Dyslalia occurs:
- Phonetic - distortion of pronunciation (When a child says various sounds incorrectly - R, L and others).
- Phonemic - replacement of sounds (Replacement of letters, for example S - Sh: went-ambassador).
- Phonetic-phonemic – articulatory disorders.
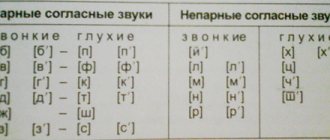
There are simple and complex dyslalia. Simple implies disorders associated with the perception of one sound or one phonetic group. Complex – when sounds from different phonetic groups are not perceived. Phonetic groups are sonorants (P, Rb, L, L, N, N', M, M', J), whistling (S, S', Z, Z'), sibilants (Zh, Sh), africates (Ch, Shch).
Simple dyslalia has forms that include various types of disorders:
- Sigmatism
- Parasigmatism
- Rotacism
- Pararotacism
- Lambdacism
- Yotacism
- Gamacism
- Kappacism
- Hitism
Features of sigmatism
- The defect in speech is built symmetrically, that is, if a hard sound suffers, then the soft one is also distorted.
- If only soft sibilants are used, then the sibilants will be pronounced softer.
- Nasal sigmatism is also determined, but it does not exist as such. If there is a nasal pronunciation of whistling and hissing sounds, then the pronunciation of all sounds will be nasal, and this is rhinolalia. However, nasal sigmatism can occur in deaf and mute people when sounds are presented to them.
- Hissing and whistling sounds are sharply contrasted in terms of acoustic characteristics, but less contrasting in terms of articulation.
Rotacism
This is a violation of the pronunciation of the sounds “R” and “R”. Rhotacism is very common due to the articulatory difficulty of pronunciation. Babies have a regular "R" sound in their babble. But children begin to pronounce a real, pure “R” after 2 years. Articulatory preparedness plays a role here. Normally, the respiratory stream flows through the center of the tongue, the tip of which vibrates, the side edges are pressed against the upper outer teeth.
In case of deviation from the norm, the following are distinguished:
- Lateral rhotacism - one edge of the tongue does not adhere to the upper molars. There is a squelching shade - an average between "r" and "l"
- Guttural rotacism - the activity of the root of the tongue is impaired
- Velar rhotacism - vibration occurs when the root of the tongue approaches the boundaries of the hard and soft palate
- Uvular rotacism - the small tongue of the uvulus vibrates.
- Rolling – forced use of the tongue
- Single-stroke or fricative - pronouncing the English sound “r”
- Kucherskoe “r” is a back-lingual sound like the English “r”.
Causes of lambdacism
Deficiencies in pronunciation [L-L'] are typical for children suffering from functional and mechanical dyslalia, dysarthric disorders, and open rhinolalia. Organic defects in the peripheral speech organs, impaired muscle innervation, and functional insufficiency of sound pronunciation can lead to lambdacism:
- Shortened hypoglossal ligament.
It does not allow the upward movement of the tongue, which is necessary for the formation of the desired articulatory pattern. As a result, the child finds an available compensatory position (interdental, labiodental, etc.), which replaces correct articulation. - Macroglossia and microglossia.
If the language is underdeveloped, it becomes impossible or difficult to pronounce all linguistic phonemes, including dental [L-L']. The small size of the organ makes it impossible for the tongue to approach the upper incisors. With a massive tongue, both its upper rise and narrowing of the tip are difficult. - Changes in muscle tone.
With dysarthria, the tongue may be flaccid, paretic or tense and spastic. These factors significantly distort articulation. The tone of the orbicularis oris muscle is also impaired, which is accompanied by difficulties in voluntarily opening and holding the lips. - Palatal clefts.
Compensatory features for rhinolalia are a high elevation of the root of the tongue, a shift of articulation into the depths of the oral cavity, and non-participation of the tip of the tongue in the formation of sounds. [L] is usually absent or appears bilabial. - Hearing loss.
Hearing loss can be accompanied by both mixing and substitution of sound due to impaired acoustic differentiation, and distorted pronunciation due to inaccuracy and blurred articulation. - Other reasons.
Lambdacism can be caused by the lack of formation of correct speech kinesthesia as a result of speech deprivation and sickness in children. Another reason is copying incorrect sound pronunciation, including dialectal features in a bilingual environment.
Yotacism
Replacing the letter "y" with "l". There are three defects in the pronunciation of back-lingual sounds:
- Gamacism - sound "g"
- Kappacism - the sound "k"
- Hitism (x) - replacing the sounds “x” with “f”, especially before “v”. Or "хх" on "х". For example, cunning - cunning.
Gamacism and cappacism are usually found together in practice. They are characterized by:
- The absence of the sounds “G” and “K”.
- Replacing “k” and “g” with “t” and “d”. For example, a rabbit is a troll.
- Replacing "k" with "k".
All these defects arise due to certain systems of activity. Most sounds are front-lingual and these sounds are also pronounced as front-lingual.
Paralambdacism
This term refers to the replacement of the correct “l” sound with another. For example:
- “g” – pronounced “kogeno” instead of “knee”
- “v” – pronounced “stov” instead of “table”
- “e” – pronounced “yokot” instead of “elbow”
- “l” – pronounced “lyozhka” instead of “spoon”
All these flaws in pronunciation can be treated by regularly doing exercises with a speech therapist and at home. Specialists are often expensive, but there are cases when just one lesson with a doctor on speech production gives a positive result, and consolidation can already be done at home.
Complex dyslalia
Complex dyslalia includes cases in which combinations of various defects are observed. The most common of them:
- Rotacism and lambdacism
- Rotacism and sigmatism
In cases of a shortened hyoid frenulum, a posterior lingual sound “r” or a replacement of “r” with “d” and lower softened sibilants are observed. For example, the frame is a queen.
- Rotacism, lambdacism and sigmatism
- Phonetic-phonemic disorders
- A combination of phonetic and phonemic, that is, some sounds are replaced, others are distorted.
- The defect is associated with the contrast of sounds in terms of hardness-softness, ringing-dullness with one or another type of defect in the pronunciation of one sound (sigmatism, rhotacism).
- Total dyslalia - when in the child’s pronunciation, of all consonant sounds, only “t” and “d” and nasal, sonorant sounds remain, and vowels are in order. For example: sam-dam, hat-slipper and others.
Sometimes only one sound “t” remains - this defect is called Hottentatism (from the African tribe “Hottentot” - in their speech there are only two consonants - “t” and “d”).
The purpose of expanding the space for the implant
Sometimes patients are interested in whether it is possible to do without additional measures and “just install a smaller prosthesis.” The answer from a competent dentist will always be negative. An artificial crown must withstand full load, and for this it must have normal dimensions and take up the same amount of space as the extracted tooth.
Thus, the doctor decides to expand the place for the implants in order to:
- eliminate possible obstacles to the installation of an artificial root and its subsequent integration with bone tissue;
- get enough space for an artificial crown, which is fixed on the implant after its implantation;
- ensure high aesthetics of the restored dentition.
Sometimes, when teeth are significantly misaligned, it may seem better to move the rest of the row to spread them out evenly and close the gap. But with this approach, the chewing load falls on fewer teeth, which means new problems will soon appear.
Features of complex dyslalia
The more complex the combination of dyslalia, the more complex the background against which it occurs: a delay in general and mental development. In cases of complex dyslalia, an in-depth additional study of the child is necessary, not only in terms of the characteristics of his behavior, but also intellectual capabilities, as well as characteristics of hearing and vision. Complex dyslalia is a signal that something is wrong with the child’s hearing or vision. In children with hearing impairments, very often the front-lingual sounds are either sharply distorted or replaced by the sound “t”.
If a child has hearing loss of the 2nd or 3rd degree, then an auxiliary criterion will be the peculiarity of the voice; it lacks the necessary metal, the voice seems to be “cotton-like.”
Children with severely reduced vision and blind children may also experience pronunciation defects such as complex dyslalia. This is due to the fact that in such children, sigmatism occurs 3-4 times more often than in the norm. This is due to visual control. But if we establish a connection between interdental sigmatism and visual defects, then, consequently, all hearing-impaired people should have interdental sigmatism, but this is not the case. After all, the child does not see the sounds “k”, “g”, “n” - they are not impaired, but they have complex dyslalia.
A visual defect interferes with speech in general - the blind do not speak by imitation, the visually impaired cannot ask anything, they are passive. Initiative speech develops by age 4. The pronunciation system is formed when the teeth begin to change, hence interdental sigmatism appears. Complex dyslalia occurs against the background of delayed speech communication due to visual defects.
With hearing defects, disorders of the maxillomuscular system are often encountered: progenia, prognathism, anterior open bite, lateral open bite.
Automation of the sound "L"
To fix the sound after at least a month of work, you need to use the following methods:
- Pronounce soft syllables and words. For example: “Lyu: cradle, people, love.”
- Learn and speak simple phrases. “LE-LE-LE – leaves were lying on the ground” and others. You can compose them yourself.
- Come up with and repeat funny poems and tongue twisters starting with “L”.
- When a sound is produced in direct syllables, you need to fix it in reverse ones. OL, EUL, etc.
Be sure to control the position of your tongue in the mirror. And do not overload the texts with words with the letter “R”. The child must focus on one complex sound.
Automation of the hard “L” occurs by analogy. First, the child repeats after the adult, then does the exercises himself.
The exercises suggested above can be done independently at home. But if there is no improvement, you should definitely go to a speech therapist.
Methods for eliminating dyslalia
- Work to overcome dyslalia is always associated with the formation of new skills and abilities, that is, a speech therapist-defectologist rebuilds the child’s existing pronunciation system. Read more about when a child needs a speech therapist.
- Classes to overcome dyslalia have a developmental role: speech therapy is aimed at developing skills and abilities. This work is educational, and the learning process, unlike the process of imitation, is a conscious process.
- The guideline in speech therapy work is the pronunciation norms adopted in the Russian language. Read more about establishing the correct pronunciation of the sounds R and L.
- All work on correcting pronunciation is pedagogical. In cases of medical influence, only a favorable background is created, but it does not correct the defect. Training, demonstrations (when a speech therapist shows the correct articulation of various words in the mirror), etc. are used as pedagogical paths.
- During the classes, the psychophysiological mechanism that ensures normal pronunciation is worked out, as well as the motor-articulatory, auditory and speech-motor system so that the child is capable of normal pronunciation.
Date of publication: 02/04/2016. Last modified: 05/05/2021.
Correction
Health care
The participation of medical specialists may be required in case of lambdacism caused by dental problems, neurological pathologies (cerebral palsy), or hearing loss. Thus, with a shortened frenulum, in some cases, preliminary frenuloplasty is necessary, and with a cleft palate, uranoplasty is necessary. Hearing loss requires adequate selection of hearing aids. In case of a violation of muscle innervation, speech therapy work is preceded by a complex of medication, physiotherapeutic treatment, and massage.
Speech therapy assistance
Before starting to establish standard sound pronunciation, preparatory work is carried out to form the correct articulatory posture and develop phonemic hearing. At the first stage of correction of lambdacism, the following speech therapy techniques are used:
- Articulation gymnastics.
Includes exercises for developing the circular muscles of the lips (“Smile”, “Tube”), muscles of the tongue (“Needle”, “Watch”), stretching the hyoid ligament (“Horse”, “Mushroom”), developing the upper position of the tongue (“Painter” , “Swing”, “Turkey”), etc. It is also necessary to pay attention to the correct speech exhalation (exercise “Steamboat”). - Practicing basic sounds.
The supporting phonemes for [L] are [T] - gives the correct position of the tongue and [Y] - ensures the correct supply of the air stream. - Speech therapy massage.
Indicated for insufficient tongue mobility, weakness of the tip and lateral edges, spasticity of the back. Typically, such problems are observed with dysarthria. The most effective in this case is probe logomassage.
Sound production begins after completion of the preparatory stage. For various forms of lambdacism, differentiated methods and techniques are used: by imitation, based on basic sounds, using staged probes.
As soon as the sound [L] is received, they move on to consolidating it in syllables (direct, reverse, with a combination of consonants), words, phrases, stories. The differentiation stage is only necessary in cases of paralambdacity. The duration of correctional speech therapy sessions depends on the cause and mechanism of lambdaism, the presence of other phonetic defects that need correction.