The impact of sound pronunciation disorders on a person’s life is quite large. An inferiority complex often occurs, which is especially pronounced in adolescents. If a person cannot overcome it by adolescence, then there is a high probability of developing mental disorders, complexes, embarrassment of oneself and the inability to express one’s own individuality to the desired extent. Many people manage to overcome the barrier and accept their difference from others. But not every adult is able to feel comfortable communicating with other people due to existing speech disorders. And, if speech defects were not corrected in childhood, they can be eliminated in adulthood.
Causes of impaired sound pronunciation in adults
Most often, impaired sound pronunciation in adults is the result of speech problems that were not eliminated in childhood. As a rule, a speech disorder is accompanied by low tone and slight incoordination of the articulatory organs: tongue, lips, jaws.
Various anomalies in the structure of the speech apparatus are often noted: an incorrectly formed bite, a short hyoid ligament, an inflated or narrow palatine vault. They can be diagnosed by a dentist or orthodontist. Also, the state of speech is affected by factors such as deterioration of physical hearing and neurological problems. Speech problems can occur due to injury or severe stress.
Several ways to make the sound L
First way. Open your mouth wide. Make sure your upper and lower teeth are visible. Then stick your wide tongue out between your teeth, pronounce the sound A and immediately press it with your teeth. As a result, you will get a combination of the sounds A and L. As soon as you are able to pronounce the sound L in this position, move your tongue to the correct position - it should be raised up and rest against the gums or teeth.
Second way. Say the sound Y. Then say simple words that contain the syllable LY, for example, lyko, skis, and so on. When you are able to pronounce the sound L in the interdental position, move the tip of your tongue to the correct position.
Types and mechanisms of sound disturbance [L]
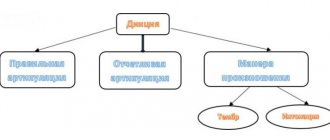
With the correct articulation of the sound [L], the lips open slightly, take the articulatory position of the vowel following it, there is a small gap between the incisors, the tongue relaxes, its tip is raised to the alveolar process and touches the gums, the lateral edges create gaps with the molars, and air passes through them with exhalation. flow, the root of the tongue is slightly raised, the vocal folds connect and tremble. The sound [L] is consonant, hard, voiced, oral, sonorant, transitive, anterior lingual.
Impaired pronunciation of the sound [L] is called lambdacism. There are several types:
- Interdental. The correct sound is heard, but the articulatory position is disturbed: the tip of the tongue is located outside, clamped between the teeth.
- Nasal. Pronunciation deviates greatly from correct articulation and acoustics. The tongue touches the palate, part of the air or all of the exhaled stream goes into the nose. A blurry combination of [NG] is heard.
- Labiolabial (bilabial). The sound is similar to [U], or English [W]. With such lambdacisism, the phoneme is reproduced by the lips, the tip of the tongue is located deep in the mouth, and is not involved in articulation.
- Labial-dental. Sound similar to [B]. The lower lip meets the upper teeth, the tongue is located deep in the mouth.
- Side. The air flow exits through one side slot, the second side of the tongue is connected to the upper molars.
- Mitigation. An intermediate sound between hard and soft [L]. The middle of the lingual dorsum rises more than required.
Replacing the sound L with other sounds is called paralambdacism:
- Replacement with [Y]. The back of the tongue arches and the tip drops. A person does not even recognize the replacement; he often thinks that the phoneme is simply missing.
- Replacement with [G]. The tip of the tongue does not rise, but is relaxed and located deep in the mouth, the back of the lingual back, curving, is adjacent to the soft palate.
- Replacement with [Y]. With such a distortion, the tip of the tongue is located at the bottom of the mouth, and does not rise to the alveolar process, and the middle of the back is bent upward.
- Replacement with [U]. Articulation involves the lips instead of the tongue.
- Replace with [B]. With this variant of paralambdacism, the lower lip is adjacent to the upper teeth. A person usually considers this speech disorder to be simple slurred speech.
In addition to the listed options for incorrect pronunciation of the phoneme [L], its complete absence is possible.
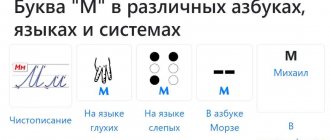
History of the origin of the letter L
In ancient times, the letter L had a different name. Now we call it -el-, but once it was “people”. The letter had a strange name, didn’t it?
She also appeared in a strange way.
In those distant times there was a word meaning “man.” This word was pronounced “lyudin”. The root of that word is still alive today in the word “commoner.”
There was even a settlement in the Kaluga region called Lyudinovo. The name of the town was given for its large population.
"Lyud" from Indo-European means "to grow." If we somehow connect this with a person, then we can say that a person, a human being, is the one who grows.
In Rus', the letter L was associated with such beautiful words as: love, affection.
The most beautiful name is for the letter L -El- in the Cyrillic alphabet. In Phoenician it is “lamed”, and in the Greek alphabet it is generally “lambda”. According to some information, it was from the Greek lambda that the letter L, which today occupies a place in the Russian alphabet, originated.
We can compare and understand that they are indeed very similar: our L and the Greek lambda Λ, λ.
The process of working on sound [L]
If the pronunciation of several phonemes is defective, as well as if speech disorders occur in adulthood after suffering stress or injury, it is necessary to seek qualified help from a speech therapist. If an adult pronounces only one or two phonemes incorrectly, he can cope with the speech problem on his own at home, without the help of a specialist.
The process of eliminating defective pronunciation of any sound consists of four stages: preparatory, production itself, automation, differentiation.
You cannot skip a stage and move on to the next one without completely mastering the previous one.
Preparatory exercises for sound [L]
The preparatory stage serves to create the correct articulatory position. It involves performing special speech therapy exercises. To correctly reproduce the sound [L], it is important to raise the tip and back of the tongue, learn to relax the lateral edges and make a targeted exhalation.
To practice lifting the tip of the tongue, the following exercises are used:
- Open your mouth, lips are not tense, a relaxed tongue is quickly placed first on the upper lip, then on the lower. Gradually complicate the action by moving the tongue into the mouth, fixing it at the alveolar processes.
- Open your mouth. Using a flat tongue, lick the relaxed upper lip, moving from top to bottom, then hide the tongue towards the middle of the palate.
- Smile and open your mouth. Press your flat tongue against the upper alveoli and loudly tear away. Start slowly, gradually accelerating.
- Smile with your mouth open. Use the flattened edge of your tongue to slap your upper lip back and forth, trying not to separate your tongue from your lip. Start performing actions slowly, gradually pick up speed and connect the vocal cords, achieving the combination [Bl-bl].
- Tighten the bent tip of your tongue and move it back and forth across the palate at different speeds. The interdental space is equal to the thickness of a finger. The lips open slightly and do not touch the incisors. The jaws are static.
Raising the back of the lingual back is practiced by singing the vowel phonemes [O], [U], [A], [Y]. To train the skill of lowering the sides of the tongue and purposefully exhaling a stream through the gap between them and the molars, you need to tightly hold the flat tip of the tongue with your teeth, exhale air, puffing out your cheeks, and at the same time lightly tap them with your fingers to make a squelching sound.
When the articulatory organs are ready and the exercises can be performed flawlessly, at a fairly rhythmic pace, you can start setting up the sound.
Methods for producing the sound [L] in adults
The production of the [L] sound in adults is carried out using the same methods as in children; the choice of technique depends on the mechanism of the defect.
Staging sound in the event of its absence is possible in three ways:
- From the reference phoneme [A]. Place the flat edge of the tongue on the lower lip and lightly press it with the incisors. The tongue is motionless. Do it multiple times. Then you need to extend the sound [A] at the moment of biting your tongue, gradually increasing the speed. The syllables AL and LA should be heard. After receiving the necessary syllables, move the tongue behind the teeth to the correct position for articulation [L].
- Mechanically from the reference phoneme [U]. Place your tongue between your outstretched lips. Stretch [U], at the same time separate the lips with your fingers, moving them towards the front wall of the incisors.
- From the reference phoneme [ы]. The production is performed in the same way as from the phoneme [A].
Similar methods of setting [L] are used for interdental [L] and when replacing it with phonemes [Y] and [G]:
- With nasal lambdacism, it is necessary to achieve precise movement of the air flow: the air should be exhaled through the mouth.
- When replacing [L] with the phoneme [Y], one must learn to hold the tip of the tongue, pressing it firmly against the upper incisors, and relax the middle of the lingual back, lifting the root. In order for the tongue to take this position, you need to place the flat tip on the lower incisors and stretch [Y] or place a round object in the middle of the tongue, lifting the tip of the tongue to the upper alveolar process.
- When replacing with [U], you should achieve a static state of the lips.
- If there is a replacement for [B], the activity of the lower lip must be eliminated. To do this, you must first learn to lower it, opening the incisors, and hold it in this position, then raise the tongue to the upper molars. Do it repeatedly. If you can’t do it correctly, you can place a tense finger under your lower lip and help them.
The performance is completed when the person can pronounce the sound in isolation.
Automation and differentiation of sound [L]
Correct pronunciation of a sound requires mandatory automation, that is, consolidation in spontaneous speech. It should begin with pronouncing forward and backward syllables. At first, you need to speak the syllables slowly, drawing out each sound. This helps the speech organs take the correct position. The speed of pronouncing syllables gradually increases, approaching the usual rate of speech. After successfully pronouncing a sound in syllables, you can automate it in words and then in sentences. Automation is positively influenced by memorizing poems rich in fixed sound, retelling and composing texts.
The final step in working on sound pronunciation is the stage of differentiation. This is the discrimination of phonemes that are similar in articulation and sound. At this stage, a person learns not to replace them in speech and not to confuse letters in writing. This is most important for those who have previously experienced paralambdacity.
Differentiation, by analogy with automation, begins with the distinction of phonemes in syllables, then proceeds to words and phrases. When differentiating, it is important to use tongue twisters. After the final stage, children freely use the correct sound in their own speech. But an adult may take much longer due to too much mispronunciation.
Thus, you can learn to correctly speak the sound [L] to an adult on your own in the absence of other speech problems. The difficulty is that self-control will be required for quite a long time. It is needed in order to eliminate the existing automatic skill of incorrect pronunciation.
How to teach a child to say the letter K
Parents often ask a speech therapist how to teach their child to pronounce the letter k. There is only one answer - the most effective method is constant pronunciation.
The simplest task is to regularly pronounce words with the letter “k”: cabbage, strawberry, potato, card, book, dill, spark.
At the same time, it is important to focus the child’s attention on this letter and pronounce it clearly and slowly. Children most often achieve the main progress in pronunciation in classes at preschool educational institutions.
Speech therapy lesson on differentiation of sounds [g] and [k]
How to teach a child to say the letter k if he refuses to do speech therapy? Home training often does not bring the expected result, but in kindergarten the speech therapist uses a playful approach and engages the child in play. A ready-made outline is used for the lesson.
Lesson progress on differentiating “g” and “k”:
- The teacher asks the child to guess riddles, the answers to which contain the sounds being practiced. Then he announces the topic of the lesson and the purpose.
- Kids are asked the question: “What is the difference between “g” and “k”? Children should say that they have different sounds, teeth and tongue positions when pronouncing. The speech therapist invites children to pronounce words with their hand on their throat. The sound is very different.
- Work is underway with notebooks. The guys write down the syllables: gu-ku, gi-ki, go-ko, ga-ka and pronounce them. A fast pace and its alternation with a slow one is important.
- At the end of the lesson, the children pronounce pure sayings: “ha-ha-ha - the geese came out into the meadows.”
Articulation gymnastics for the sound L
After the main block of the lesson, children do a warm-up and then do an exercise in which they need to insert the missing letters in a word.
Important! During the lesson, the speech therapist pays attention to the children for whom pronunciation is most difficult, and then conducts individual work with them.
What are the reasons for the incorrect pronunciation of L?
Until the age of 4, the speech apparatus is not adapted to pronouncing this sound, so lambdaism at this age is considered a variant of the norm.
There are several reasons why a child speaks incorrectly:
- Improper breathing during speech.
- Disturbances in the development of speech hearing - the child has difficulty hearing the speech of other people and does not perceive meaning well.
- Insufficient development of the articulatory apparatus, weakness of facial muscles and tongue. These muscles play a leading role in the pronunciation of sounds.
- Deviations in the structure of the hyoid ligament (frenulum) - speech disorders are possible if the ligament is short.
Improper breathing can be due to several factors:
- The child's lung capacity is reduced.
- The respiratory muscles are weak, so the child cannot speak loudly.
- When exhaling, the air stream comes out in jerks, so it becomes difficult to finish a long sentence.
- Incorrect distribution of air, resulting in inhalation starting in the middle of the word.
Side effects of L Thyroxine
If you take the drug under the vigilant supervision of a doctor and follow all his recommendations, taking the drug does not cause any side effects. Otherwise, symptoms of an allergic reaction are observed - skin rash, hyperemia, itching, urticaria.
Other symptoms occur with a high dose or incorrect treatment tactics. They appear rarely and represent the following conditions:
- Headache, tremors of extremities, anxiety, excitement, sleep disturbance.
- Cardiac disorder - arrhythmia, palpitations, angina pectoris, tachycardia.
- Dyspeptic manifestations.
- Pathological course of menstruation.
- Allergic symptoms.
- Excessive sweating, weight loss, fever, constant weakness, fever.
Speech therapy classes: consolidation of pronunciation
Speech therapy classes in a playful way arouse great interest among children. As a result, it is possible to achieve positive results faster. The most frequently used games are:
- "Track". A path is drawn on a piece of paper from the written letter to the drawn object, the name of which contains this letter. The patient moves his finger from the letter along the line to the drawing, pronouncing the problematic consonant, and at the end of the path he names the drawn object.
- "The Fox and the Koloboks." A figurine of a fox and 10 koloboks are cut out. The speech therapist asks the patient to name a specific word. If the task is completed successfully, then the bun runs away from the fox; if not, then the fox eats another bun.
- Subject cards. The cards depict objects whose names contain a problematic consonant. The preschooler is asked to name the depicted object.
- Speech therapy cards with the sound L.
Usually, parents cope with all of the above activities on their own. But if a lot of time has passed, and speech therapy training at home has not yielded a positive result, then the help of a speech therapist is required.