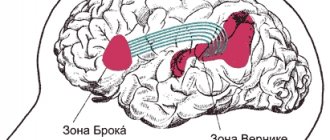
Types of speech disorders and speech disorders in children
The most well-known speech disorder is stuttering, in which the natural flow of speech is interrupted by abnormal stops, or repetition of parts of words or sounds. Problems with speech disorders currently occur in almost every fourth child. Speech disorders negatively affect the development of a child’s attention, memory, imagination, thinking, and written language. Voice disorders, which include problems with rhythm, volume, or quality of voice, are also common. Associated with speech disorders in children are problems with chewing and swallowing.
Regular sessions with a children's speech therapist most often allow you to successfully correct speech problems that have arisen. It is necessary to contact a specialist immediately when relevant problems are detected in a child, so that distorted skills do not have time to take hold and form a stable functional system.
Timely correction of speech disorders plays a big role in the child’s overall mental development, the formation of correct communication skills with people around him and healthy self-esteem.
Indications for individual lessons with a defectologist
Children with special needs experience certain difficulties in learning new material, controlling their emotions and behavior, and the ability to build relationships with older people or peers. Often they cannot absorb knowledge as easily as the children around them, and they lose interest in learning. Features associated with the pace of development and diseases lead to the fact that teachers or parents of other children react to them as bullies and demand “correct” behavior.
Parents of such special children, due to the lack of special education, cannot always understand how difficult it is for them to learn and adapt. The level of complaints against your child, others, and the educational institution is growing. A consultation with a defectologist will help moms and dads:
- objectively assess the causes of difficulties in learning and socialization;
- understand what they can do to change the situation;
- get information about what classes will help in this case.
A recommendation to visit a specialist should not be interpreted as a cursory assessment of the child's mental state. Individual lessons with a speech pathologist are indicated in the following cases:
- children with hearing or vision impairments;
- children with autism spectrum disorders;
- preschoolers and schoolchildren with speech impairments;
- children with acquired or congenital diseases of the musculoskeletal system;
- children with lesions of the central and peripheral nervous system;
- children with mental and psychomotor development delays;
- patients with mental retardation;
- children who have difficulty learning in kindergarten or school.
A timely start to work gives the best results: the younger the child, the more plastic his brain. Assimilation of the material and correction of unusual behavior are easier. And parents sooner have the opportunity to accept the situation and not demand the impossible from their child.
When assessing the behavior and development of children, you should pay attention to such features as:
- absence of any speech up to 2 years and small vocabulary;
- absence of any phrasal speech after 2 years;
- a child from 2.5-3 years old does not imitate the activities of his parents, does not repeat simple actions at their request (bring an item, beat a rhythm, show his tongue);
- violation of word pronunciation at the age of 4 years (speaks individual syllables, rearranges syllables, confuses sounds);
- the preschooler does not write sentences, a story, the speech is agrammatic, there are no conjunctions or prepositions,
- a child over 4 years old cannot learn a poem, does not name objects, cannot classify them, does not know how they differ;
- a preschooler or schoolchild does not perform operations with counting and cannot learn to count;
- the child cannot make a whole from parts (puzzles, cut-out pictures)
- fine motor skills are not developed or develop with a delay.
What techniques are used to provide speech therapy assistance?
Speech and speech therapists use a variety of techniques, including:
Language intervention activities: The specialist will interact with the child through play and conversation, using pictures, books, objects or games to stimulate language development. The speech therapist helps model correct vocabulary and grammar using repetition exercises to develop language skills.
Soft palate massage
The massage is aimed at activating the tone of the soft palate and increasing the palatopharyngeal reflex. The main indication for massaging the muscles of the soft palate is the nasal tone of the voice. These movements are used only when the muscle tone of the soft palate is reduced. General recommendations for massage are as follows: the massage effect is usually directed not only to the muscles of the soft palate, but also to the lingual-palatine and pharyngeal-palatal arches; massage must be combined with passive and active gymnastics aimed at stimulating the palatine and pharyngeal muscles; massage movements are performed with the thumb or index finger of the right hand. Massage of the soft palate may include the following movements.
- Perform stroking, rubbing, kneading and screwing movements in the direction from the hard palate over the entire surface of the soft palate.
- Stroking, kneading and rubbing movements from right to left, grasping the lingual-palatal arches.
- Pressing movements made by the thumb or index finger over the entire surface of the soft palate in the longitudinal and transverse directions.
- The child pronounces the sound a or e for a long time. At this time, use your thumb or index finger to make rubbing and kneading spiral movements in the transverse and longitudinal directions.
- The child pronounces the sounds a or e briefly, abruptly, using a firm sound attack. At this time, perform jerking movements with the thumb in the area of the soft palate and palato-lingual arches. IN
postoperative period for rhinolalia, massaging movements should be carried out extremely carefully (only after the doctor’s permission) in two directions: longitudinally, along the line of the surgical suture, and transversely, along the border of the hard and soft palate. The movements at the beginning of the course of postoperative massage should be very light, stroking, and only gradually should one move on to kneading and pressing movements. It is very important to combine an activating massage of the soft palate with active and passive-active exercises aimed at reflex contraction of the muscles of the soft palate, muscles of the pharynx and muscles of the posterior pharyngeal wall.
Passive and passive-active exercises that stimulate the work of the velopharyngeal muscles.
Using a spatula, which touches the root of the tongue, induce a reflex contraction of the muscles of the back wall of the pharynx and soft palate. Imitate chewing. Drink water in small sips or imitate swallowing movements (successive repeated swallowing movements lead to an increase in the time during which the soft palate is in a raised position). Coughing - this movement is performed repeatedly on one exhalation (leads to complete closure of the velopharyngeal ring). Yawning is a movement imitated by the child following the speech therapist. Repeatedly pronounce the vowels a, e with a firm voice attack. Gargle with small portions of warm water.
What is speech therapy massage
One of the effective methods of corrective action for speech and swallowing disorders is speech therapy massage of the face and adjacent areas. The modern technique of speech therapy or therapeutic speech massage was developed by Dr. Elena Dyakova in 2003 for use in speech therapy.
Speech therapy massage allows you to accelerate the normalization of impaired functions of the oro-facial and speech muscles in a child, and accelerate their development. Over the past 15 years, this method has proven its effectiveness and is widely used by Russian and European speech therapists. Since 2014, speech therapy massage has been included in mandatory educational programs for the training of speech therapists in Russia.
The effect of speech therapy massage is based on normalizing the tone of muscles directly or indirectly involved in the processes of sound production and swallowing, normalizing their blood supply, eliminating developed pathological blocks that impair blood flow and compress nerve fibers. Also, speech therapy massage allows you to make the ligamentous apparatus more elastic and eliminate fascial disorders. Speech therapy massage allows you to normalize many components of speech: breathing, vocalization, articulation, as well as swallowing, sucking, chewing and the emotional state of children suffering from speech disorders or myofunctional dysfunctions.
Contraindications and conditions
Despite its high effectiveness with the comparative simplicity of the exercises, massage from a speech therapist has a number of contraindications. In particular, it is not used in the presence of infectious diseases, including influenza. Obviously, massage should not be performed if you have herpes and other skin diseases. Other contraindications include conjunctivitis and stomatitis.
Speech therapy massage is performed in a well-ventilated area at room temperature. It is advisable to carry it out every day or at least every other day in cycles of 10-20 sessions. Then the specialist individually draws up a plan for a repeat massage course, if necessary.
Do you have any questions or want to schedule your child for an initial consultation? Contact us by phone. We are also always glad to see you in our center at the address St. Petersburg, Yu. Gagarin Ave., 77 (directions are indicated at the top of the site).
How speech correction occurs using speech therapy massage
The muscles of the mouth, lips, cheeks, tongue, jaw and facial muscles, the muscles of the neck, shoulders and respiratory muscles form a single muscular system involved in creating the child’s speech function - all this forms a single muscular system. Numerous studies have shown that the elasticity of muscle fibers, their volume, strength and contractile function, and performance are significantly increased with the help of massage.
It is no coincidence that all professional athletes use the services of massage therapists. In addition, massage can reduce the tone of spastic muscles and increase the tone of flaccid muscles. Therefore, a targeted study of the condition of the speech muscles and targeted massage effects can increase the effect of speech therapy, enhanced by speech therapy massage. This reduces the time required for treatment.
Speech therapy massage is the most gentle therapeutic method. For example, in the case of treating stuttering caused by spasms in the muscles of the speech apparatus, a speech therapy massage specialist will begin working with the muscles furthest from the spasmed muscles in order to cause a reflexive gradual decrease in spasticity of the muscles of the target group. Working through a carefully constructed chain of muscles, using special massage techniques, the specialist will begin to work on the main muscles associated with the pathology only when they are most susceptible to the effects, and the child does not experience discomfort.
Lip muscle massage
Relaxing massage.
- Using the palmar surface of the index fingers, make stroking movements along the upper lip from the corners of the mouth to the middle.
- The same movements are made along the lower lip from the corners of the mouth to the middle.
- The movement is performed with the pads of the index and middle fingers alternately with the right and left hands. The movement begins from the tragus of the auricle, the fingers easily slide along the cheek and then around the lips. In this case, the index finger slides over the skin of the upper lip, and the middle finger over the skin of the lower lip, coming together at the opposite corner of the mouth.
- Using the pads of the index and middle fingers, stroke the nasolabial folds, moving from the wings of the nose to the corners of the mouth.
- With the same fingers, lightly tap around the lips in a clockwise direction. Massage movements can be carried out with the mouth in different positions: closed and slightly open.
Invigorating massage . Rubbing techniques are used in the form of semicircular and spiral movements, kneading in the form of rubbing and vibration.
- The palmar surface of the index fingers makes movements along the upper lip from the middle to the corners of the mouth. The same movements are used on the lower lip.
- With the thumbs of both hands, make movements from the middle of the upper lip to the corners of the mouth and slightly down, and then with the index fingers - from the middle of the lower lip to the corners of the mouth and slightly up. The movements alternate.
- Stroke the nasolabial folds, moving from the corners of the lips to the wings of the nose.
- Using your thumb and forefinger, grab your upper lip into a vertical fold, squeeze it and rub it between your fingers. The capture is carried out in the central part of the lip.
- Use your thumb and forefinger to grab the skin around your lips and perform a pinching technique.
- The ends of the index and middle fingers are tapped intensively around the lips.
- Rubbing movements carried out by the thumb and forefinger in the direction from one corner of the mouth to the other along the upper and then lower lip.
- Spiral movements made with the thumb and forefinger along the upper and then lower lip.
- Spiral kneading of the nasolabial fold area. The phalanx of the thumb is located in the oral cavity under the nasolabial fold, the index and middle fingers are located on top.
- Point squeezing of the lip between the thumb and index finger. Localization of points.
- The speech therapist places his index fingers on a point located between the middle of the upper lip and the corner of the mouth on both sides. A movement is made towards the middle so that the upper lip is gathered into a vertical fold. A similar movement is carried out on the lower lip.
- The specialist places the index and middle fingers near the corners of the mouth and slightly stretches the lips, as if smiling; with a reverse movement, the lips return to their original position. Movements are light and smooth. These exercises can be performed with the mouth closed or open.
Effects of speech therapy massage
- The muscle tone of the oral, facial, vocal and respiratory muscles is normalized.
- Muscle groups that do not contract sufficiently are activated.
- Increases oral range of motion.
- Pathological neurological symptoms such as synkinesis, hyperkinetic disorders, convulsions and drooling are reduced.
- Proprioceptive and kinesthetic sensations are stimulated, helping to facilitate movements that help muscles form coordinated, voluntary movements and eliminate abnormal functional speech patterns.
- Functional muscle balance is restored in the mouth, face, neck and body.
- All components of speech are normalized: breathing, vocalization, resonance and articulation.
- Oral defense is overcome.
- Increased sensitivity of the oral cavity is reduced.
- The child's emotional state is normalized.
What methods and techniques of speech therapy massage exist?
The following basic techniques are used for speech therapy massage:
- Touching: includes kneading and stroking the face and neck with fingers and objects of varying textures and temperatures (brushes, soft toys, fabrics, wet paper towels, cold sponges).
- Pressure: Involves applying varying levels of pressure (ranging from “light” to “felt”) on the oral structures and face with the fingers of sterile gloved hands.
- Vibration: includes the use of various vibration massagers with different attachments on external and internal oral structures: special Five Vibe vibrators for hyposensitive children, Z-Vibe - for stimulation of oral structures (for example, gums). Vibrating toothbrushes are also used to stimulate oral structures. In the absence of special vibrators, vibration techniques are performed with gloved fingers.
- For independent stimulation of oral structures, children are offered special chewing tools Grabber or Y-Chew.
- To work with young children, Preefer and Animal Tips probes are used, which can be dipped in children’s favorite treats so that the baby becomes interested and actively participates in the treatment process.
Sensory massage stimulates internal oral structures to help a child who is overly sensitive to touch become calmer and more relaxed. Teaching feedback about the movements and functions of the speech system helps the child increase awareness of oral-motor functions and “wake up” their mouth by increasing the muscular response of the lips, tongue and jaw.
Stimulation using vibration of the oral structures and bones of the skull allows the child to better feel the position and role of all elements of the speech system, activates his vestibular system, helps reduce pain due to spasms and reduce oral sensitivity.
How to massage the tongue for dysarthria.
Massage for dysarthria consists of many stages. Let's look at the main ones.
Before the session begins, the specialist must create conditions in which the child can feel comfortable. After relaxing the oral muscles, which in turn is achieved by lightly stroking the face, the main part of the speech therapy massage begins:
- stroking the lips and nasolabial folds;
- mild tingling along the edge of the lower jaw;
- stroking from the earlobes along the cheeks to the sinuses;
- lip massage;
- stroking the brow tissue from the eyebrows to the hair;
- massage using light pressure movements from the hair roots down.
Each movement can be repeated 5-8 times. With each repetition, the strokes become a little stronger, but in no way painful.
For which children and for what speech disorders is speech therapy massage indicated?
You need to know that speech therapy massage is not intended to replace any standard treatment for stuttering or other speech disorders. It is used as an additional treatment method to make traditional forms of speech therapy more effective and reduce the time it takes to achieve a positive therapy effect.
Speech therapists and defectologists of the VIRILIS Group of Companies have extensive experience in helping children with the following conditions and diseases:
- Dislalia- a violation of the pronunciation of sounds associated with the anatomical features of the child’s speech apparatus, or resulting from unfavorable conditions for the development of speech or hearing impairment.
- Dysphonia or aphonia is a disorder or lack of sound production due to disorders of the vocal apparatus. It may manifest itself as a complete absence of voice, or in the form of maintaining only whispered speech.
- Rhinophonia is a violation of the timbre of the voice while maintaining normal articulation of pronounced sounds.
- Rhinolalia (nasality) is a violation of the timbre of the voice and the pronunciation of sounds due to congenital anatomical defects (cleft lip and alveolar process, cleft gums, hard and soft palate), or disturbances in the patency of the nasal cavity due to adenoids, tumors, chronic inflammatory processes.
- Dysarthria is a violation of the pronunciation of sounds due to insufficient innervation of the speech apparatus. Such disorders are characterized by limited mobility of the soft palate, tongue or lips. Dysarthria can lead to deviations in the acquisition of sounds, and, as a result, to reading and writing disorders, or even to speech underdevelopment.
- Stuttering is a violation of the smoothness and fluency of speech, caused by the convulsive state of the muscles of the speech apparatus and stagnant foci of excitation in the cerebral cortex.
- Bradylalia (slowing the rate of speech), tachylalia (accelerating the rate of speech), paraphrasia (accelerating speech with grammatical errors) and cluttering (“swallowing” the endings of words).
Stuttering, logoneurosis, hesitation in speech, dysrhythmia
Stuttering in children is a disorder of the tempo-rhythmic aspect of speech caused by repeated convulsions in the articulatory, vocal or respiratory parts of the speech apparatus. Stuttering in children is characterized by “getting stuck” on individual sounds, their repeated, involuntary repetition, accompanying movements, speech tricks, logophobia, and vegetative reactions.
Neurological therapy classes for the correction of stuttering in our center can be based on various author’s methods: Cheveleva, Vlasova and Rau, Shklovsky, Volkova, Mironova, etc. The main methods of speech therapy work for stuttering are breathing-vocal gymnastics, relaxation of tense articulatory muscles, speech exercises on rhythmization of speech, normalization of its tempo, development of expressive speech intonation, logorhythmic exercises.
Children with stuttering, logoneurosis, and even hesitations in speech must be examined by a neuropsychologist and speech therapist.
Competent correction of stuttering, which leads to sustainable results, must necessarily include a neurocorrectional set of measures (neuropsychological correction, neuroacoustic programs) and a system of “correct” speech therapy classes.
Stuttering in children is unintentional stops and hesitations in oral speech that arise as a result of a convulsive state of the speech muscles.
It must be remembered that in addition to speech spasms, stuttering in children is accompanied by a disorder of higher nervous activity, which in some cases may be associated with a neurotic reaction, in others with organic damage to the central nervous system. Therefore, it would be wrong to consider stuttering in a child as a purely speech problem; The study and correction of stuttering in children is impossible without the integration of knowledge from the field of neuropsychology and the development of brain areas.
This is where the root of problems with speech hesitations lies.
Depending on the pathogenetic mechanisms underlying stuttering, there are 2 forms of stuttering in children: neurotic (logoneurosis) and neurosis-like. Neurotic stuttering in children is a functional disorder; neurosis-like is associated with organic damage to the nervous system and brain.
In the most extreme cases, stuttering can make speech and communication nearly impossible. The severity of stuttering may vary for the same child in different situations.
Depending on the nature of the course, the following variants of stuttering in children are distinguished:
- wavy (stuttering increases and decreases in different situations, but does not disappear);
- constant (stuttering has a relatively stable course)
- recurrent (stuttering occurs again after a period of speech well-being).
Children who stutter often exhibit enuresis, night terrors, increased anxiety and vulnerability. Therefore, ignoring stutters and “running” this problem is DANGEROUS.
Perinatal brain damage in children can be associated with toxicosis of pregnancy, hemolytic disease of the fetus, intrauterine hypoxia and asphyxia during childbirth, birth injuries - and all this can subsequently lead to stuttering and hesitation in speech.
Children who are physically weak, with an underdeveloped sense of rhythm, general motor skills, facial expressions and articulation are more susceptible to the development of stuttering.
The increase in the incidence of stuttering is directly related to the introduction of computer games and various computer technologies into everyday life, which unleash a huge flow of audiovisual information on the fragile nervous system of children.
It should be remembered that the processes of maturation of the cerebral cortex and the formation of functional asymmetry in brain activity are generally completed by the age of 5, therefore exposure to any stimulus that is excessive in strength or duration can lead to a nervous breakdown and stuttering in children.
The immediate causes of stuttering in children also include immediate mental shocks or long-term mental trauma.
Stuttering in children can be caused by imitation of people who stutter, overload with complex speech material, and retraining to be left-handed. Experts point to the connection between stuttering in children and left-handedness and other speech disorders (dyslalia, tachylalia, dysarthria, rhinolalia). Secondary stuttering in children can occur against the background of motor alalia.
In the case of neurosis-like stuttering, which occurs against the background of organic damage to the central nervous system in the perinatal or early period of child development, the disorder develops gradually. Neurosis-like stuttering in children appears from the moment speech begins or at the age of 3-4 years, i.e. during the period of formation of phrasal speech.
Children with neurosis-like stuttering have impaired general motor skills : their movements are awkward, constrained, and stereotyped. Characterized by sluggish facial expressions and poor handwriting; Dysgraphia, dyslexia and dyscalculia often occur. The course of neurosis-like stuttering in children is relatively constant; Speech deterioration can be caused by fatigue, increased speech load, and somatic weakness.
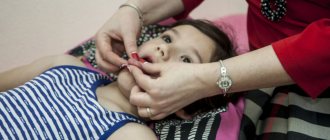
Oral massage for impaired sucking and swallowing in newborns
Incorrect latching on the breast by a baby during breastfeeding and swallowing disorders in infants can lead to the baby's refusal to eat, stagnation of food in the throat, constant regurgitation, and poor weight gain. A speech therapist, using speech therapy orofacial massage techniques (massage of the mouth, lips, cheeks), can help in this case.
By examining the baby's oral cavity with a gloved finger, a specialist can evaluate the functions of sucking, retraction, tongue position, and positioning of the larynx during feeding. Corrective speech therapy massage sessions for infants are carried out before feeding so that the child does not get tired and last only 2-5 minutes. The massage can be combined with the “finger feeding” procedure, when breast milk flows from a bottle through a tube to the finger that the baby sucks.
Massage of the inner cheek
Massage of the chewing, cheek and zygomatic muscles, and especially the pterygoid muscles, can be carried out with the speech therapist’s fingers positioned inside the child’s mouth. When massaging the left cheek, the speech therapist places the thumb of the right hand in the mouth, the remaining fingers remain outside. Massage movements are carried out with the thumb on the inner surface, and with the remaining fingers on the outer surface of the cheek. When massaging the right cheek, the index and middle fingers are inserted into the oral cavity, the thumb is on the outer surface of the cheek, performing the basic massage movements. Massage of the inner surface of the cheek can be carried out in different positions of the mouth: open and wide open - and with the jaws closed. The main techniques used are rubbing and kneading.
- Circular movements along the cheek from the periphery to the center and vice versa.
- Spiral rubbing and kneading with fingertips in a circle.
- Kneading in a circular motion and rubbing in the area of the masticatory muscle.
- Rubbing movements from the cheekbone down to the corner of the mouth. All fingers, except the thumb, are located at the edge of the zygomatic bone. Thumb - on the inside of the cheek.
- Rubbing spiral movements. All fingers, except the thumb, are located in the area of the tragus and earlobe, gradually moving towards the corner of the mouth.
- Spiral rubbing of the temporomandibular (zygomatic) joint area. In the open mouth position, find the “hole” at the earlobe. Massage the pit area with your index and middle fingers. The thumb serves as a support on the inside of the cheek.
Contraindications to speech therapy massage
Main contraindications for speech therapy massage:
- Inflammatory diseases of the scalp and neck
- Inflammatory diseases of the ENT organs
- Lymphadenitis (enlarged and painful lymph nodes in the head and neck)
- Stomatitis or gingivitis (inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity)
- Head and neck injuries
- Acute allergic reactions
- Oncological diseases
- Conjunctivitis, blepharitis
- Convulsive syndrome
- Mental illness
Contraindications
Massage courses are prescribed by a neurologist after a complete examination. It should not be used for epilepsy of various forms, as it can provoke seizures.
Temporary withdrawal is given for any infectious or somatic diseases. Probe massage should not be performed for stomatitis, caries, gingivitis, or skin diseases. Herpes and oral infections also serve as a medical outlet for procedures.
It should not be done if there is strong pulsation of the arteries, high blood pressure, or poor physical well-being.
If you have nausea, vomiting, or fatigue, you cannot conduct a session; it is better to reschedule it for another time. A speech therapist examines each child before performing a massage.
Calling a speech therapist to your home, performing speech therapy massage at home
Calling a speech therapist to your home is the best option to help your child:
- The doctor will arrive quickly, at the time agreed upon for the visit, and the child will not have to be taken to the clinic and wait in line.
- A safe and familiar home environment promotes calm behavior of the child without fears, tears and whims.
- Transportation to the clinic can be difficult if the child is intoxicated or has respiratory problems.
- At home, contact with sick children in the clinic is excluded, which is especially important for children who are often ill.
- In a calm home environment, the children's doctor will devote more time to both the child and the parents, without haste he will answer in detail any questions about treatment and speech therapy massage.
Carrying out at home
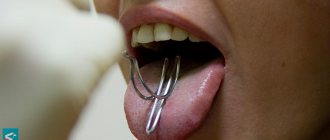
Massage has a serious impact on the body. The person who does it must have an appropriate medical education and constantly improve his qualifications. Speech therapists can only do speech therapy massage, both probe and manual.
You should not try to do it yourself. Before the start of the course, the specialist examines the child, examines the articulation organs, determines the tone, and compiles a selection of exercises. A full set of probes is not always needed; often 4-5 are enough.
It is easier for children to tolerate the procedure in another room. Psychologically, it is easier for them to endure discomfort for a while.
The degree of impact of the instruments is chosen by a specialist. Basic techniques:
- pressure;
- slip;
- compression;
- trituration.
The choice of technique is made by a speech therapist. It will be difficult for a parent without special knowledge to choose one. Probe massage can cause harm - tearing the frenulum, causing hypertonicity, strengthening the gag reflex, etc.