The structure of the human speech apparatus
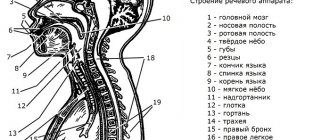
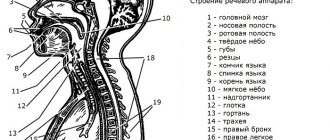
The structure of the speech apparatus in the diagram looks like this:
The speech apparatus is a group of organs of the human body that ensures the organization of the speech process. It includes two interconnected departments: central and peripheral, the so-called executive.
The first is represented by the brain and other formations of the central nervous system, which perform a regulatory function.
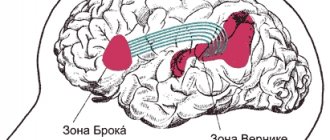
In the formation of oral speech, the main role is played by the frontal gyrus of Broca's center, forming the motor area. Foreign speech is perceived by the speech-auditory area formed by the temporal gyri of Wernicke's center. The parietal lobe of the brain is responsible for understanding.
Word acquisition during writing and reading occurs in the visual area in the occipital lobe. Thus, in childhood, when a child observes the articulation of adults, the development of this area affects his speech.
The executive department consists of bones, muscles, nerves and, in turn, has three divisions through which the speech process is carried out.
Let's talk about each of them.
Respiratory section of the speech apparatus
The breathing process is regulated by the central nervous system and consists of successive cycles of inhalation, exhalation, and pauses between them. In this case, the diaphragm works, with the contraction and relaxation of which the lungs change their volume, allowing inhalation and exhalation.
In this process, an air stream is formed, which, when exhaled, is involved in the appearance of voice and speech sounds. The clarity of pronunciation depends on its strength and direction.
Central department
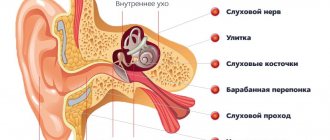
Like other manifestations of the nervous system, speech occurs through reflexes, which, in turn, are connected to the brain. The most important parts of the brain responsible for speech reproduction are: the frontal lobe, the temporal part, the parietal and occipital regions. In right-handed people, this role is played by the right hemisphere, and in left-handed people, the left hemisphere plays this role.
The frontal (inferior) gyri are responsible for the production of spoken language. The convolutions located in the temporal zone perceive all sound stimuli, that is, they are responsible for hearing. The process of understanding heard sounds occurs in the parietal region of the cerebral cortex. Well, the occipital part is responsible for the function of visual perception of written speech. If we take a closer look at the child’s speech apparatus, we will notice that his occipital part is especially actively developing. Thanks to it, the child visually records the articulation of his elders, which leads to the development of his oral speech.
The brain interacts with the peripheral region through centripetal and centrifugal pathways. The latter send brain signals to the organs of the speech apparatus. Well, the first ones are responsible for delivering the response signal.
The peripheral speech apparatus consists of three more sections. Let's look at each of them.
State of the speech apparatus
When all the components of this complex mechanism are functioning properly, the process of speech formation looks like this:
- the brain gives a command to organize speech movements;
- an air stream is formed in the respiratory section, which is directed to the larynx;
- in the vocal tract, the vibration of the vocal folds creates the voice;
- in the articulatory department, sounds are formed, which, thanks to resonators, receive strength and color, and our speech is made up of sounds.
This is when the speech apparatus is working properly. When failures occur, what then? Then various kinds of speech problems arise.
The main causes of disturbances in the functioning of the speech apparatus may be:
- defects in the structure of the speech organs;
- its incorrect operation;
- pathologies of the central nervous system.
Since speech is an important form of communication, speech disorders have a negative impact on all areas of the life of a modern person.
Speech problems need to be taken seriously. Take action in a timely manner and make every effort to eliminate speech deficiencies - this is how you can regain the freedom and joy of communication.
How to maintain the working condition of your speech apparatus? Here are some tips:
- Correct posture improves its functioning - keep your head straight and your back straight.
- If your vocal organs are overloaded, practice relaxing them to restore functionality. To do this, you can perform special exercises, for example, take a resting pose, or just be silent for a while.
- Avoid hypothermia, irritation of the mucous membrane, prevent colds.
- If you want to improve the quality of your speech, train your diction, learn to breathe correctly, and take care of its content.
Production of sounds
Today, the structure of the speech apparatus can safely be considered 100% studied. Thanks to this, we have the opportunity to find out how sound is born and what causes speech disorders.
Sounds are generated due to the contraction of muscle tissue of the peripheral speech apparatus. When starting a conversation, a person automatically inhales air. From the lungs, air flows into the larynx, nerve impulses cause vibration of the vocal cords, and they, in turn, create sounds. Sounds form words. Words - into sentences. And suggestions - into intimate conversations.
Relaxation mask
This simple technique is also very important for speakers and those who, due to the specific nature of their work, talk a lot. There is nothing complicated here either. The essence of the exercise is to alternately tense various facial muscles. You need to “put on” different “masks”: joy, surprise, melancholy, anger, and so on. Having done all this, you need to relax your muscles. It's not difficult to do this at all. Simply make the sound “T” as you exhale gently and leave your jaw in a loose, lowered position.
Relaxation is one of the elements of hygiene of the speech apparatus. In addition to this, this concept includes protection from colds and hypothermia, avoidance of irritants to the mucous membrane and speech training.
Voice department
We continue to consider the sections of the speech apparatus. So, the voice has three main characteristics: strength, timbre and height. Vibration of the vocal cords causes the flow of air from the lungs to become vibrations of small air particles. These pulsations, transmitted to the environment, create the sound of the voice.
The strength of the voice mainly depends on the amplitude of vibration of the vocal cords, which is regulated by the strength of the air flow.
Timbre can be called sound coloring. It is different for all people and depends on the shape of the vibrator that creates vibrations of the ligaments.
As for the pitch of the voice, it is determined by the degree of tension of the vocal folds. That is, it depends on how much influence the air flow can have on them.
Implementation of speech function
Two centers are responsible for the sound of speech: sensory and motor speech. The first helps to perceive phonemes and distinguish them from each other, while the second is necessary for reproducing sounds, words and sentences. In psychology, it is customary to distinguish two types of speech:
- impressive, that is, understanding someone else’s oral and written speech;
- expressive, pronounced out loud with a certain intonation, rhythm, tempo.
It is interesting that a healthy infant in the first year of his life can reproduce up to 75 shortest sounds, that is, at the physiological level he is capable of learning any language in the world. In the future, everything depends on what language is spoken in his family.
To learn to speak competently, every person must understand what subsystems there are in the Russian language. These include:
- Phonetics. The science of speech sounds - phonemes, the rules of their articulation from the perspective of physiology.
- Semantics. Helps to understand the meaning of each lexical item.
- Syntax. Allows you to understand how sentences are formed from individual words.
- Vocabulary. Studying the vocabulary richness of the language.
Speech sounds in Russian are divided into consonants (they are noises) and vowels (tones). The former are divided into voiceless and voiced, hard and soft, and the latter into stressed and unstressed. These signs are usually called semantically distinctive. There are 42 phonemes in the Russian language, of which 36 are consonants and 6 are vowels.
Active organs
As the name suggests, these organs can be mobile and are directly involved in the formation of the voice. They are represented by the tongue, lips, soft palate and lower jaw. Since these organs are made up of muscle fibers, they can be trained.
When the speech organs change their position, constrictions and closures appear in various parts of the sound-pronouncing apparatus. This leads to the formation of a sound of one or another nature.
A person's soft palate and lower jaw can move up and down. With this movement they open or close the passage into the nasal cavity. The lower jaw is responsible for the formation of stressed vowels, namely the sounds: “A”, “O”, “U”, “I”, “Y”, “E”.
The main organ of articulation is the tongue. Thanks to the abundance of muscles, he is extremely mobile. The tongue can: shorten and lengthen, become narrower and wider, be flat and curved.
Human lips, being a mobile formation, take an active part in the formation of words and sounds. The lips change their shape and size to enable the pronunciation of vowel sounds.
The soft palate, or, as it is also called, the velum palatine, is a continuation of the hard palate and lies at the top of the oral cavity. It, like the lower jaw, can move down and up, separating the pharynx from the nasopharynx. The soft palate originates behind the alveoli, near the upper teeth and ends with a small tongue. When a person pronounces any sounds other than “M” and “N”, the velum of the palate rises. If for some reason it is lowered or motionless, the sound comes out “nasal”. The voice comes out nasal. The reason for this is simple - when the palatine curtain is lowered, sound waves along with air enter the nasopharynx.
Relaxation pose
You may have already come across such concepts as posture and relaxation mask. These two exercises are aimed at relaxing muscles or, as they also say, relieving muscle tension. In fact, they are not anything complicated. So, to take a relaxation pose, you need to sit on a chair and bend slightly forward, bowing your head. In this case, the legs should stand with their entire feet and form a right angle with each other. They should also bend at right angles. This can be achieved by selecting a suitable chair. The arms hang down, resting the forearms lightly on the hips. Now you need to close your eyes and relax as much as possible.
To ensure that rest and relaxation are as complete as possible, you can engage in some forms of auto-training. At first glance, it seems that this is the pose of a dejected person, but in fact it is quite effective for relaxing the entire body, including the speech apparatus.
Stages of speech formation
The respiratory section of the vocal apparatus is responsible for supplying air, the vocal apparatus forms the voice, and the function of the articulatory apparatus is to create the resonance necessary for distinct sound and volume. Pronouncing a word consists of several stages. First, commands are selected in the cerebral cortex, that is, a specific articulatory program is formed. Subsequent stages:
- Implementation of the prepared program in the executive department of the vocal apparatus. The respiratory organs and resonator system take part. They help pronounce certain phonemes.
- To avoid errors during pronunciation, kinesthetic control is necessary, which allows you to make corrections before the phoneme is pronounced.
- At the moment the sound is heard, auditory control is carried out, allowing a person to understand the mistake made and correct it.
The pathways form the conduction section. Nerve pathways are divided into two types: centrifugal (transmit information from the central nervous system to the muscles, ligaments and tendons) and centripetal (information moves in the opposite direction - from the muscles, tendons and ligaments to the central nervous system). In the second case, the paths are also called sensitive.
Possible problems
The structure of the voice apparatus, as well as the functional features of each of its departments, will help you work out what problems may arise. In speech therapy, it is customary to distinguish several types of disorders:
- Incorrect use of speech organs.
- Violation of the structure of organs or tissues.
- Problems with the parts of the nervous system whose function is to ensure the pronunciation of phonemes.
In addition, children may experience delayed speech development (SDD), the essence of which is the inability to pronounce certain sounds, the inability to express emotions, and lack of control over intonation. Also included in the developmental developmental disorder are underdeveloped vocabulary, the absence of phrasal speech in 2-year-olds, and the absence of coherent speech in 3-year-olds. These defects should be eliminated as soon as possible by contacting speech therapists, otherwise they may cause the child to be unable to learn to write and read normally.
The vocal apparatus is the most important part of the human body; it helps people communicate with each other and find their place in society. For this reason, any problem detected in early childhood must be addressed immediately.