Let's remember the basis of any language. Yes, yes, exactly phonetics! What it is? Phonetics is the branch of linguistics that studies sounds. And sounds are an important part of our rich and endless language. With their help, our speech acquires meaning, expressiveness and is emotionally colored.
In the systematization of Russian phonetics, there are 42 sounds: 6 of them are vowels and 36 are consonants. With their help, we create letters in writing, which are then combined into words. Thanks to words, we build sentences.
We have remembered the basics, and now we will deal with the loopholes in phonetics. Today's topic is sonorous sounds. We will study in detail the concept, how they are created, and what the main characteristics are.
Sonorant sounds in Russian
Training in the pronunciation of sonorous sounds using the book
The first thing you need to do is understand which sounds are sonorous. These are voiced consonants that create almost no noise when sounded. The spelling of the term differs from the pronunciation. As an example, consider the word “trace,” which sounds like “slet.” There is a voiceless and a voiced sonorant consonant sound.
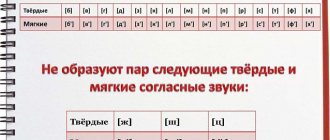
The following letters and their soft variants are related to sonorous phonemes: r, l, m, n, y.
“P” is a fairly sonorous and tremulous phoneme that occurs in the area of the alveoli (the hole where the tooth root is located).
The "L" is formed when air passes over the tip of the tongue and comes into contact with the alveoli.
“M” is a nasal sound, the formation of which involves both lips.
“H” occurs when the tip of the tongue meets the upper row of front teeth.
But when the back of the tongue rises to the palate, the letter “Y” is created. Turbulence does not occur in this case. In the international phonetics alphabet, "Y" is represented as j or "yot".
Distinctive features
How to distinguish sonants:
- Sonorant phonemes or sonants contrast phonetically with aspirated consonants, which, when pronounced, create a turbulent flow in the vocal tract.
- Sonorant elements of speech are only voiced. This is because when these sounds are articulated, the noise is suppressed by the vocal tone and becomes virtually silent. This feature allows us to talk about the closeness of sonorant consonants and vowels . When articulating aspirated consonants, as well as fricative phonemes, on the contrary, the core of the sound is noise, not tone.
- That is why at the end of a word sonorant phonemes are never pronounced dully. The same pattern is observed when a sonant precedes a voiceless consonant. So, in the Russian word “company” [m] is pronounced voiced before the voiceless [p]. At the same time, noisy voiceless consonants in such a situation will be pronounced with voicing: mowing - [koz'ba]. For the same reason, sonants do not have paired voiceless phonemes.
- Sonorant sounds, like other consonants, can form a syllable , which makes them simultaneously similar to consonants and vowels.
Characteristics of sonorous sounds
Translated from Latin, “sonorant” means “sonorous.” The voice is involved in the formation of all sonorous sounds. Minimal noise is heard. When air passes through the soft palate, sound is produced.
The main distinguishing feature is that the sound finds workarounds in any case. Depending on this, the phoneme is given a name according to the place of formation. Sonorant consonant sounds in rich Russian speech do not have phonetic pairs. In any case, they are exceptionally sonorous. The ending of the word is not announced, as is usually the case with other voiced consonants.
Production of sounds
The speech apparatus is used to produce sounds. It includes the larynx with vocal cords, oral and nasal cavities, tongue, lips, teeth, palate. All these organs are used to enable a person to pronounce words. Different sounds are formed due to the fact that obstacles appear in the path of exhaled air: teeth, lips, tongue, and therefore the sounds are different. Try to exhale air while squeezing your lips tightly - you get the sound [m].
Please note that the air does not come out through the mouth, because the lips have created a barrier, but through the nose. Let's try to make one more sound. We exhale the air, but at the same time we compress and unclench our lips. What happens? [b].
When producing each sound, the speech apparatus uses certain air barriers. In ordinary speech, we do not pay attention to whether the air passes freely or not, because the brain gives a signal which letters need to be pronounced at the moment, everything happens as if by itself. But upon closer examination, you will notice that each sound is formed in its own way.
Acoustic characteristic
Acoustic characteristics of sounds
First of all, acoustics classifies phonemes by sonority. They are vocal (sonorant vowel sound) and non-vocal (forming noise). And also the division occurs according to strength. The criterion determines consonant and non-consonant sounds. The last acoustic characteristic concerns height. Depending on the vibration of air particles, high and low phonemes are recognized.
Consonants according to the method of noise production
According to the method of noise production, or according to the method of overcoming an obstacle, consonants are divided into stops (plosives), fricatives (frictions), affricates (stop-frictions), stop-passes, and tremors (vibrants).
Closing (plosive) consonants are formed by the complete closure of the organs of pronunciation, and therefore the air, encountering this barrier, tears it apart with force, as a result of which the noise characteristic of these consonants arises.
Stops in the Russian language include: [p], [p.'], [b], [b'], [t], [t'], [d], [d'], [k], [k '], [g], [g'].
Fricative (frictional) consonants are formed by incomplete convergence of the active and passive organs of speech, as a result of which a narrow gap remains between them through which air passes; the noise is generated by the friction of air against the walls of the crack.
Fricative consonants are: [f], [f'], [v], [v'], [s], [s'], [z], [z'], [sh], [zh], [sh '], [th], [x], [x']. Affricates are sounds that are complex in the functioning of the speech organs: at the initial stage of articulation they are formed as stops, that is, by completely closing the speech organs, but at the end of articulation there is not an instantaneous opening of the stop, but its transition into a gap, as in fricatives.
In the Russian literary language there are two affricates: [ts] (t + s) and [ch'] (t' + sh').
Close-passive consonants are those whose formation is characterized by complete closure of the speech organs with the simultaneous passage of air through the oral cavity or nasal cavity. Depending on which cavity the air passes through, the occipital passages are divided into nasal and lateral.
Nasal occlusions include: [n], [n'], [m], [m']; to the lateral ones - [l], [l '] (the side of the tongue is adjacent to the upper jaw).
Trembling consonants are consonants, during the formation of which the tip of the tongue either closes or opens with the alveoli during the passage of an air stream (vibrates). Trembling ones in Russian include: [р], [р'].
A more clear description of consonants by method of formation will look like this: Hard and soft consonants, voiced and voiceless consonants, stops and fricatives, and others - the table will show everything.
Table of classification of consonant sounds in Russian
| Method of education | Place of education | ||||||
| Labial | lingual | ||||||
| Labiolabial | Labiodental | Forelingual | Middle language | Rear lingual | |||
| Dental | Anteropalatal | Midpalatal | Postopalatines | ||||
| Occlusive | Oral | [b] [ts] [b'] [n '] | [d] [t] [d'] [t'] | [g] [k] [g'] [k'] | |||
| Nasals | [mm'] | [n] [n'] | |||||
| Slotted | Median | [v] [f] [v '] [f'] | [z] [s] [z'] [s'] | [w] [w] [w'] [w'] | [th] | [x] [x'] | |
| Lateral | [l] [l'] | ||||||
| Africans | [ts] | [h'] | |||||
| Trembling | [r] [r'] | ||||||
Sonorous sounds in speech therapy
A speech therapist is most often contacted when correcting incorrect pronunciation is required. If a child has good hearing, but cannot clearly reproduce sonorous consonants, then this phenomenon in speech therapy is called “dyslalia.” Speech correction using special exercises will help with this.
Causes of pronunciation problems:
- Physiological and neurological. These may be consequences of ear, throat, and nasal diseases.
- Lack of parental attention. They may not make enough effort for the child to learn to pronounce words correctly.
- Bilingual education. If family members speak different languages with different phonetic systems, then the correct pronunciation can be confused.
- Bad example. If others speak incorrectly, then the child will use such a model.
- Difficulty distinguishing sounds. Even if a person has perfect hearing, this will not protect him from this problem.
There are no clear rules for correct pronunciation. In some countries, the placement of consonants is not given much importance.
Phonetic analysis and speech therapy
The name of sonorant sounds comes from the Latin word “sonorus”, which literally translates as “sonorous”. The choice of this name is explained by the fact that the voice participates in the formation of sound, despite the fact that the air flow that forms it in the oral cavity is able to find its own bypass paths, which is why it becomes not noisy at all.
In addition, at the end of a spoken word with such inclusions, deafening does not occur, as often happens in many other cases.
Sound characteristics
In order to understand what sonorant means in phonetic analysis, it is necessary first of all to understand the main characteristics of its sound pronunciation. Thus, experts distinguish at least two different groups, which directly depend on the position of the so-called velum palatine:
- Oral. This group of sonorous type sounds is characterized by the raising of the wall of the palate and its adjoining of the pharynx in the area of its posterior wall, as a result of which the passage into the nasal cavity for air flow is automatically blocked. As a result, the formation is oral or clean without the slightest hint of turbulence and other noise vibrations.
- Nasal or nasal. In this case, due to the fact that the velum goes down, the passage into the nasal cavity for a stream of air, on the contrary, opens, due to which it functions as a kind of auxiliary sound resonator during pronunciation.
Features of parsing
To consolidate the knowledge acquired in this area, it is recommended to resort to an exercise that has been popular since Soviet times, which involved parsing a word into individual phonemes. As for completing the task, most often it involves following the following algorithm of actions:
- At the first stage, the word is pronounced out loud (possibly several times for better perception of all its constituent elements).
- The second step involves writing this word in full accordance with the spelling rules.
- The transition to the next stage consists of breaking the word down into syllables with the obligatory designation of the only correct place of stress.
- Breaking down into individual syllables allows you to accurately indicate possible places where a word is transferred from one line to another, which is also an important exercise for phonetic analysis.
- Next, each letter is analyzed with a detailed description of all its sound characteristics (presence of a pair, hardness or softness, etc.). At the same stage, sonority should be identified, if it is present in the word being analyzed.
- After all the stages have been completed, all letters and sounds are counted, although these results often do not coincide, and this is the absolute norm.
Based on the results of the work performed, another analytical action is carried out aimed at determining the relationship between spelling and pronunciation. Simply put, the test taker is faced with the task of determining whether what was written corresponds to what was spoken.
Possible problems and their solutions
Recently, an increasing number of parents have had to visit speech pathologists due to poor pronunciation in their children. And most often, the reason for contacting is a child’s violation of the pronunciation of paired and unpaired consonants. This pathology tends to be called dyslalia, which is characterized by good hearing, but difficulty reproducing certain letters.
The placement of such letters can and should be done, the main thing is to give the speech therapist the opportunity to understand the root causes that provoked the current problem. Typically this list includes the following negative factors:
- Problems related to physiology. Sometimes impaired pronunciation is caused by anatomical features, which, in turn, can be primary (congenital) or secondary (acquired) in nature, often caused by the development of chronic ENT diseases.
- Neurology. Mental abnormalities can also cause delayed speech development or pathology.
- Educational deficiency. You should not think that speech abilities always develop automatically, because each child is individual, and what is easy for one is not given to another. That is why experts strongly recommend paying maximum attention to the development of children's speech in order to avoid the consolidation of any serious defects or errors in it.
- Bilingualism. Children raised by bilingual parents also often have serious pronunciation problems, especially if the adverbs used in the family are of incompatible phonetic structure.
- Environment. If in the child’s society there are other children or adults with problematic pronunciation, then there is a high probability that it was this factor that provoked the speech errors.
- Hearing impairment. An ideal ear for music is not a 100% guarantee of correct recognition of all phonemes in speech.
It is important to remember that the choice of correction and its success will directly depend on how correctly the specialist was able to establish the cause of the development of dyslalia. For example, if an anatomical pathology is detected, surgical intervention becomes indicated. If the reason for everything is the baby’s social circle, then it is advisable to change it. The speed of response is also of great importance, because the sooner treatment is started, the more lasting and sustainable results can be achieved in the future.
Complex therapy, which involves not only regular classes with a speech pathologist, but also constant home exercises with the child, has proven to be most effective.
How to learn to pronounce sonorous consonants?
A speech therapist, using the correct technique for producing sonorous sounds, will help rid the child of dyslalia. The sooner parents turn to a professional, the faster the speech disorder will be resolved.
Methods for treating dyslalia:
- Operation. Required if the cause of the problem is a defect in the structure of the body.
- Change of social circle. If a child has a misunderstanding of pronunciation due to social factors, then another medium for communication can be found.
- Working with parents. First of all, they must set the right example. Often, mom, dad and other relatives begin to lisp, which confuses the baby. Training in articulation techniques, motor skills, and solving problems with air direction is a preparatory stage carried out by a speech therapist.
- Learning words, phrases, sentences from memory, and automating sonorous sounds. Next you will need to break the words into syllables and letters.
- Pronunciation training in everyday life, automation continues. The child must regularly hone his skills in practice, overcoming anxiety.
To get rid of a speech defect, you should visit a speech therapist to establish sonorous sounds. At the same time, do home exercises. Even difficult situations can be corrected with six months of hard work.
What are the consonant sounds?
As you know, in Russian phonetics, vowels and consonants are distinguished. The composition of consonant sounds in the Russian language is heterogeneous. Some of them are formed with a greater amount of noise. This is how voiceless consonants arise:
[k] [k'] [p] [p'] [s] [s'] [t] [t'] [f] [f'] [x] [x'] [ts] [h'] [ w] [w']
When they form, the air stream encounters obstacles in the oral cavity, which causes noise.
In the production of other consonants, the proportion of noise is smaller, although noise predominates over voice. These are voiced consonants:
[b] [b'] [c] [c'] [d] [d'] [e] [d'] [g] [g'] [h] [h']
Characteristics of vowels
The main feature of vowel sounds is that when they are formed, a stream of air, having formed a tone in the vocal cords, no longer encounters any obstacles in the oral cavity. That is, they consist of only tone (voice) without added noise.
The vowels are the sounds a, o, u, i, ы, e. The articulation of each vowel sound depends only on the position of the active organs of speech (lips, tongue, soft palate and lower jaw).
The functional feature of vowel sounds is that they form a syllable, i.e. play a syllabic role.