Stroke is a condition in which an acute disturbance of blood circulation occurs in the cerebral arteries, which ultimately leads to a persistent decrease or loss of function of the limbs and internal organs innervated by the affected area of the brain. Experts distinguish two forms of stroke: hemorrhagic and ischemic, while the ischemic form is observed 2.5 times more often than the hemorrhagic one. With an ischemic stroke, the lumen of the cerebral artery is blocked (occluded), due to which nutrients cease to flow to the neurons. In the hemorrhagic form, the mechanism of stroke development is different; a cerebral arterial vessel ruptures with blood spilling into the brain tissue and soaking it. As a result of a hemorrhagic stroke, displacement (dislocation) of the brain is possible with the development of severe complications, including death. Damage to the left hemisphere leads to dyslexia or complete loss of speech ability. Speech after a stroke can be restored, and in most cases, effective recovery depends on timely medical care.
How to restore the ability to speak in an adult after losing it?
How long it takes for speech function to recover depends on how severely the brain was damaged.
Therefore, in some patients, the ability to speak is restored quite quickly (within a few weeks or months), while in others it takes years, and it is difficult to predict how long it will take. To restore patients who have suffered a stroke, the following types of rehabilitation are used:
- Drug therapy.
- Classes with a speech therapist.
- Physiotherapy.
- Massage.
- Surgical intervention.
Medicines
During rehabilitation after a stroke, the doctor prescribes several groups of drugs to the patient that help reduce side effects, improve the condition and help the patient quickly return to their normal lifestyle:
- Muscle relaxants.
- Antidepressants.
- Anticonvulsants.
- Antiplatelet agents.
Muscle relaxants
On a note. In the third month after a stroke, the patient may develop muscle hypertonicity, which greatly slows down the rehabilitation process.
Then muscle relaxants are prescribed that can reduce excessive muscle tone. The best muscle relaxants for stroke:
- Sirdalud (cost in Moscow from 227, in St. Petersburg from 176).
- Tizalud (cost in Moscow from 160, in St. Petersburg from 125 rubles).
Antidepressant series drugs
Almost 80% of patients suffer from depression after a stroke, which slows down the recovery process. In this case, antidepressants are prescribed. The best antidepressants for stroke:
- Nortriptyline (cost in Moscow from 990, in St. Petersburg from 1,000 rubles).
- Paxil (cost in Moscow from 650, in St. Petersburg from 660 rubles).
Anticonvulsants
When seizures occur, anticonvulsants are prescribed, but they should be taken with caution, as this group of drugs can cause side effects. The best anticonvulsants for stroke:
- Finlepsin (cost in Moscow from 215, in St. Petersburg from 193 rubles).
- Convulex (cost in Moscow from 116, in St. Petersburg from 135 rubles).
Antiplatelet agents
If after a stroke the patient’s blood becomes more viscous, this slows down the recovery of brain tissue. In this case, the help of antiplatelet agents is required to prevent the formation of blood clots. The best antiplatelet drugs for stroke:
- Reopoliglyukin (cost in Moscow from 102, in St. Petersburg from 110 rubles).
- Clopidogrel (cost in Moscow from 226, in St. Petersburg from 205 rubles).
Important! Any medications should be prescribed only by the attending physician. Do not self-prescribe medications, otherwise this can only worsen the patient’s condition.
Medication alone does not provide much benefit, but it does help progress recovery when used with other types of therapy, such as speech therapy and physical therapy.
- Exercises after a stroke at home for recovery
Classes with a speech therapist
At the first lesson, the speech therapist draws up a plan for each patient individually. The following exercises are required:
- Reading tongue twisters.
- Drawing.
- Mimic and speech therapy massage.
If all the specialist’s recommendations are carefully followed, about 20-30% of patients with moderate and severe speech disorders begin to speak normally by the time they are discharged from the hospital. Classes can also be held at home. The exercise program must be combined with medications, physical therapy and other types of rehabilitation.
Physiotherapy
This type of rehabilitation stimulates muscle recovery and helps to achieve better results from classes with a speech therapist and from taking medications.
- Magnetotherapy. This procedure stimulates all processes in the brain, and also improves the functioning of the endocrine and nervous systems. A rather painful method, but it is considered one of the most effective. The patient's condition improves after 2-3 weeks.
- Dorsanval. Prescribed for poor blood supply to the brain and limbs. After a whole course of procedures, which is at least 5-7 sessions that take place over 2-3 weeks, the patient’s condition improves significantly.
Massage
Therapeutic massage for stroke significantly improves blood supply to the affected tissues, which increases the flow of oxygen and other nutrients to them. In addition, massage helps relieve muscle and psychological tension. A therapeutic massage course usually consists of 10 sessions , but can be adjusted individually for each patient.
Note! A massage course can only be conducted by a qualified specialist with a medical education.
Surgery
A method such as surgery is resorted to in extreme cases, when other methods do not improve the patient’s condition and cannot restore lost speech. To restore speech, a neurosurgical operation is performed, which creates additional connections between healthy tissues and vessels in the speech area of the brain, without affecting the damaged areas.
Types of disorders
No one knows exactly how the brain will be damaged when a stroke occurs. But these damages will affect the person’s future ability to speak clearly and understand the speech of others. What kind of speech disorders does a brain stroke lead to, and whether the ability to speak will be restored, we’ll figure it out further.
Dysarthria
If a stroke affects the subcortical structures of the brain, this type of disorder appears. With dysarthria, the patient's speech becomes unintelligible, pronunciation slows down, weakness of articulation and increased salivation appear. But the patient is able to understand the speech of others, as well as read and write. To restore speech, special exercises are prescribed to help strengthen the muscles of the speech apparatus.
Aphasia
With this disorder, the patient's brain loses the ability to create adequate nerve impulses in the area responsible for speech. Aphasia is divided into 6 types, which we will discuss further:
- Motor aphasia. If the stroke affects the upper part of the main artery of the brain, this type of disorder appears. The patient pronounces individual words and entire sentences, but the order of words may be disrupted. Sometimes patients can repeat words syllable by syllable. It is advisable to begin treatment of motor aphasia 7 days after the stroke. To do this, doctors recommend singing songs and pronouncing simple words.
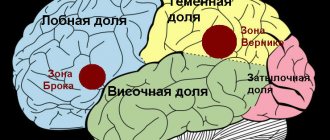
- Sensory aphasia. The sensory type of aphasia appears when Wernicke's center is damaged.
The patient can hear, but ceases to understand speech. This type of pathology can manifest itself in a mild form, then the patient is able to recognize simple phrases and words. On a note. With regular sessions with a speech therapist, the disorder can be partially cured. - Dynamic aphasia. When the posterior frontal areas of the brain are damaged, this pathology occurs. It distorts the thought process, making it difficult for the patient to compose and pronounce coherent sentences. The disorder is treated in classes with a speech therapist.
- Acoustic-mnesthetic aphasia. With acoustic-mnestic aphasia, the patient is unable to retain information in his head, and auditory-verbal memory decreases. The disorder appears when the posterior and middle parts of the temporal lobes of the brain are damaged.
- Amnestic aphasia. If a stroke affects the lower temporal region of the brain, amnestic aphasia develops. This is the most minor speech disorder that can occur during a stroke. The main problem with this form of the disorder is that it can be difficult for the patient to select certain phrases and words because they are forgotten.
- Total aphasia. If the brain suffers extensive damage as a result of a stroke, total aphasia develops. The patient completely loses the ability to speak and understand the speech of others, and there is passivity on his part. For this form of the disorder, treatment must begin as quickly as possible.
Dyspraxia
In this disorder, the nerve impulse from the brain enters the facial muscles incorrectly or with a delay, so it is difficult for the person to reproduce familiar sounds. The patient may experience the following problems:
- Facial muscles cannot work correctly, making it difficult to speak clearly.
- The patient has difficulty pronouncing some sounds.
- It is difficult to pronounce words clearly, especially if someone asks for it.
Reference. On days 7-10 after the stroke, the patient can begin drug therapy and begin classes with a speech therapist. If you follow the advice of your doctor, you can get rid of dyspraxia almost completely.
Speech impairment due to stroke
Stroke can be hemorrhagic or ischemic. With a hemorrhagic stroke, too much blood flows to the brain, and arteries may rupture, but with an ischemic stroke, on the contrary, not enough blood flows to the brain.
Hemorrhagic stroke is less common, but causes more serious consequences for the patient. But in both cases, the areas of the brain responsible for speech may be damaged in a person.
- Is it possible to do Bubnovsky exercises for arthrosis of the joints?
If speech fails, then the disturbances occurred in the left hemisphere of the brain. With such a stroke, the right side is paralyzed and there is no speech.
Strokes with paralysis on the right side occur more often than on the left. And this is better for the patient, since in this case it is easier to make a diagnosis, since speech disorders are always manifested.
Such disorders are called aphasia. In this case, disturbances can occur in different parts of the brain. Depending on this, the consequences may be different. How to restore speech after an ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke?
Let's look at the types of aphasia and their consequences:
- Amnestic . A person can communicate, but periodically forgets the names of the objects he is talking about.
- Semantic . In this case, you need to talk to the patient exclusively in simple sentences; he simply will not understand complex ones.
- Sensory . A complex type of aphasia in which the patient does not understand speech at all. For him it comes down to a set of sounds. At the same time, he practically cannot understand the meaning of what was said.
- Motor . A person understands everything, but cannot say anything coherently, confuses sounds and words, or gets stuck on one sound combination.
- Total . The patient does not understand anything, does not recognize anyone, cannot say anything. Most often, this phase occurs immediately after a stroke. After some time, it can turn into motor.
No one can give a 100% guarantee that the patient will be able to speak at all. But if you act quickly, correctly, follow all the recommendations of specialists, create an atmosphere of patience, love and care around a sick relative, support him as much as possible in his desire to recover, then he has a much better chance of quickly recovering his speech loss.
Simple speech problems can be solved in 2–6 months with special regular training and exercises. If the degree of violation is greater, then more time will be required.
Sometimes this can last up to several years. A forecast of 5-10 years is considered a period after which changes for the better are hardly possible. However, miracles of recovery happen, but they most often lie in the realm of intangible reality.
People say, “Houses and family walls heal.” This relates to the question of how relatives of a stroke patient should behave. The first questions they ask the doctor are: “Is speech restored after a stroke? Is it even possible to restore speech after a stroke? How long does it take for speech to be restored after a stroke? Relatives can be understood. But a lot depends on their behavior, on their actions.
Here are the usual recommendations from doctors to the patient’s relatives:
- The patient must feel that his family needs him, that he is valuable to her, that his relatives believe in him, love him, sincerely wish for his recovery and do not doubt it at all. In this case, he will have additional motivation to get back on his feet as quickly as possible. This means there will be energy for this.
- You need to constantly talk with the patient and in his presence. Then he will feel involved in the family. But the most important thing: if the topic is important to him, he will try to talk.
- It’s good if his favorite music, the songs he used to sing, are played in the house. The inner desire to sing along can well stimulate the awakening of his speech impulses.
- But it is better to remove excess noise, variety and volume of sounds so as not to overload the patient. You need to talk to him quietly, calmly, without explosive emotions. Surround him with your kindness. At the same time, there is no need to emphasize every time that he is terminally ill.
- Relatives need to have maximum patience, since they are the ones who must become constant assistants for the patient when performing the exercises that the speech therapist will show. And under no circumstances should you react with irritation if you can’t do the exercise.
What is a stroke
The essence of a stroke is the cessation of blood supply and functioning of a part of the brain as a result of damage to a vessel.
The larger the affected area, the more severe the stroke. Necrosis of a portion of the brain substance is called an infarction [3]. There is a high risk of death in the first few hours, and then in the period up to 28 days after a vascular accident. The annual mortality rate from stroke in the Russian Federation is 374 cases per 100,000 [10]. In 2018, 35% of patients died in the acute period of stroke; by the end of the first year, this figure increases by 15%, and in general, in the first 5 years, the mortality rate of strokes is 44% [11]. The mortality rate from stroke was 92.9 per 100,000 population, and the hospital mortality rate was 19.1% [5].
Long-term disability is most likely for patients who have suffered a stroke. The prevalence of primary disability due to stroke in 2018 was 3.2 per 10 thousand population [2]. Of these, 31% need constant care, 20% have severe mobility limitations, and only 8% return to work [3]. The prevalence of recurrent strokes in 2014 was 0.79%, of which ischemic
strokes account for 87.5% [9].
A set of activities after the crisis
Despite the fact that each type of aphasia has its own exercises for restoring normal speech after a stroke, it should be remembered that all disorders are mixed in nature and require a systematic, special approach.
A set of special classes will help not only regain lost skills, but also improve a healthy person’s oratory abilities and diction.
- How can exercise therapy help restore knee joints with arthrosis of degrees 1 and 2?
During training, it is recommended to adhere to the recommendations of the speech therapist, which include:
- Pull the lip folds into a tube, hold for 3-5 seconds, then repeat (up to 10 approaches).
- Use the lower part of your jaw to grab the top of your lip, hold for 2-3 seconds, release (5-10 times).
- Similar to the previous exercise, only in reverse - pinch the lower part with your upper lip.
- Open your mouth slightly, stretch your neck forward, stick out your tongue (as far as possible), hold for a few seconds (5-10 repetitions).
- We take turns licking the upper and lower lip folds, from left to right, then vice versa (up to 10 approaches).
- Draw a tube with your tongue.
- Lick the lip folds in a circle.
- Close your mouth and reach your lower palate with your tongue.
- Clicking your tongue like a horse while running.
- Close your mouth, open your teeth, move your tongue in a circular motion between the labial folds and teeth.
- Try to smile, showing all your teeth, then repeat the movement with your jaw closed.
- Hiss like a snake, moving your tongue out of your mouth.
- Send a kiss while smacking your lips loudly.
- Use your tongue to reach your chin, after the tip of your nose.
Speech therapy exercises after stroke
Exercises for aphasia can be performed in different sequences 2-3 times a day, combining them with other activities to restore speech functions. Logically complete phrases with an assistant, learn tongue twisters, poems, counting rhymes, songs, listen to your favorite pieces of music.
In order for speech to be restored completely (as far as possible), it is necessary to approach the implementation of the recommendations of the speech therapist or the attending physician with all responsibility. There should be complete silence in the room during classes.
Late and remote periods
At a later stage, the body’s potential for rehabilitation after a stroke gradually decreases, but the patient must continue to study and train self-care skills. This period already passes at home, so responsibility for the health and mental state of the patient falls entirely on his loved ones.
You can change your usual exercise therapy complex by adding new exercises and classes with simple exercise equipment, for example, an expander. It is recommended to talk with the patient as often as possible, ask questions, thereby encouraging him to be vocal.
A year after the stroke, the exercises no longer have a pronounced effect, so in the long-term recovery period, the main attention should be paid to consolidating skills and periodic visits to the doctor for follow-up examinations.
Conditions for successful rehabilitation after a stroke
A stroke is a difficult ordeal, especially for older people, who can suffer from it with unpredictable consequences. How long it will take to recover - even doctors cannot answer this question for sure. But in order to shorten the rehabilitation period after a stroke, the patient must provide a number of conditions:
- rehabilitation should take place under the strict guidance of a qualified doctor according to an individually developed program;
- the rehabilitation process must be continuous and comprehensive. This means that it is necessary to work on restoring all body functions simultaneously and sequentially;
- in the home environment, it is necessary to create all the conditions for the successful rehabilitation of the patient: equip the sleeping place with an anti-decubitus mattress, allocate a place for doing therapeutic exercises and purchase the necessary exercise equipment, as well as additional equipment - walkers, wheelchairs, canes, special personal hygiene products;
- provide a balanced diet throughout the entire period of rehabilitation;
- take care to create a favorable home atmosphere, sensitive and caring attitude towards the sick person.
Other methods of treatment and prophylaxis
Complex speech impairment after a stroke can be eliminated using other methods of therapy, which only a qualified neurologist can recommend. For these purposes, he will conduct a comprehensive diagnosis, based on the results of which he will prescribe appropriate treatment, including:
- Physiotherapy – electrical stimulation of speech muscle tissue. It is most often used for the motor type of aphasia. But modern doctors resort to it in rare cases.
- Acupuncture - used to restore articulation and speech function. Prescribed for motor type of pathology.
- Functional biofeedback. This technique is based on visual influence on the speech muscles. It is not recommended for use in patients with perception disorders.
Complex therapy, including these methods of influence, helps improve speech functions. The complexity of the rehabilitation period and how long it will take to treat the consequences of a hemorrhagic or ischemic stroke depend on the location of the hemorrhage and its extent. In some cases, recovery takes only a month, in others up to 2 years.
Problems with speech after a cerebral hemorrhage can consist not only of direct damage to the centers, but also of paralysis of facial muscle tissue. As a result, the articulatory muscles stop doing their job, and therapy and rehabilitation are carried out as for coordination disorders.
Acupuncture – used to restore speech function
Recovery in a boarding house
Rehabilitation of an elderly person after a stroke at home requires the full-time employment of one of the relatives for the next six months. While the patient is bedridden, he cannot be left at home alone for two reasons: he is helpless and it is necessary to deal with him several times a day. The volume of care is so large and multidirectional that soon the caregiver himself will need support and replacement.
In boarding houses for the elderly, professionals are involved in the rehabilitation of patients. Special equipment is used for treatment. An individual program is developed for each patient. Restoration methods that have been developed over the years produce positive results within a month.
Speech therapy exercises to restore speech after a stroke at home
Let us now consider what methods a specialist can offer to restore a patient’s speech, and how they should be applied.
Articulation and breathing exercises
First, the person is asked to simply breathe, then, as he exhales, pronounce certain consonant sounds, one sound per exhalation. After this, while exhaling, all these sounds are pronounced in a row. There are no more than four of them. Sounds can be pronounced while exhaling, also with the chin raised.
Articulation gymnastics after a stroke
It includes exercises for the tongue, lips, voice, and facial muscles.
Exercises for the tongue and soft palate
- Stick your tongue out of your mouth and hold it there for a few seconds.
- Pull it down again and bend it up, hold it for a while.
- Pull it down and direct it first to the right corner of the mouth, then to the left.
- Move the tip of your tongue back and forth across the roof of your mouth.
- Direct your tongue to the right and left cheek.
- Click your tongue, first once, then twice, then three.
- Relax your tongue and, moving it back and forth, lightly bite with your teeth.
- Lick your lips first in one direction, then in the other.
Lip exercises
- Move your lips forward.
- Make a smile with your mouth closed.
- Bare your teeth and raise your upper lip, hold this for a couple of seconds.
- Puff out your cheeks and pump the air from side to side, rolling the air around your mouth.
- Relax your lips and blow through the gap in them.
Voice exercises
Speech gymnastics is performed for ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke.
- We pronounce all the vowel sounds separately, first long, then short, while exhaling. After this, as you exhale, we pronounce all the sounds in a row.
- We say the sound Y only articulatory, without sound, and feel the tension under the chin.
- We pronounce all the vowel sounds in a row, flowing into one another, alternately emphasizing different sounds.
- We pronounce consonant sounds, first unvoiced, separately, then one after another on one exhalation. After this, we pronounce voiced sounds in the same way. We add consonant sounds with vowels into certain syllables, while alternating paired unvoiced and voiced consonants.
All combinations of sounds, their permutations and combinations are determined by the speech therapist.
Tongue twister exercises after a stroke
First, we ask the patient to finish the tongue twister he knows, gradually increasing the number of words he says. If possible, we bring the exercise to perfection.
Exercises for facial muscles
- Raise your eyebrows, lower them, frown, relax.
- Open your mouth wide, try to stretch it, then relax it.
- Smile without opening your mouth.
- Inflate and deflate your cheeks.
- Pull your lips out as if for a kiss.
- Extend your tongue as far as possible in different directions from your mouth.
- Move your lower jaw carefully, first to the left, then to the right, then in a circle.
Speech therapy massage after stroke
After completing a set of exercises, it is necessary to apply a facial massage to each area of the face.
It is important that massage movements are selected only by a specialist. Some areas of the face will need to be relaxed, while others will need to be toned. If you approach this on your own, you can cause irreparable harm.
In addition to massaging the facial muscles directly, they massage the tongue, lips, inner surface of the cheeks, ears, scalp, and hands. All this relieves muscle stiffness and thus liberates speech.