Benefits of exercise
Sound gymnastics is a series of exercises that involve pronouncing specific sounds in a certain way. This causes vibration in the vocal cords, which gradually passes into the respiratory organs and into the chest.
The purpose of sound charging is:
- Relieving bronchospasms.
- Acquiring proper breathing skills.
- Improved sputum discharge.
- Relaxation of the muscles of the bronchi.
- Normalization of microcirculation in the area of the alveoli of the lungs.
- Stimulation of the diaphragm.
- Improved mood.
- Normalization of alveolar ventilation.
- Restoring normal breathing.
Breathing exercises and sound exercises are often combined; together they will be more effective.
Preview:
Municipal autonomous preschool educational institution
municipal formation city of Krasnodar
“Development Center – Kindergarten No. 171 “Scarlet Sails”
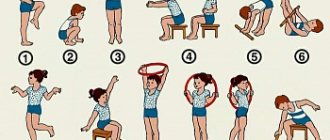
Card file of sound gymnastics exercises
Klimova Svetlana Ivanovna
Exercise No. 1 “Sing the sound “a”.
Stimulates the functioning of the lungs, trachea and larynx. At the end of the utterance, breathing deepens and oxygen consumption increases.
To increase the volume of exhaled air, we ask the child to stretch out the vowel sound, for example, as long as the thread unwinds or the spring stretches.
Exercise No. 2 “Merry mourners.”
Exercise, along with improving ventilation, helps relieve stress.
Indications and contraindications
Sound gymnastics is indicated for diseases of the respiratory system that are accompanied by bronchospastic syndrome. This is a dangerous and serious condition of a sharp narrowing of the lumen; very little oxygen enters the bronchi, and the body is excessively saturated with carbon dioxide. During this, the person feels suffocated, short of breath, and breathing becomes heavier.
Sound gymnastics, as a type of breathing exercise, is used for the following pathologies:
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
- Bronchial asthma.
- Bronchitis (chronic obstructive, asthmatic).
- Expiratory dyspnea.
Sound exercises are contraindicated during the onset of an attack of bronchial asthma and in case of exacerbation of a chronic process in the lungs.
If breathing training is accompanied by discomfort, coughing, tickling, shortness of breath or other deterioration in health, the exercise must be stopped.
General rules
In order to achieve maximum effect in classes, you should adhere to the basic instructions:
- Exercises should be carried out with proper breathing. You need to inhale through your nose, it should last 1–2 seconds, pause for 1 second and exhale through your mouth, lasting 2–4 seconds. Then pause again for 4-6 seconds. In this case, you should adhere to the rule that the exhalation must be 2 times longer than the inhalation.
- The pronunciation of sounds depends directly on the purpose of training and the disease. So, for example, in the case of asthmatic bronchitis, the sounds should be loud and sharp. If you suffer from chronic bronchitis, the sound series is pronounced slowly and quietly, almost in a whisper.
- To carry out gymnastic exercises, you need to choose a room that is well ventilated so that the lungs are filled with oxygen. It would be best to choose a place to train outdoors.
- Sound exercises should be performed a couple of hours before or after meals. It is better to stick to the specified period of time.
The duration of the training depends on the person’s well-being and how easy it was for him to complete the previous lesson.
After performing gymnastics, the patient should feel relief and improved well-being, and in no case fatigue.
Sound exercises
It is best to do gymnastics while sitting, placing your hands on your knees and leaning slightly forward. Take your time, stick to your rhythm, remember to breathe correctly during the exercises:
- The sound "a". Its pronunciation helps improve the ventilation function of the lungs and the effective functioning of the respiratory muscles.
- The "u" sound. Has a calming effect and leads to relaxation.
- Slowly pronouncing in a whisper the sounds “a”, “o”, “u”, “e” and the short words “dry” and “deaf” has a calming effect on the upper respiratory tract and helps cleanse the vocal cords.
- When combining “kch”, “dg”, “bp”, “kg”, mucus removal improves and the throat muscles relax.
- The buzzing sounds “zh” and “z” and the growling “r”, when pronounced loudly, give the effect of a vibration massage, while relaxing the bronchial muscles.
- For your child, you can offer to imitate the sounds of a beetle “zh-zh-zh”, a train “chug-chug”, a mosquito “pi-i” and an airplane “oo-oo-oo”.
- The use of hissing and whistling “s”, “f”, “ts”, “ch”, “sh” in gymnastics accelerates the removal of air from the lungs, and this prevents emphysema. It is better to inhale through your nose and exhale through your mouth, drawing in your stomach.
- For older children and adults, you need to do the obligatory “pf-f-f” exercise once. Its peculiarity is that the combination of these sounds is pronounced with tightly compressed lips. This is considered a cleansing exercise. After doing this, pause, take a breath and pause again. If the exercise is performed by a child, an adult can stand behind him during the exercise and move his palms from the lower back up to the sides, stopping in the middle of the baby’s sides when the exhalation ends. This is done to make breathing easier.
- Next, pronounce the sound “mm-mm” while exhaling; it should be drawn-out, wave-like and relaxed. This exercise is done 5-7 times.
- A combination of the sounds “zhzhruh”, “zrukhh”, “brukhh” and “prrukh” will be useful for relieving bronchospasm.
Each workout can be increased by two new exercises. It is optimal to conduct a lesson for 5 minutes, then increase to 7–10 minutes. Maximum 2 repetitions per day. If a child complains of shortness of breath after sound exercises, it is necessary to do a light massage of the lower chest, over the clothes.
With proper and regular exercise, relief from bronchospasm will occur faster and a long-awaited improvement will appear.
Sound gymnastics by Lobanov and Lazarev
SOUND GYMNASTICS LOBANOV
A type of breathing exercise
Gymnastics consists of special exercises related to the pronunciation of sounds and their combination in a certain work and in a strictly defined way. Gymnastics begins with the obligatory performance of 2 exercises: a cleansing breath - “p, f, t, r” and a closed groan “mmm”.
When pronouncing sounds, vibration of the vocal cords is transmitted to the lungs, trachea, bronchi and from them to the chest; this vibration affects the bronchi and thereby helps prevent bronchitis.
Sound gymnastics is characterized by the following breathing features: inhalation through the nose (1-2 sec) pause, active exhalation through the mouth (2-4 sec), pause.
The inhalation is smooth, silent, uniform, deep. Exhale twice as much as inhale.
Sound exercises must be performed slowly, calmly, without tension, each sound must be pronounced in a strictly defined way, only then sound gymnastics gives a therapeutic result.
Vowel sounds are pronounced in the sequence - u, o, a, e, i.
Consonant sounds are pronounced in the sequence - b, d, g, v, z.
Sonorant consonants - m, n, l, r.
The exercises act like vibration massage.
For unvoiced sounds - p, t, k, f,
s
- the greatest force of articulation is required, and therefore the greatest tension in the muscles of the chest and diaphragm.
Consonant sound r
- trembling, can have from 1 to 14 vibrations when pronounced:
r
,
rrr, rrr
, etc.
Sound combinations s, r
- effective for bronchial asthma, asthmatic bronchitis.
Sound r
- pronounced energetically, loudly, in a long wave -
r
-R-R
For heart disease, the sound r
- pronounced quietly, softly, briefly.
Sounds - w - m
-
z
- pronounced with compressed lips.
Sound k
- (kh) - pronounced with lips.
Sound k
- (kh) - pronounced with a wide open mouth with intensification as you inhale.
For sound gymnastics to be effective, the following rules must be followed:
- If possible, conduct classes outdoors or in a well-ventilated area.
- The clothes are soft and loose.
- Classes are carried out before meals or 1.5-2 hours after meals, preferably in the morning. In the first 2 classes, only 2 exercises are performed - pfft
and -
mmm
- then 2 new ones are gradually added.
Carry out sound gymnastics 1-2 times a day for 5-6 minutes. Exercises can be performed sitting, standing, lying down. Before and after each exercise, take a cleansing breath - pfft
— performed quietly, lips pursed.
Following - pfft
- comes the 2nd mandatory exercise -
mmm.
- — pfft
-
mmm
-
pfft
-. - Vowels - u, o, a, e, i -
pfft. - Consonants - 1-4 - pfft
-.
- Sound combinations 1 — Mmm,
2, 3 ,4 —
pfft.
SOUND BREATHING
M.
L. Lazarev
- The effect of performing rhythmic sound breathing occurs only if the breathing is performed for a sufficiently long time (at least 3 minutes).
- Rhythmic sound breathing can be done both at rest and while walking.
- It is recommended to carry out rhythmic sound breathing most intensively in the autumn-spring period.
- It is effective to use rhythmic sound breathing while keeping a child in bed during illness.
- Rhythmic sound breathing can be used as a way to correct the mental state of children, for example, during a lesson.
The sound breathing complex is aimed at stimulating metabolic processes in cells through sound vibration. In addition, sound vibration improves microcirculation in the area of the pulmonary alveoli, stimulates the activity of the diaphragm, improves mucus drainage, relaxes the bronchial muscles, and increases emotional tone. The exercises of this complex can be performed daily.
The relaxation series (hissing) can be performed as a sound pause between any types of physical activity, as well as before bedtime. We should especially highlight the sound “s”, which has the greatest relaxing properties.
With laryngitis, only voiceless consonants are pronounced so as not to injure the ligamentous apparatus. When pronouncing long sounds, it is advisable to drag them out as long as possible.
Sound “v” (vibration at face level).
Stimulation of blood microcirculation and metabolism in the The effect is achieved for rhinitis,
sinusitis, and sinusitis.
I.P. - standing. The legs are stable. Eyes closed. The lips resist gently. After a deep breath, pronounce the sound “v”
until the air is completely exhaled from the lungs. The sound is pronounced quietly. It is necessary to achieve a feeling of vibration throughout the body, mainly in the face area, trying to make the sound last as long as possible. The lips must be relaxed until a “tickling” sensation appears in them. Repeat 4 times.
Sound “z” (vibration in the head and neck area).
Stimulation of blood microcirculation and metabolism in the head and neck area Effective for tracheitis.
I.P. - standing. The body is relaxed. Eyes closed. The palm of one hand is on the front of the neck. A breath is taken. As you exhale, pronounce the sound “z” for an extremely long time, quietly. Repeat 4 times.
Sound “zh” (vibration in the chest area).
Stimulation of blood microcirculation and metabolism
in the chest area.
Effectively removes mucus from the bronchi and lungs. I.P. - standing. The body is relaxed. Eyes closed. Palm on front of chest. A breath is taken. As you exhale, the sound “zh” is pronounced long and quietly .
Repeat 4 times.
The sound “m” (vibration of tissues in the chest and solar
Improving blood microcirculation and metabolism in the chest
I.P. - standing. Eyes closed. Palm on the solar plexus area. A breath is taken. “m” quietly and for an extremely long time.
(deep sound). Repeat 4 times.
“F-h-ts-ch-sh-sh-s” (relaxation of all respiratory and other
muscles of the body).
I.P. - lying down. Eyes closed. An even sound is pronounced, which lasts as long as possible. The sound is pronounced quietly. Repeat each sound 2 times.
SOUND PLAY EXERCISES
These exercises can be performed by children during morning exercises and in the middle of the day. In the summer, it is better to carry out the complex in the fresh air during a walk.
/.
"On the horizontal bar."
Standing, feet together, hold a gymnastic stick in both hands in front of you. Raise the stick up, rise on your toes - inhale, lower the stick back onto your shoulder blades - long exhale. As you exhale, say “f-f-f-f-f.”
Repeat 3-4 times.
2.
“March at a pace.”
Standing, gymnastic stick in hands. Walk with your knees high. Inhale for 2 steps, exhale for 6-8 steps. As you exhale, say “ti-sh-sh-she.” Repeat for 1.5 minutes.
3.
"Pump".
Stand straight, feet together, arms down. Inhale, then tilt the torso to the side - exhale, hands slide along the body, while loudly pronouncing “ssss.”
Repeat 6-8 bends in each direction.
4.
"Traffic Controller".
Standing, feet shoulder-width apart, one arm raised up, the other to the side. Inhale through your nose, then change the position of your hands and, during an extended exhalation, say “r-r-r.”
Repeat 5-6 times.
5.
“Balls are flying.”
Standing, hands with the ball raised up. Throw the ball forward from your chest. Say, while exhaling, a long “uh-h-h-h.”
Repeat 5-6 times.
6.
“Grow big.”
Stand straight, legs together, raise your arms up, stretch well, rise on your toes - inhale, lower your arms down, lower your entire foot - exhale. As you exhale, say “uh-uh-h.”
Say 4-5 times.
7.
“Skier.”
Simulation of skiing for 1.5-2 minutes. As you exhale, say “mm-mm-mm.”
8.
"Pendulum".
Standing with your feet shoulder-width apart, hold the stick behind your back at the level of the lower corners of your shoulder blades. Tilt your torso to the sides. When bending over, exhale and say “t-u-u-x-x-x.”
Repeat 3-4 bends in each direction.
9.
“The geese are flying.”
Walk slowly for 1-2 minutes. Raise your arms to the sides - inhale, arms down - exhale, say “g-oo-oo-oo”.
10.
"Semaphore".
Sitting, legs moved together. Raise your arms to the sides - inhale, slowly lower them down - long exhale, say “ssssss”. Repeat 3-4 times.