Logomag
mother:__________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________
father:______________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________ 5. Family history:
illnesses of parents; alcoholism; addiction; professional
harmfulness; left-handedness: forced, pathological, hereditary;
did either parent attend a speech therapy group?:___________ _________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________
6. During pregnancy:
Mother's age at the time of birth__________________________________________
From what pregnancy? _____________-____________________
How were the previous ones completed?_______________________________________________
Toxicosis (in which half of pregnancy?)________________________
Rhesus conflict (yes, no)?__________________________________________
Threat of miscarriage (due date)?__________________________________________
Diseases suffered during pregnancy__________________ _________________________________________________________________
7. Childbirth:
What week?_________________________________________________
Obstetrics (forceps, caesarean, stimulation, extrusion)____
__________________________________________________________________
Duration__________________________________________________________
Asphyxia (umbilical cord entanglement)__________________________________________
Fetal position_________________________________________________
8. Postnatal period:
Apgar score___________________________________________
When did you scream? _________________________________________________
Height at birth ____________________Weight______________________
When was it applied to the breast?_____________________________________________
Feeding (breastfeeding, artificial, donor)_____________________
Regurgitation, leakage from the corners of the mouth______________________________
On what day were you discharged from the hospital? ______________________________
9. Development of a child up to three years of age:
Behavior________________________________________________________
Dream_____________________________________________________________
Psychomotor development:__________________________________________
began to hold his head _______________crawl________________________
sit ________________
get up ________________walk ____________
The appearance of the first teeth ________________________________________________
Diseases. Observation of specialists (cardiologist, neurologist, ENT,
nephrologist and others) _____________________________________________
Speech development of the child:_____________________________________________
humming ______________babbling ____________first words _____________
speech in phrase _____________________________________________________
Self-care skills_______________________________________________
10. Child development after three years:
Diseases__________________________________________________________
Was speech development interrupted/if interrupted, for what reason?
how long did it last, with what consequences/__________________________
________________________________________________________________
How quickly did your vocabulary grow? ____________________________
Does the child care facility visit ___________________________________
Play activities ______________________________________________
Favorite toy ________________________________________________
Does he use toys for their intended purpose?________________________________
Contact information _____________________________________________________
11. Are you ready for school?
Speech understanding:
(following instructions ________ understanding prepositions _____________ number _______________ gender _____________ case ___________________)
Connected speech:
writing a story based on a picture ___________________________________
writing a story based on a series of paintings ______________________________
retelling_________________ story description______________________
Examination of grammatical structure:
formation of diminutive forms _____________________
adjectives with nouns _____________________
agreement of nouns with numerals ______________________
Dictionary status:
subject dictionary ______________________________________________
dictionary of signs ____________ verb dictionary __________________
Development of elementary mathematical concepts:
_________________________________________________________________
12. Interest in learning
Favorite subject
Questionnaire for parents (history collection)
Questionnaire for parents
Dear parents, we ask you to carefully read the questions and answer them. Your answers will be used to improve your child’s speech development in kindergarten.
General information about parents
Mother's full name , age ______________________________________________________
Father full name, age ________________________________________________________________
- From what pregnancy is the child and from what birth? __________________
2. Nature of pregnancy (toxicosis, falls, chronic diseases, infectious diseases)_________________________________________________
3. Childbirth - early, urgent, rapid, dehydrated (underline as appropriate)
4. Stimulation - mechanical, chemical, electrical stimulation (underline as appropriate)
5. When he screamed ______________________________________________________________
6. Asphyxia - white, blue (underline as necessary)
7. Rh factor (compatibility) ________________________________________
8. Weight at birth __________________ height at birth____________________
9. Feeding:
a) when they brought it to feed - immediately, after a few days, ___________________
b) how he took the breast ________________________________________________________________
c) how he sucked _________________________________________________________________
d) were regurgitation or choking observed? ________________________________
10. On what day was he discharged from the maternity hospital ___________, if delayed, why_________________________________________________________________________
11. Holds his head with ______________________
12. Sits with ______________________
13. Stands with ______________________
14. Walks with ______________________
15. First teeth ______________________
16. Past diseases:
a) Up to a year ______________________________________________________________
b) After a year _________________________________________________________________
c) Infections ____________________________________________________________
d) Bruises, head injuries ________________________________________________
Convulsions at high temperature _____________________________________________
17. At what months did the child begin to develop:
a) Partying ______________________________
b) Babbling _________________________________
c) First words _________________
d) First phrases ___________________
18. Was speech development interrupted ___________________________________
19. Speech environment _________________________________________________
20. Has the child worked with a speech therapist before ____________________________
21. The child’s attitude towards his speech ________________________________________________
Thank you for your participation!
Delayed speech development
Shamshuro Elena magazine "Nanny", 2001 No. 4
According to the latest data, almost every fourth child suffers from delayed speech development. It was hard to believe! Suspecting before that the baby was “not like everyone else,” I assured myself that her temperament, her “individual characteristics” were “to blame” for this. Having sounded the alarm at 2 years and 8 months, I began to nervously turn the phone dial in an attempt to find out what I could do, how and who could help my daughter, whom doctors diagnosed with Delayed Speech Development (DSD).
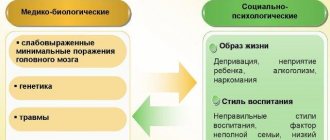
This is a subtle and complex disease, the causes of which are sometimes difficult for doctors to understand. Therefore, the first thing parents who suspect their child has speech problems should know is that it is necessary to conduct a comprehensive examination of the child by a pediatric speech therapist, neurologist (ECG, ECHO-EG), psychoneurologist, otolaryngologist, defectologist and psychologist. Experts tend to see the cause of speech underdevelopment in the presence of MMD (minimal cerebral dysfunction), since half of these children exhibit clinical symptoms and electroencephalographic phenomena indicating a disruption in the functioning of the subcortical structures of the brain. However, there is no need to be afraid of the diagnosis of MMD. That is why they are “minimal” violations, so as not to interfere with the normal development of the child. Studying the anamnesis of children with delayed speech development, experts have found that disruption of the normal development of speech in children can be caused by various adverse effects during intrauterine development, premature, prolonged or rapid labor, a long anhydrous period, birth injuries, fetal asphyxia during childbirth and even early transferring the child to artificial feeding. Severe childhood illnesses, especially in the first three years of life, traumatic brain injuries or frequent falls simply left unattended, hearing loss of varying degrees - all this can cause delays in speech development. When exposed to unfavorable biological (or social) factors, those areas of the brain that are currently developing most intensively are most significantly damaged. Studies have shown that delayed speech development often affects children whose mother or father has any mental disorders, often quarrels or abuses alcohol. And further. Babies with RDD are, as a rule, children not from the first, but from repeated pregnancies, late children or children from single-parent families, brought up in a poor language environment, in bilingual families. And although negative social factors do not have a direct pathological influence on the child, they always, in one way or another, refracted in his biological nature, affect mental development, inhibiting it to a greater or lesser extent. Of course, the hereditary factor also plays a significant role. If one of the parents or one of the close relatives suffers from tongue-tiedness, then it is likely that the baby will also have problems with speech. Often, delayed speech development is associated with delayed psychomotor or mental development. The baby begins to hold his head up, sit, and walk later than other children. These are exactly the symptoms that should first of all alert adults. Such “problem” children may experience daytime and nighttime enuresis up to primary school age. It is very important that parents, having noticed signs of delayed speech development in their child, not only rely on the help of specialists, but also actively work with the child themselves. Hello fingers!
Why is it important for a child to work his fingers? In the cerebral cortex, the sections responsible for the development of articulatory and fine manual motor skills are located close to each other and are closely interconnected. However, the hand develops earlier in the process of ontogenesis, and its development, as it were, “pulls” with it the development of speech. Consequently, by developing fine manual motor skills in a child, we stimulate the development of his speech. Therefore, if a child’s leading hand is the right, his left hemisphere is more developed; among left-handers there are many more children with developmental disabilities, because they have the most developed right hemisphere rather than the left hemisphere, in which the speech and motor centers are located. The use of various massage techniques and motor stimulation is of great importance for the development of perception and sensations from a very early age. It is very important to use this massage early, already in the second or third month of the baby’s life. It should be done 2-3 times a day with a 1-2 day break. Clearly define the place and time of massage in the child’s daily routine, for example, before feeding. This training is good to conduct not only with children who have health problems, but also with “non-problematic” children. At the same time, by the age of six months, infants begin to actively babble and speak their first words. Most children who have completed this course can construct a basic phrase at the age of one year and two to three months. Subsequently, the speech development of children proceeds intensively and without deviations. In cases where a child has deviations in psychophysical development, the use of massage (in the system of correctional and developmental education) should be continued in preschool and primary school age. To develop gross (gross) and fine motor skills, a child also needs: mosaics, construction sets, cubes, puzzles. Teach kids to fasten buttons and tie shoelaces (at 2-3 years old). After all, a significant part of children with speech underdevelopment are “motorally” awkward and have difficulty switching from one movement to another. They draw and sculpt poorly. You need to work with such kids using interesting visual material. It is recommended to use outdoor games that develop the ability to navigate in space, move rhythmically and deftly, change the pace of movements (“Fox and Geese”, “Cat and Mice”, “Geese-geese”, etc.), as well as games in which movements are accompanied by speech. If the child is already about 4 years old, you can enroll him in some kind of artistic club, for example, modeling or drawing. Or take up music and teach your baby to listen to it. Games such as “Guess what sounded?”, “Recognize by voice”, “What instrument is playing?”, “Catch the whisper” and others are of great importance for the development of auditory attention. After all, almost all children with developmental disabilities have insufficiently developed attention (less volume of memorization and reproduction of material), they cannot concentrate, and are often distracted. Work on developing visual attention can be carried out by selecting paired objects and pictures (use any type of lotto). The ability to differentiate pictures by their color needs to be developed with the help of multi-colored stripes, sticks, circles, etc. It is advisable to use educational board games such as “Colored backgrounds”, “Colored dominoes”, “Little artist”. At later stages, you can offer children tasks like: “Which pencil should you take to draw the sun, grass, tomato?” To develop visual perception of shape, the following activities are recommended: selection of geometric shapes by analogy (find a shape of the same shape and color); selection of geometric figures by incomplete analogy (find a figure of the same shape, but a different color, find a figure of the same shape, but a different size); recognition of geometric shapes by shape, size and color; the relationship of geometric figures with the shape of objects. In addition, you need to teach the baby to find the missing part of an object, to guess which toy or object is missing from the table. Games like “What’s missing?”, “What’s added?”, “Do it as it was” will help you with this. It is important to remember that all games should be short in time; they should not tire the child. It is necessary to clearly explain the rules of the game, give the same permissive signal - “now you”, “you can”, “start”.
Learning to speak The vocabulary of children with speech underdevelopment is poorer than that of their peers who are developing “according to plan.” Phonetics is characterized by shortcomings associated with incorrect pronunciation of individual sounds. In the field of word formation, it is difficult to distinguish between shades of word meaning. The predominant errors in grammar are errors in control, mainly verbal. Children incorrectly use prepositions with nouns and replace forms of one case with forms of another. Violation of gender agreement forms for neuter nouns (“clean window”), violation of collateral forms, simplification of complex conjunctions, etc. are also typical. Such children sometimes do not understand the meaning of many words, do not know how to compose sentences or a story based on a series of pictures. The appearance of coherent speech is often delayed for up to 3 years or more. In this regard, constant work is necessary to enrich the active vocabulary, the grammatical structure and the development of the child’s coherent speech. If you are lucky and meet a good speech therapist on your way, he will recommend interesting speech therapy manuals for classes with your baby. Please note: up to the age of three with a baby, it is better for parents to do this. A child is unlikely to want to practice with someone else's aunt. And for a child with mental retardation, every day is important. There is no time to waste. You should not boast that your child at 2.5 years old can already count to 10 or has memorized a long poem by Agnia Barto. For young children this is not the main thing. The most important thing for them is to learn to navigate the immediate objective world. The baby should know that this gray animal that meows and purrs is a pussy, and this one grazing in the meadow is a cow; that you need to drink tea, eat and chew a bun, the car is moving, and the plane is flying high, etc. The child must understand that the word “table” refers not only to your three-legged table, which he likes to climb under, but also to a desk, coffee table, and kitchen table. At an early age, it is important to expand children’s vocabulary primarily through nouns, followed by verbs and adjectives: “Who is this?” - “It’s a boy”, “What is he doing?” - “The boy is playing”; "What is this?" - “This is a stream”, “The stream is ringing, flowing, babbling.” Next, you need to work on these models, including new words with the most frequently used prepositions: “in”, “on”, “behind”, “about”, “above”, “under”. For example, “Where is the toy?” (Answer: “Near the book”). When you begin to see the first results of your work, help your baby master the mechanism of combining words in a sentence. The main questions with the help of which grammatical forms are fixed in the models of phrases and sentences are questions of indirect cases (for example - “What does Tanya take out of the magic chest?” - “A doll, cubes, beads.” - “What will Tanya use to transport her toys? " - "By helicopters - by helicopter; by car - by car." - "What doesn't Tanya have?" - "Bus, boats", etc.) After about six months you will see that the baby is already able to include various phrases in a sentence: they can be expanded due to the possible combination of words according to the type of coordination, control and adjacency (for example, “This is a small spring stream. The spring stream flows (murmurs) cheerfully (ringing).” In addition, it is necessary to teach children to differentiate words that sound similar ( duck - fishing rod, barrel - kidney, butterfly - daddy), distinguish a given sound from a number of other sounds and from words, determine the place of the sound in a word (at the beginning, in the middle, at the end), come up with words starting with a given letter. The most difficult for children with underdevelopment of speech is the syllable structure and sound content of words. Therefore, they should be taught to pay attention to changes in the meaning of words when syllables are omitted and rearranged (“horns - mountain”). It is also necessary to teach children to perceive and reproduce a given number of claps and a given rhythm. ATTENTION, parents! The sooner work begins to overcome speech underdevelopment, the more effective the results will be! Children with delayed speech development should attend specialized psychoneurological or neurological nurseries, then a speech therapy kindergarten. If this is not possible, then it is necessary for the child to be treated by a speech therapist from a children's clinic.
Editor: Maria Chulova (27.09.03)
Help > Child development > speech development
Visitor comments: average score: 9/10 Unknown anonymous score: 10/10 03-11-2003 11:48:11 A wonderful article with competent and very popular professional advice. This information is constantly requested by parents. I would also like to note the excellent presentation of the material. E. Shestova (practicing speech therapist, category 14).
Yana Poley rating: 10/10 11-08-2004 19:37:08 I am a speech therapist, I work in a clinic... I liked the article, it would be nice if more parents read it. A small note - in the clinic, alas, it is difficult to organize classes for small children (up to 4.5 years old) and there are practically no kindergartens where they work with children; often it is not easy to place even a 4-year-old child in a specialized kindergarten. And everything else is told simply superbly - clearly, clearly, and understandably for parents. After such an article, you don’t even have to go to a specialist:)) It’s so nice to discover many of your thoughts and recommendations...:) Of course, if something is bothering you, yes, even if everything is fine in your mother’s opinion, it’s a good idea to go to the clinic and get a detailed consultation on homework with your child... and no one bothers you to come to such consultations several times (for example, I schedule a visit after 3 months or after 6, depending on the severity of the delay and the mother’s responsibility). And you should never expect that everything will work itself out things will get better, it’s better to wait it out than to miss some point in development. I would also recommend coming at least once for a consultation to a mother who is just expecting the birth of a child. In principle, a good specialist will have something to say to this mother as well, as preventive advice. So the article is true, correct, I would even rate it 10 C+. Sincerely, Yana Borisovna
15-11-2004 06:55:11 Yes, what is written in this article describes my situation.
We live in China, the child goes to a Chinese kindergarten, while my husband is Austrian and speaks German, and I am Ukrainian and speak Russian. At home we speak English. Our son speaks English, Chinese, Russian, not like all children, but with success. The vocabulary of words is very small, but he is only 4 years old. The article is wonderful, we will work together with the baby! For children
with delayed speech development and other speech problems
- with school failure and behavioral disorders
— with a violation of social adaptation
— with cerebral palsy and other disorders of the musculoskeletal system
- with intellectual disability
a consultation appointment was organized to help draw up an individual plan for a set of correctional classes and choose the right specialist (therapeutic teacher, speech pathologist, speech therapist, psychologist, neuropsychologist, psychiatrist, exercise therapy doctor) to obtain the most effective result.
A free consultation is conducted by an experienced neurologist and therapeutic teacher
Melanchenko Elizaveta Aleksandrovna
Detailed information and pre-registration by phone. +7(926) 013-80-40
Taking anamnesis in children
Anamnestic data about children is collected by interviewing parents and relatives, as well as people who spend a lot of time with the child (nannies, teachers, caregivers). In medical practice, interviewing the child himself is also used. A correctly collected anamnesis helps to clarify the characteristics of his immunity, physical and mental reactions to the disease.
When collecting information about the baby, they find out how the pregnancy and childbirth went, what the woman suffered during pregnancy, whether the due date was on time, whether the child developed correctly; determine the characteristics of his nervous system, appetite, availability of vaccinations and much more.
The child's history will be incomplete if there is little information about his heredity. The doctor should try to collect as much information as possible about the patient’s relatives, and especially about repeated cases of the same disease in the family.