What else can you do?
If you have a child in your life diagnosed with ODD, especially in its severe form, do not despair. This is the case when “patience and work will grind everything down.”
Yes, it takes a lot of time, a lot of physical and mental strength, but the result will definitely come. This disease is treatable, even if it costs thousands of small steps.
Your inner state of calm, firm confidence in a favorable outcome and inexhaustible warmth - this is what you can share with a little person, and what will give him the strength to cope with his illness.
Reasons for OHP
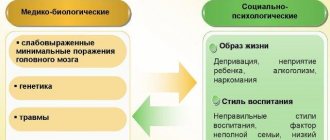
The causes that provoke ONR mainly relate to the period of pregnancy and childbirth, and the first years of the child’s life. They are the ones who cause severe forms of the disease.
Social reasons are no less important. This includes a lack of communication, living with deaf family members, lack of attention to the child in the family, and unfavorable conditions in which he lives and is raised.
How to treat this disease, what measures should be taken to restore speech function?
Possible complications
OHP, like other speech disorders, is characterized by the presence of complications. First of all, these are dysgraphia, agraphia, and alexia. As OHP is eliminated (its correction), it is necessary to carry out work to eliminate its complications. Children with the first and second degrees of OHP have greater risks, less often for types 3 and 4.
Choose a feedback specialist, study individually or in a group. Speech therapist help online Speech therapists, defectologists, preparation for school. Distance learning online. Speech therapist via Skype Specialized education to help children and adults with speech disorders. Retraining to become a speech therapist
How is the diagnosis made?
Babies develop speech at different rates. To establish a speech therapy conclusion, the child must accumulate a passive and active vocabulary, be able to compose coherent small sentences, and form the plural. It is by the age of 3 that the main components of speech begin to form. Therefore, the diagnosis begins to be made at this age.
At the beginning of the school year, speech therapists conduct classes for children to identify speech disorders. Differential diagnosis is based on the general didactic principles of accessibility, perception, and gradual complication. Children are encouraged to draw, work on letter assignments, and solve conflicting problems. This could be writing a short essay about vivid impressions or finding a hidden letter in a picture.
To examine phonemic perception, the teacher asks the child to draw a word and find mistakes.
To test letter recognition, the baby is given printed and written versions of letters. He must either complete the missing part, or find differences, or convert the printed font into handwritten one.
The results may help select a group of children with whom speech therapists should work and with whom further in-depth examination will be required.
The main condition for diagnosing pathology is multicomponentity. Clinical diagnosis examines impairment of oral and written language.
A good exercise for correcting speech is “learn the letters”
Symptoms
General underdevelopment of speech in children (as well as in adults) is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- The child begins to pronounce the first words and sentences after 3 years;
- the child understands the speech of adults, but cannot formulate a sentence himself;
- it is difficult to pronounce even simple sounds;
- after 7 years the child does not pronounce the sounds “L” and “R”;
- rearranging letters in words;
General speech underdevelopment. Symptoms
- the child speaks in short sentences (2-4 words) or abbreviates words. For example, “obaka” - dog or “I drink” - I want to drink tea;
- incorrect declension by cases and tense;
- pronunciation of sentences is too fast or slow, making it difficult to understand what the child is saying;
- when talking, the child pays more attention to gestures than words;
- there are no prepositions in the sentences;
- poor memory, which results in a small vocabulary and incorrect pronunciation of words.
Stuttering is the most striking sign of OHP, and the child can pronounce a word one syllable at a time. General speech underdevelopment not only prevents children from communicating normally with peers and adults, but also causes severe psychological stress.
It is important that parents spend a lot of time with their children and often may not notice the onset of development of OHP, so it is necessary to undergo annual examinations by specialists.
The concept of abnormal manifestations of speech
General underdevelopment of speech (GSD) - it means a speech disorder when normally hearing children with preserved mental abilities have unacceptable and completely defective speech: from its sound to its meaning.
This concept was caused by a vital necessity and became firmly established in educational structures for children, in which speech therapy groups were formed. The term OHP was coined by the founder of Russian speech therapy, R. E. Levina (the levels of OHP according to Levina are given below).
Regardless of the origin of the defect, there are systemic complications of speech. Signs of a speech disorder:
- Speaking begins at approximately 3-5 years of age.
- Incorrect wording of words and phrases.
- Pronounced sounds are distorted.
- Incomprehensible conversation.
To distinguish between speech impairment, a speech therapist must conduct a thorough study of the disease of a particular child!
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of OHP is made by a speech therapist, and further treatment can be complex (speech therapist, psychologist, surgeon and other specialists), depending on the cause of the development of the pathology.
To confirm the diagnosis, the doctor takes the following measures:
1. Collection of data from parents:
- the presence of a hereditary predisposition;
- when the first deviations are noticed;
- clarifies the child’s approximate vocabulary;
- how the pregnancy proceeded, what illnesses the mother had during this period;
- at what time the child was born, how the birth took place;
- mother's age at the time of childbirth;
- whether the child has had head injuries or recent illnesses.
2. Examination of the child:
- the doctor asks you to say certain words. This allows you to determine the correct pronunciation of sounds;
- after this, the speech therapist asks you to make a sentence (this point depends on the age of the child) based on the picture. Speech is also assessed based on the length of the sentence, the correct use of cases, verbs and prepositions;
- tests memory. To do this, the child is shown 5-7 objects, after which they are removed, and the child must list which objects he remembers;
- asks the child to recite a poem or retell a short story;
- Also, for children under 7 years old, the doctor asks age, first name and last name. The child must be able to answer independently.
3. Hardware examination:
- An ENT specialist must check the condition of the speech apparatus, especially the condition of the tonsils and adenoids. With pathological development of these organs, nasal sound, hoarseness, and difficulty pronouncing sounds that are difficult for a child are possible.
- If the child has had head injuries, an x-ray may be required. To check the nutrition of brain cells.
If the child stutters severely and is tense, an examination by a psychologist may be required.
Prevention and prognosis
The success of speech therapy work to correct speech disorders depends on its timeliness. It is recommended to start treating OHP as early as possible - from 3-4 years. Today, many preschool institutions have experienced specialists who successfully use music, art therapy, speech therapy and play techniques for teaching speech skills.
Prevention of general speech underdevelopment is aimed at preventing the progression of clinical symptoms of the diseases against which it appears - alalia, rhinolalia, dysarthria, aphasia. Parents must create a favorable speech environment for raising their child and stimulate the early development of verbal and nonverbal processes.