RESTORATION OF SPEECH IN PATIENTS WITH APHASIA AT THE EARLY STAGE AFTER STROKE
A stroke (synonymous with acute cerebrovascular accident) is the death of a part of the brain associated with the cessation of its blood supply. Impaired blood supply to certain areas of the brain leads to the appearance of aphasia. Aphasia comes in various forms and degrees of severity - from minor difficulties in articulating or naming objects to complete loss of understanding speech or verbal expression of thoughts. In the first days after a cerebrovascular accident, speech disorders in patients manifest themselves in the form of total aphasia: the patient does not speak and does not understand speech addressed to him. With total aphasia, the patient cannot understand written and spoken speech. Usually the lesion is localized in the left hemisphere and is quite extensive.
If total aphasia is caused by vascular origin, then patients often experience a tendency to slow speech recovery. In this case, the type of speech disorders may be similar to Broca's aphasia, or some other types of this disease. Typically, total aphasia occurs as a result of a stroke, when the sensory and motor parts of speech are simultaneously affected. This process involves the entire region of the cerebral middle artery. Total aphasia after a few days or weeks can be replaced by gross motor aphasia: the patient begins to understand speech addressed to him, but communicates with others using a speech “embolus” - a stereotypically repeated sound combination, syllable or word, sometimes well intoned.
Speech therapy classes for total aphasia begin with the restoration of listening comprehension. The method of stimulating the understanding of speech by ear for patients with total aphasia is based on their correlating intonations with gestures, inducing certain motor and facial reactions in the patient, and using the phonological features of intonations. To stimulate listening comprehension of speech, a patient with total aphasia is asked to perform various actions according to oral instructions.
Restorative learning is based on one of the most important properties of the brain - the ability to compensate. To restore impaired functions, both direct and bypass compensatory mechanisms are used.
The first is associated with the use of direct disinhibiting methods of work. They are mainly used in the initial stage of the disease and are designed to use reserve intrafunctional capabilities. Techniques and methods of disinhibition during the learning process come down mainly to various activation of speech activity and the removal of inhibitory background. Patients are persistently stimulated through various tasks for active verbal communication. The following techniques and exercises are used:
- Ordinal counting from 1 to 10.
— Count from any arbitrary number (from 5, 6, etc.).
— Highlight any number (or two). We count from 1 to 10, but when
In this case, we pronounce the highlighted numbers loudly, the rest - in a whisper (in an undertone).
- The same techniques, only the counting occurs in reverse order.
- Naming the days of the week.
- Listing the months of the year.
Bypass methods involve voluntary mastery of the way of perceiving speech and one's own speaking. This is due to the fact that bypass methods require the patient to implement the affected function in a new way, which differs from the usual one established in premorbid speech practice. Restoring a number of speech functions requires the connection of non-speech supports. Therefore, the sequence of work on speech and non-speech functions is decided in each specific case, depending on the combination of verbal and non-verbal components of the syndrome. Bypass methods imply compensation based on the restructuring of the most impaired function due to cross-functional restructuring. In other words, the restorative effect is achieved through the introduction of new, “workaround” ways of performing certain speech or gnostic-praxic operations. Speech restoration is facilitated by:
- involving the patient in simple non-speech activities, for example:
- constructing cubes, putting together puzzles, sketching, drawing objects, plots, etc.
— game of lotto, dominoes, playing cards.
— laying out serial pictures, plots.
- using tasks that require speech understanding:
- showing body parts,
- showing objects, actions in pictures,
- following simple instructions.
- stimulating simple dialogues that require a response in one or two words or a gesture.
- Encouraging reading and writing by offering activities such as:
- placing captions under pictures,
- work with subject lotto,
- naming (or choosing from the proposed) numbers, letters,
- recording from dictation (or choosing from the suggested) numbers, letters,
- writing and reading familiar and simple words and phrases.
Rehabilitation training is carried out according to a special, pre-developed program. The program should include certain tasks and corresponding work methods, differentiated depending on the form of aphasia, the severity of the defect, the stage of the disease, and the individual characteristics of speech disorders. After conducting a speech therapy examination of a patient with total aphasia, we developed an individual plan for speech therapy work.
Patient E. 72 years old. Acute cerebrovascular accident of the left middle cerebral artery on March 31, 2014.
Neuropsychological speech therapy examination.
He makes no complaints due to the complexity of his speech disorder.
Objectively:
- Impressive speech: understands situational and everyday speech, understanding complex lexical and grammatical constructions is difficult. The latency period for completing tasks has been increased.
Expressive speech: represented by “embolus” (dvvvu).
Phonemic hearing is impaired.
Oral articulatory praxis is impaired.
Reading and writing are in decline.
Nominations are shown based on pictures selectively.
Automated, de-automated speech is impaired.
- Shape and position of the tongue in the midline. No deviations were found.
Swallowing is not impaired.
Subtle differentiated movements of the tongue and sound pronunciation could not be studied.
The tone of the tongue muscles is increased.
Conclusion: efferent-afferent motor aphasia. Sensory aphasia. Speech impairment of the first degree of severity.
Work plan:
- Restoring understanding of spoken speech: captioning pictures; cheating; decomposition of pictures.
- Overcoming oral-articulatory apraxia, working with automated rows (disinhibition)
- Non-verbal activities (solving examples, dominoes, lotto, classifications, eliminating the odd one out).
Thus, speech restoration in severe forms of aphasia includes both stimulation of listening comprehension and disinhibition of the expressive side of speech.
Speech therapy work for aphasia is a long and labor-intensive process that requires the cooperation of the doctor, speech therapist, patient and his immediate environment, and speech restoration should not take place empirically, but skillfully, at a serious professional level. Therefore, it is important to select patients for intensive rehabilitation treatment and training. The prognostic significance of individual factors affecting the effectiveness of recovery (age, premorbid level, motivation, signs of left-handedness, somatic diseases and their dynamics) should be taken into account.
List of used literature:
- Rustle - Trotskaya, M.K. Strategies and tactics for speech restoration. / M.K. Rustle - Trotskaya. – M.: EKSMO Press, V. Sekachev, 2001. – 432 p.
- Shklovsky, V.M., Wiesel, T.G. Restoration of speech function in patients with different forms of aphasia, M.: “Association of Defectologists”, V. Sekachev, 2000. - 96 p.
- Wiesel, T.G. Neuropsychological blitz examination - M.: V. Sekachev, 2005.-24 p.
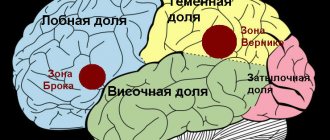
Main types of speech disorders
There are two main forms of disorders - aphasia and dysarthria (the first is more common). With aphasia, there is a deterioration in speech functions as a result of damage to the speech centers in the brain. It can be complete (when speech is completely absent) and partial. The first time after a stroke is often accompanied by a lack of speech, but thanks to high-quality rehabilitation measures the situation improves.
There are six main forms of aphasia:
1. Motor. It is divided into two main types - afferent and efferent. In the case of the first, a person experiences difficulties in choosing the articulatory posture necessary to pronounce specific sounds. With efferent speech, instinctive speech is preserved, but repetition is severely impaired. Patients are bothered by kinetic apraxia, which makes it impossible to switch from one position to another.
2. Dynamic. The main characteristic speech defect is severe difficulty or inability to actively speak. The patient is unable to formulate a statement normally because external and internal speech is impaired. Echopraxia often appears when a person automatically repeats his interlocutor’s words and movements.
3. Touch. It is divided into three main types: cortical, subcortical and transcortical. In the first case, the patient does not understand or pronounce sounds. In the second case, the transmission of impulses from the centers that perceive sound information is distorted. With the third, the ability to perceive light speech structures is preserved, but writing is impaired and visual function deteriorates.
4. Semantic. Patients have a complete lack of understanding of complex speech formulations that reflect spatial relationships. Difficulties often arise in completing tasks containing complex syntactic structures. Patients are able to forget the names of familiar objects (for example, spoons, tables). Reading is slow, acalculia may develop. This is a neuropsychological symptom that manifests itself as a counting disorder
5. Acoustic-mnestic. This form is characterized by difficulties associated with retaining in memory information perceived by a person by ear. Many patients are not even able to repeat after a speech therapist a simple sequence consisting of 3-5 words, or to grasp the meaning of speech at a fast pace or when talking with two or more people at once.
6. Total. This form is characterized by a complete absence of speech (due to damage to many speech areas of the brain). This is the most severe form, which requires long-term correction with drug therapy and exercises.
Dysarthria is a speech disorder associated with impaired mobility of the organs of articulation (tongue, palate and lips). It can develop when various structures are affected, but most often the cranial nerves involved in the functioning of the speech muscles are affected. Dysarthria consists of difficulty pronouncing certain words or sounds (speech is sluggish and slurred).
Methods of correctional work for aphasia
The same teaching methods are used for left- and right-handed people. The main principle of speech restoration is to use the compensatory capabilities of the undamaged area of the brain. The duration of speech therapy sessions for all forms of aphasia is two to three years (in the hospital, then at home), but the patient should not be told about this. After examining the patient, the neurologist determines the form of aphasia. Corrective and rehabilitation work with a speech therapist begins with permission and under the supervision of the attending physician from the first weeks after a stroke or injury. In the early stages, the duration of classes should not exceed 15 minutes twice a week. In the later stages it lasts 30-40 minutes three times a day. The first stage is the same for all types of aphasia: speech disinhibition. They talk to the patient, observe his auditory perception, answers to questions, and understanding of speech. Further work is carried out depending on the form of the disease on all aspects of speech.
Causes of the disease
In rare cases, the disease becomes a consequence of leukodystrophy, a congenital pathology that affects the white matter of the brain and spinal cord. To eliminate it, the patient is given a bone marrow transplant, but there is little chance of recovery. Much more often, aphasia in children is provoked by the following conditions:
- Tumors inside the brain. Neurons in the parietal zone are destroyed by medulloblastomas, gliomas and astrocytomas. The larger the tumor becomes, the more noticeable speech impairments become.
- Traumatic brain injuries. The patient's neurons responsible for the perception of information that comes from the organs of articulation are injured. A hematoma forms inside the brain.
- Strokes. They are rarely diagnosed in children.
Hemorrhagic strokes are characterized by tissue compression and hemorrhage. In the ischemic type, neurons in the damaged area die due to arterial spasm caused by blood flow disturbances. Our center’s specialists will conduct an extremely accurate diagnosis of aphasia and select effective treatment.
Treatment
Therapy for speech dysfunction is carried out in two directions:
- Eliminating the causes of aphasia and restoring the functions of the affected areas of the brain by prescribing medications and physiotherapeutic methods.
- Correction of aphasia through speech therapy sessions.
An individual treatment plan is developed for each patient. In our clinic, in addition to a speech neurologist and speech therapist-aphasologist, neuropsychologists, massage therapists, acupuncturists, and osteopaths are involved in the treatment process. An excellent effect is achieved by using the method of transcranial magnetic stimulation, which has been used since the beginning of the 21st century. successfully used all over the world. Our specialists have been trained in this technique and have certificates for the right to use it.
Do not delay your visit to our clinic. The earlier medical treatment and speech therapy work for aphasia is started, the greater the chance of complete restoration of speech skills.