Development of the phonetic-phonemic side of language in ontogenesis
The phonetic-phonemic side of the language is an indicator of the general culture of speech, the compliance of the speaker’s speech with pronunciation norms.
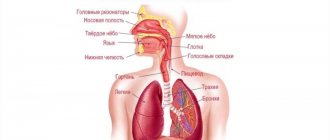
The phonetic side of speech refers to the pronunciation of sounds as a result of the coordinated work of all parts of the speech-motor apparatus.
The peripheral department of the speech motor analyzer is the speech apparatus, which includes the following:
- The respiratory apparatus, which is the energetic basis of speech (diaphragm, lungs, bronchi, trachea, larynx);
- The vocal apparatus that produces sound (larynx with vocal folds);
- An articulatory apparatus that converts sound produced in the larynx into various speech sounds (oral and nasal cavities).
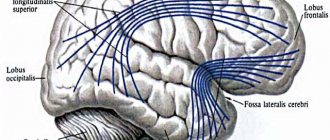
The conducting part of the analyzer includes three pairs of cranial nerves (glossopharyngeal, recurrent, sublingual), subcortical formations that provide information transmission to the cerebral cortex.
The central part of the speech motor analyzer is the parietal cortex, which analyzes information about the position of the organs of the speech apparatus during speech, and the frontal or Broca's center, which programs and controls the execution of movements. The phonemic aspect of language refers to the ability to distinguish and differentiate phonemes of the native language.
The phonemic aspect of speech is provided by the work of the auditory analyzer. Its peripheral part is located in the cerebral cortex and receives auditory information, including speech sounds.
The conductive part transmits information to the cerebral cortex, which partially analyzes it - determines the direction and distance to the sound source. This function is performed by a large number of transmission connections (VIII. pair of cranial nerves, medulla oblongata, cerebellum, midbrain, medial geniculate body and auditory radius).
The central part of the auditory analyzer is the temporal region of the speech dominant hemisphere (the left hemisphere in right-handed children), Wernicke's center, where speech analysis takes place: It controls the presence of sound in a word, the characteristics of its positional sound, the number and order of sounds in a word, the discrimination of sounds similar in acoustic parameters.
In the book “Educating Correct Pronunciation in Children” M.F. Fomicheva emphasizes that the perception and reproduction of the sounds of the native language is a coordinated work of the linguo-auditory and linguomotor analyzers, where a well-developed phonemic hearing allows one to develop clear diction - mobility and subtle differentiated work of the articulation organs, which ensures the correct pronunciation of each sound (1989).
Research by a number of psychologists, educators, and linguists (D.B. Elkonin, A.R. Luria, D.N. Bogoyavlensky, F.A. Sokhin, A.G. Tambovtseva, G.A. Tumakova, etc.) confirms that basic awareness of the phonetic features of a spoken word also affects the child’s overall language development—the acquisition of grammar, vocabulary, articulation and diction. And it is better that a child with language impairment not only goes to school phonetically correct, grammatically correct and lexically developed, but also knows how to read.
In ontogenesis, the development and formation of the phonetic and phonemic aspects of language occurs gradually.
The main role in language acquisition is played by hearing. Along with the development of hearing, the child develops vocal reactions: various sounds, various combinations of sounds and syllables. At the age of 2-3 months, the child begins to growl, and at the age of 3-4 months, slurred speech... babble. At this age, the primary development of phonemic hearing occurs: The child listens to sounds, finds the source of the sound, and turns his head towards the speaker.
At 6 months, clear sounds appear in the child’s babble, but they are not yet stable enough and are pronounced in the form of short combinations of sounds. In vowels, a clearly sounds, in consonants - p, b, m, k, t. At this stage, the child understands the adult’s intonation and reacts to the tone of voice.
The child pronounces simple sounds well: Vowels - a, u, and consonants - p, b, m, n, t, e, k, d.
The development and formation of pronunciation in all children occurs at different times. Some children speak more and more clearly, others less and less clearly. The quality of pronunciation depends on the condition and mobility of the articulatory apparatus, which is just beginning to actively function. About this A.I. Maksakova.
Preventive measures and prediction of treatment results
With timely speech therapy assistance, the prognosis for FFND is favorable. Speech defects can be corrected within 1-12 months, depending on the severity of symptoms. Success in the treatment of FFND depends on the correct actions of the parents, as well as the qualifications of the speech therapist.
Preventive measures for FFNR in speech therapy include planning pregnancy, excluding contacts of a pregnant woman with infectious patients throughout the entire period of bearing a child. During pregnancy, a woman should avoid drinking alcohol, smoking, and avoid stressful situations. The cause of speech development disorders in a child can be operations during pregnancy, rapid or prolonged labor, as well as the onset of labor ahead of schedule. If pregnancy complications occur, you should definitely contact a gynecologist for examination and treatment.
An important factor in the formation of speech is the normal psychological situation in the family. If parents have conflicts, the child may react to this with a violation of speech function. Regular activities with the child, reading books, learning to write and other activities have a beneficial effect on speech development.
Alcoholism in one of the parents, as well as drug addiction, can be a provoking factor for FFND. The child experiences stress, which greatly interferes with his development. Psychological assistance should be provided to the family, as well as treatment for alcoholism and drug addiction.
When a preschooler or schoolchild exhibits manifestations of delay and underdevelopment of speech function, you should independently contact a speech therapist as early as possible. After he conducts an examination and confirms that it is FFND, corrective classes will be prescribed. Treatment is considered most effective when patients present early.
Development of phonemic hearing
In modern pedagogical, psychological and methodological literature, various terms are used to define phonemic listening: speech auditory processing, phonemic auditory processing, phonemic awareness.
The term "speech hearing" refers to the ability to distinguish individual speech sounds in a speech stream, which allows you to understand words and their meanings. Speech communication is impossible without speech hearing. Children develop their listening skills by listening to others speak or creating their own words. Listening to language is an integral part of language intuition. As children learn to read and write, the mechanism of speech perception changes as the ability to analyze letters and sounds according to the rules of their native graphic language develops. All this is connected with the need for orientation in the morphemic composition of words and word formation. Methods for developing speech hearing are different: listening and speaking practice; phonetic analysis and synthesis, etc.
In the methodological literature on Russian methods of speech and language development, the term “speech hearing” is used. In psychological research and speech therapy, listening to speech is called phonemic awareness.
In the first weeks of a child’s life, auditory attention is actively formed. When a baby hears the sound of a human voice, it stops suckling at its mother's breast and stops crying when spoken to. By the end of the first month, the baby can be soothed with a lullaby. At the end of the third month of life, he turns his head towards the speaking person and follows him with his eyes. During the babbling period, the child repeats and tries to imitate the visible articulation of the adult's lips. Repeated repetition of the kinesthetic sensations of a certain movement leads to the consolidation of the motor ability of articulation. From 6 months, the child imitates individual sounds and syllables and adopts the tone, tempo, rhythm, melody and intonation of speech. By the age of two, children are already able to recognize the subtleties of their native language, understand and respond to words consisting of only one phoneme. Thus, the child develops phonemic awareness, the ability to perceive the sounds of human speech.
From 3 to 7 years, the child increasingly develops the ability to auditory control over his pronunciation, and the ability, in some cases, to correct it. At the age of 3-4 years, the child’s phonemic perception improves so much that he begins to distinguish between vowels and consonants, then soft and hard, sleepy, hissing and whistling. At the age of 4 years, a child should normally distinguish all sounds, that is, phonemic perception should be formed. At the same time, the child completes the formation of correct pronunciation.
The development of sound pronunciation depends on the child’s ability to analyze and synthesize speech sounds, that is, on a certain level of development of phonemic hearing, which ensures the perception of speech phonemes. Phonemic perception of speech sounds occurs through the interaction of auditory and kinesthetic stimuli entering the cerebral cortex. Gradually, these stimuli become differentiated, and it becomes possible to distinguish individual phonemes. Here, primary forms of analytical-synthetic activity play an important role, thanks to which the child generalizes the characteristics of certain phonemes and distinguishes them from others.
Through analytical and synthetic activity, the child compares his imperfect speech with the speech of his elders and forms a healthy pronunciation. Lack of analysis or synthesis usually hinders the development of pronunciation. However, if the presence of primary phonemic hearing is sufficient for everyday communication, then it is not enough for mastering reading and writing.
A.N. Gvozdev, V.I. Beltyukov, N.Kh. Shvachkin, G.M. Lyamina proved that it is necessary to develop higher forms of phonemic hearing, in which children can decompose words into their constituent sounds, determine the order of sounds in a word, i.e. analyze the sound structure of a word.
D.B. Elkonin called these special actions of analyzing the sound structure of words phonemic awareness. In the context of literacy acquisition, these activities are formed through a process of special education in which children are taught the means of sound analysis.
Correction of speech dysfunction
After a complete examination and assessment of speech, the speech therapist draws up a lesson plan and writes recommendations for a kindergarten or school on how to carry out correction. He can also independently treat FFND by prescribing a set of individual sessions with the patient (home sessions are possible). During therapy, the speech therapist must correct errors in spoken words, develop phonetics skills, and also prepare the patient for writing and reading.
Classes with a speech therapist can be group or individual. Group classes involve working with several children. In individual lessons, the child studies alone. The advantage of group classes is that children can learn to talk to each other through dialogue, skits and other types of communication. At the same time, they compare sounds, learn to find mistakes from each other, and construct sentences correctly.
If a preschooler has a severe form of speech impairment, he can be sent to a special speech therapy kindergarten for classes. Children with speech impairments are gathered here, so classes are aimed at improving speech, reading and writing. Children are enrolled in the group of such a kindergarten from the age of 5-6 years. The duration of correction is 10 months.
Goals of FFN therapy:
- The patient masters correct pronunciation and articulation.
- Formed analysis and synthesis of speech.
- Enrichment of vocabulary.
- The appearance of coherent speech.
- Correct composition of phrases and sentences.
- Teaching correct writing and reading.
- Improved attention and memory.
To conduct classes, the speech therapist uses gymnastic exercises to develop articulation, drawings, toys, games, cards with written syllables and words, and books. It is very important to create a calm and comfortable environment during practical classes. It helps reduce the child’s excitability and improves contact between the child and the teacher. To reinforce the material, the speech therapist gives tasks that need to be done at home.
Along with speech therapy and pedagogical classes, the child needs the help of a psychologist. A psychologist will help you cope with stressful situations and family problems. It also helps develop memory, thinking, and fine motor skills. To do this, they carry out memory training (cards with pictures, tables), art therapy, games with small objects, using ice to stimulate blood circulation in the hands and other techniques.
It is recommended that correction be carried out before entering school so that speech disorders do not disrupt the patient’s mental health or interfere with learning.