Stuttering is a speech disorder in which a person involuntarily often repeats individual sounds, syllables and even words, sometimes lengthening them. Speech becomes fragmentary and difficult to distinguish. It takes a lot of effort for a person to utter even a short phrase. Another name for the disorder is logoneurosis. The disorder is less common in adults than in children.
How and why does stuttering occur?
The mechanism of stuttering is still not fully understood. In the literature it is described as follows.
- For a number of reasons, Broca's speech center becomes excited and begins to work faster than usual. As a result, the speech circle opens. This means that the connection between the centers where speech is formed is disrupted.
- Overexcitation is transmitted to other areas of the cerebral cortex responsible for motor activity.
- As a result, the muscles of the speech organs (tongue, lips) cramp. Sometimes the spasm affects not only the pronunciation muscles, but also the respiratory muscles.
- Then the work of Broca's center returns to normal, and the speech circle closes again.
In most cases, difficulties arise with the pronunciation of consonant sounds, as they require more effort. The hardest part for a person is the beginning or middle of a phrase. Sometimes a cramp reduces not only the speech muscles, but also the muscles of the arms, legs, and face. Men are most susceptible to the appearance of logoneurosis, since their left hemisphere, where Broca's center is located, is usually less developed than in women. Also, stuttering usually manifests itself in people whose blood relatives suffer from the same disorder. If speech centers are weak from birth, then any unfavorable factors can easily disrupt their work.
Experts identify the following reasons for the development of logoneurosis:
- Severe stress - loss of loved ones, emergency, natural disasters, accidents, military operations, constant scandals at home. Due to emotional overload, disturbances occur in the coordinated functioning of the muscles that are responsible for sound pronunciation.
- Diseases of the central nervous system - this can include skull injuries, severe infections affecting the brain, previous strokes, any neoplasms that put pressure on the speech centers. All this interferes with the normal transmission of impulses from the brain along nerve fibers to the muscles.
In the latter case, logoneurosis has nothing to do with emotions. In other words, a person stutters even if he is in a calm environment.
These reasons in themselves do not lead to stuttering. In essence, they are triggers. Whether a person starts to stutter or not depends largely on the state of the central nervous system. If she is strong and relatively healthy, then this will not happen. If the central nervous system is weakened, then stuttering is likely to develop.
Causes of speech impediment
The causes of stuttering are usually divided into two large categories: producing causes and predisposing causes. The first type is random, impetus events and actions. The second type is the conditions that give rise to the occurrence of the disease.
Producing causes
Anatomical and physiological
- Brain injuries
- Organic brain disorders
- Exhaustion of the nervous system
- Intoxication
- Somatic chronic diseases
- Diseases of the nose, pharynx, larynx
- Speech delays
Mental and social
- Psychotrauma (short-term and long-term)
- Improper upbringing in the family
- Improper speech formation in childhood (speech while inhaling, rapid speaking)
- Overload of speech material
- Polyglossia
- Imitation of stutterers
- Retraining left-handedness
Predisposing causes of stuttering and unfavorable factors
Under certain conditions, the risk of developing stuttering increases. The likelihood of speech defects increases in the following cases:
- Neurotic burden of parents : nervous, infectious diseases of parents (for example, syphilis, alcoholism, drug addiction, intoxicating the nervous system of the fetus)
- Neurotic characteristics of the child : increased irritability, fears (for example, night terrors in children, urinary incontinence, increased irritability, emotional tension, all kinds of twitching in the muscles)
- Constitutional predisposition : state of v.n.d., susceptibility to autonomic function
- Hereditary burden : diseases transmitted from parents (for example, weakness of the speech apparatus is inherited)
- Brain damage : post-infectious, organic, traumatic brain injuries (eg, concussions, encephalopathy)
unfavorable conditions can also leave their mark :
- physical weakness of children;
- hidden mental impairment of the child;
- lack of positive emotional contacts with a loved one;
- insufficient development of articulatory motor skills, sense of rhythm and facial-articulatory movements
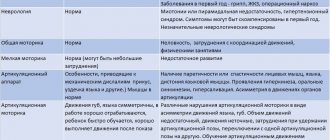
If a child belongs to one of the listed risk groups, then you should carefully monitor his behavior and speech. It is also worth remembering that boys stutter 4 times more often, and more than half of those who stutter acquire the disease between 2 and 5 years, 90% get sick before 10 years.
How does stuttering manifest itself?
Based on the shape of the seizures, three forms of stuttering are distinguished:
- clonic - it is characterized by involuntary repetition of individual sounds and syllables, as short spasms follow one after another;
- tonic – characterized by speech delay, as the muscles contract strongly for a long time;
- mixed - a combination of both forms of logoneurosis.
Logoneurosis can occur in three variants:
- constant - a person stutters in any environment, with any form of speech;
- wavy - it appears and disappears depending on the situation and the person’s condition;
- recurrent – stuttering may disappear for a long time, but under the influence of unfavorable factors it appears again.
Experts also distinguish clinical forms of stuttering - neurotic and neurosis-like . They develop for different reasons and in different ways. Let's look at each of them in more detail.
The neurotic form responds well to treatment, since the speech function itself is impaired, and the brain structures are healthy. Stuttering occurs mainly due to acute or chronic stress. Most people develop logophobia, that is, an obsessive fear of speech situations. A person begins to stutter as soon as he thinks about the need to communicate or about failures associated with speech. Such people often feel rejected; they prefer to keep live contact to a minimum.
The neurosis-like form does not depend on the situation, since stuttering is associated with structural damage to the brain. Logoneurosis is often accompanied by convulsions of the whole body, for example, frequent nodding of the head, movements of the fingers, swaying of the body. A person quickly gets tired during a conversation, his answers become monosyllabic. Memory deterioration, fatigue, and decreased attention are also observed.
Severity
When assessing the severity of the pathology, the severity of symptoms, their impact on the child’s communication with other people, and the presence of concomitant disorders are taken into account.
Highlight:
- mild degree - it is characterized by rare, unexpressed hesitations that do not interfere with talking and communicating. But even with this degree, parents need to contact a specialist in order to begin correction in a timely manner before the deviations become entrenched;
- medium - hesitations are more noticeable and make communication more difficult;
- severe - speech impairments are pronounced, they make communication almost impossible. Other symptoms also appear.
If stuttering is not eliminated, the cause of the pathology is not eliminated, then it gradually progresses, and very quickly.
Which specialist should I contact?
As mentioned above, stuttering is caused by a number of reasons, and therefore the approach to treatment must be comprehensive.
- A neurologist evaluates the state of the central nervous system and treats diagnosed disorders.
- A psychologist helps to cope with emotional turmoil, overcome fear of communication, and correct character weaknesses.
- The speech therapist teaches you how to breathe correctly, control your voice, and conduct a smooth and rhythmic conversation.
Acupuncture procedures that have a positive effect on brain function, sessions with a psychotherapist and a physical therapy instructor will also be useful.
However, the most important thing in the treatment of stuttering is motivation, since the duration of the course is several weeks. The exercises are based on repeated repetition of the same actions, constantly overcoming the fear of communication. Efficiency directly depends on the efforts and desires of the patient himself.
Publication date: 04/13/2021. Last modified: 11/19/2021.
Treatment of stuttering in children
Getting rid of stuttering requires patience and persistence. It is important to follow the recommendations of a speech therapist in order to develop correct speech skills and eliminate pathology. But we also don’t recommend overdoing it: if your baby is sick or doesn’t feel well, postpone classes. In this state they will be of no use.
Treatment of stuttering in children is complex, using several therapy methods. Below we will talk about them in more detail.
Working with a speech therapist
Treatment of stuttering in children by a speech therapist can be carried out in a kindergarten, in a community clinic or in specialized institutions.
At the first stage, a speech therapist or speech pathologist conducts a survey and examination, identifying the cause of stuttering. Examinations are prescribed: MRI, electroencephalography or rheoencephalography. After this, an individual correction scheme is drawn up. Parents need to follow this plan to get rid of stuttering.
Working with a speech therapist is the key to successful correction. Even if you practice at home on your own, you need to regularly see a specialist. He evaluates the dynamics and, if necessary, adjusts the lesson plan or supplements them.
Working with a psychologist
To help get rid of stuttering, a psychologist or psychotherapist conducts classes in a playful way. The purpose of such activities is relaxation, distraction, and development of emotional stability. Both individual sessions and group work are possible.
When the cause of speech impairment is conflicts in the family, stuttering can be eliminated only by improving relationships within the family. In such cases, psychotherapy is also indicated for parents. It is necessary to create a calm environment and improve relationships between all family members. It is important that the child knows and feels that he is loved and appreciated.
Drug treatment
Drug treatment of stuttering in children is aimed at normalizing the neurological state and emotional background. Prescribe sedatives and drugs to relieve muscle spasms.
Usually vitamin complexes are also included in the treatment regimen. Folk remedies are also effective: herbal decoctions, baths, inhalations. Remember that any medicine is prescribed only by a neurologist, even herbal medicines. He takes into account the results of the examination and the cause of the child’s stuttering. Self-medication is fraught with worsening of the condition.
In complex cases, when there is damage to the central nervous system, hospital treatment or the prescription of other groups of drugs may be necessary.
Hardware techniques
Physiotherapeutic methods are used. Electrosleep and electrophoresis with sedatives are effective. You need to complete the course of treatment completely. Most often, several of these courses are prescribed, with breaks.
Computer programs have also been developed to help eliminate stuttering. Check with your speech therapist to see if they are appropriate for your situation. And remember that no program can replace comprehensive measures and independent work.
Speech therapy massage
Speech therapy massage plays an important role. It relaxes those muscles that tighten when pronouncing phrases and relieves spasms of the speech apparatus, thus helping to eliminate stuttering.
A therapeutic massage of individual parts of the body is also carried out: head, neck, shoulders, chest. Various techniques are used, including acupressure. In this case, the specialist influences the speech center through reflexogenic zones.
One of the advantages is the ability to perform at home. The first sessions are conducted by a specialist, showing the movements and correct placement of hands to the parents. In the future, the mother or other relatives perform the massage themselves. This is convenient when several courses of treatment are indicated.
Breathing exercises
The technique allows you to correct shallow, incorrect breathing and normalize the tone of the muscles involved in articulation. After classes, a preschooler masters diaphragmatic breathing, normalizes speech breathing, learns to regulate the respiratory rhythm and rate of speech, and strengthens the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall.
The specialist also teaches parents this technique so that they can perform the movements at home, since regularity of exercises and continuity of the course of therapy are important.
There are various techniques, for example, you can use Strelnikova’s exercises. They help create the correct air flow needed to pronounce words and phrases. The exercise complex is performed in various body positions, at rest and during movement. Gradually the tasks become more difficult.
You also need to train your voice. Logorhythmics classes are useful. You can get rid of stuttering by reading poetry out loud or singing it. You can even sign up for choral singing. This trains your voice and breathing.
At home, you can invite your child to blow soap bubbles, blow a cotton ball off the table, or blow up regular balloons. It is useful and fun to make boats and race to “drive” or blow them from one end of the basin to the other. Try practicing with toy wind instruments: pipes, trombone, saxophone.
Basic methods of stuttering prevention
Primary prevention of stuttering is aimed at eliminating risk factors. Includes giving up bad habits during pregnancy and regular monitoring by a doctor, as well as following recommendations on lifestyle and treatment of concomitant diseases. It is important to prevent birth injuries and any injuries in subsequent years of the child’s life.
Secondary prevention of stuttering is working with children at risk. They do not yet have the disease, but they have a predisposition. They should be observed by a neurologist if there are any problems, as well as by a speech therapist, psychologist, and receive appropriate treatment.
Family plays a big role:
- It is necessary to create a favorable atmosphere at home, avoid conflicts and quarrels, and treat the child kindly. Try to communicate more and pay attention more often to his needs and desires. When you speak, do not distort words or lisp, but pronounce them clearly, moderately loudly and slowly, but expressively;
- If you have a close relative with a stutter or other speech impairment, you need to minimize his communication with the baby. Give up the idea of raising a child prodigy, do not make demands on him that are beyond his age. When choosing entertainment, activities, games, even educational ones, pay attention to his mood, character traits and nervous system: what suits one child may not suit another;
- If children of preschool age have any speech impairment, then they should study in a speech therapy group, or the parents themselves should find a teacher and provide regular classes. It is necessary to eliminate all speech disorders before school so that they do not progress and do not give impetus to the development of stuttering. This will interfere with the assimilation of the school curriculum. Also, the student will begin to avoid peers, in adolescence he will develop complexes, fear of speaking in public, fear of communication;
- Develop a daily routine and rest schedule, and strictly adhere to it with the whole family. Avoid emotional and physical overload. Horror films with a crime plot are contraindicated for all children, and even more so for those at risk;
- When two languages are used in a family, it is better to teach the child one language. By about 4 years old, he will master it, after which preschool children will be able to learn a second language, and he will not have problems with speech.
In addition to primary and secondary prevention of stuttering, there is also tertiary prevention. Its goal is to prevent the progression of the disease and the development of complications. It consists of timely treatment, rehabilitation of young patients and social adaptation.
About the disease
Stuttering is a violation of the smoothness and rhythm of speech, in which the child has difficulty pronouncing words and phrases, repeated repetition of syllables or short words, and lengthening of pauses before the start of pronunciation.
The disorder is based on spastic contraction of structures that provide speech function (muscles of the larynx, tongue, soft palate, lips). Spasms are caused by excessive stimulation of the corresponding centers in the brain (speech, emotional). As a result, articulatory, vocal or respiratory contractions occur that prevent the child from speaking smoothly and rhythmically. Most often, stuttering occurs in children 2-4 and 5-7 years old. This disorder is found 4 times more often in boys than in girls. In 50-80% of cases the condition can be corrected. The key to success is timely seeking qualified help. The earlier therapy is started, the greater the chances of getting rid of the speech defect forever.