the scientific style? It is the language of encyclopedias, textbooks, dissertations, monographs and scientific articles. As O. Stycheva, candidate of pedagogical sciences, notes, the scientific style is easy to recognize by the following features:
- professional terminology;
- evidence - the presence of facts, figures;
- strict adherence to spelling or pronunciation standards;
- objectivity and completeness of information.
There is no room for the author's subjective opinion here. The purpose of the text, presented in a scientific style, is to prove the truths revealed through research.
By the way, O. Stycheva’s article also serves as an example of such a text:
A characteristic feature of the style of scientific works is their saturation with terms, including international ones. L.V. Shcherba wrote that on average, terminological vocabulary in scientific information is about 25%, however, the collections of scientific works we analyzed indicate that, in general, the scientific style of Russian speech tends to increase this percentage
.
Scientific speaking style: Unsplash
Conversational style of speech: genres
Depending on the situation at the time of communication, the following genres (varieties) of conversational style of speech in oral form are distinguished:
- Conversation (conversation).
- Phone conversation.
Genres of conversational style in writing:
- A note.
- Communication via the Internet.
- SMS.
- Private letters.
- Entries in a personal diary.
Of course, the main genre of conversational style of speech is conversation or conversation. Depending on the number of participants, this may be a dialogue or monologue.
Dialogue is an exchange of remarks, questions and answers between two or more people. Dialogue is characterized by frequent changes of roles “speaker – listener”, so that the interlocutors alternately act in one or another role. Replies can also express addition, clarification, extension, agreement, objection, encouragement, etc.
Monologue is speech in the first person, addressed to the listener or to oneself, not intended for a response.
In a conversational style, dialogue and monologue in their pure form are rarely encountered: a monologue can be interrupted by remarks from the interlocutors, and the dialogue, in turn, can include mini-monologues and micro-stories.
Linguistic features of everyday language
The linguistic features of the conversational style can be characterized by two epithets - informal and free. It is allowed to use diminutive endings, abbreviations, phraseological units, dialectisms.
Varieties of everyday speech allow you to verbalize the same thought in different words, even those whose meaning does not coincide with the meaning of the object or phenomenon.
For example, “I’m going to the glass” (steklyashka is a glass store or a store located on Steklyanaya Street).
The characteristics of colloquial speech are expressed not only in the context itself. These are also non-verbal signs.
Example text in conversational style
As an example of a conversational style of speech, below are excerpts from the books of the modern (brilliant) writer Fredrik Backman. The spoken language in his works comes out very realistic and lifelike.
An excerpt from Fredrik Backman’s book “Grandmother told me to bow and tell her that she asks for forgiveness”:
Stretching out on the floor, the grandmother rummaged under the bed and pulled out a package. It wasn't meat or cigarettes. These were sweets.
– You must give the chocolate to your Friend.
Several moments passed before Elsa realized which friend she was talking about.
Elsa looked at her grandmother in confusion:
- Bah, are you out of your mind? Do you want my death?
Grandma rolled her eyes.
- Stop being a fool. Are you saying that the knight of Miamas does not dare to go on a mission?
Elsa squinted her eyes offendedly:
- You take it weakly.
- Look at the root! - Grandma grinned.
Excerpt from Fredrik Backman's book Britt-Marie Was Here:
“I’ll sit here until you stop dying.” “If you want to eat, you’ll have lunch,” the Personality grinned and extended her hand to the half-eaten pizza lying on the stool.
- Lunch? Now? – Britt-Marie muttered, because it wasn’t even eleven.
- Do you want to eat? Here's pizza! – invited the Personality.
Only now did what was said reach Britt-Marie's consciousness.
– What do you mean “pulled”? Did they shoot at me? – she exhaled, feeling her head in search of an opening.
- Yes Yes Yes. Hit the head with a soccer ball,” the Personality nodded, spilling vodka on the pizza.
Judging by the look of Britt-Marie, she would prefer a gun to a ball. As a less dirty item.
PS: Did you like the article? Share the link on social networks! Thanks and have a nice day.
Sources used:
- E. Demidova “Style... Style... Style...”.
- GIA. Russian language. Universal reference book. Author: Angelina Rudneva.
- resh.edu.ru
- Photo - dreamstime.com
Morphological features
Morphological features of colloquial speech allow common mistakes in colloquial speech to be integrated into a conversation without special emphasis. Surzhik and dialects are a vivid example of this.
Business conversation, as a special type of oral speech, must comply with all the rules of the language, but the syntax of colloquial speech does not always correspond to the rules of the Russian language. Pronunciation may differ from spelling, but over time, spoken language began to be written down in the text in the same way as it is heard. For example:
I'll go outside today - I'll go outside today.
From a spelling point of view, this is not correct, but the framework of the conversational style allows for such spelling and word formation. The characteristics of everyday style are originality, individuality, and a special color of speech.
Definitions used in the contract
The work is “Russian language for students and freshmen”, created by the author. Description of the work - the manual contains the basic theoretical concepts of the school course of the Russian language and explains the procedure for analyzing language material addressed to students and especially graduates of secondary schools, due to the lack of a single set of textbooks in Russian for secondary schools.
This section reflects the following features of official business style:
- no personal pronouns;
- full names of the characters and their social status;
- Replace them later with special names such as author, company;
- Standardized Sales: This Agreement, hereinafter referred to as the “Agreement”, is based on the following
- exact indication of the place and time of conclusion of the contract;
- complication of a simple sentence of several isolated members;
- Dividing text into blocks using subheadings and numeric characters.