Dislalia
The most common speech therapy problem for children aged 4-5 years and older. This term refers to the incorrect pronunciation of sounds, sometimes two or three sounds, and sometimes half the alphabet. You can confidently make such a conclusion about dyslalia if:
- the child’s vocabulary of passive and active vocabulary corresponds to age;
- he constructs phrases and sentences correctly;
- words are consistent in gender, number and case.
If, in addition to defective pronunciation of sounds, there are other violations, then we can talk about a general underdevelopment of speech.
Speech therapy DIAGNOSIS (For speech therapists)
Speech therapy diagnoses
Dysarthria
When diagnosed with dysarthria in children, not only the pronunciation of sounds is impaired, but also the tempo, modulation, expressiveness of the voice, rhythm and breathing, that is, all departments involved in “speaking” are in deficit: the respiratory, vocal, and muscles of the articulatory apparatus. The reason is disruption of the transmission of impulses from the central nervous system to these departments, that is, the signal is sent to the address, but does not arrive accurately, as a result, the blood supply is disrupted, muscle tone changes - we observe either flaccid, pale, sedentary muscles (hypotonicity), or excessively tense (hypertonicity). In any case, the mobility of the speech organs is limited.
With dysarthria, we can not only hear the defect, but also see it. The baby does not speak yet, but we notice how quickly he gets tired while eating, sucks the breast or bottle sluggishly, and often spits up. Later, these children take a long time to get used to solid food. When they start speaking, their speech is slurred, not only complex but also simple sounds are poorly pronounced. With dysarthria, in some children the cheek seems to squelch when pronouncing, some sounds are pronounced between the teeth, there is increased salivation, speech sounds uneven, the child seems to be chanting, pushing out sounds, in others, on the contrary, the voice sounds quiet, nasal tones are often found.
The diagnosis is expressed in varying degrees of severity. The most complex of the forms: anatria - a complete inability to speak, to control one’s speech apparatus; dysarthria is typical for children with cerebral palsy; erased dysarthria is more common. A form such as a dysarthric component (impairment in one muscle group) can easily be confused with dyslalia, however, in this case, speech therapy work takes longer, as it is associated with the restoration of muscle movements. For a more successful and high-quality correction, observation by a neurologist is required.
Dislalia
Some publications still write that the most common speech therapy diagnosis in children is dyslalia. Indeed, this is what happened ten years ago. Good phonemic hearing, literate speech, developed according to age, but only the sound side suffers: distortion of sounds and their omissions - this is what is characteristic of this diagnosis and was characteristic of most children. Unfortunately, today, in addition to defects in the sound side of speech, phonemic insufficiency, impaired attention and memory are added, that is, dyslalia is no longer limited only to distortion of sounds.
In children under 5 years of age, when not all the muscles are dexterous, mobile and ready for clear pronunciation, disturbances in sound design are allowed, so in the card when the child is registered for kindergarten, the speech therapist at the clinic will write this down - physiological dyslalia. And all the work with the child at this time is preventive, imitate animal and mechanical sounds, tell articulation tales together and do articulation exercises - everything is beneficial, and the tongue itself will find its correct position. If after 5 years the defective pronunciation remains, then dyslalia passes to functional. This means that the muscles of the tongue or articulatory apparatus require professional help and corrective work. Mechanical dyslalia stands out separately, when children have gross violations in the anatomical structure of the jaw, teeth, palate - in these cases, correction is impossible without dental surgeons or orthodontists .
Alalia (motor and sensory)
Now about the most severe speech disorder, which is so important to correctly diagnose in order to separate it from mental retardation, hearing loss and autism. Alalia in children (as is clear from the particle absence) is a complete or partial absence of speech with good physical hearing and primary intact intelligence, due to underdevelopment or organic damage to the speech parts of the cerebral cortex. And here I would like to remind you how, from simple to complex, a child masters speech skills, stages of a difficult speech path:
- partying,
- babble,
- babbling monologue,
- individual words,
— phrases.
Here is the norm for mastering speech.
Other options, such as the absence of humming or babbling, babbling passages instead of words, late formation of phrasal speech - parents! attention! - this is an alarm! “He’s smart, he’ll talk later,” you reassure yourself, emphasizing the positive aspects: the baby strives to communicate, he’s smart, loves to design, plays story games, that is, a strong non-verbal side, but you forget that speech delay will sooner or later entails a delay in the cognitive sphere.
Alalia seems to be disguised; it is heterogeneous and diverse in its mechanisms, causes of occurrence, manifestations and severity of speech deficit. There are two forms of alalia in children:
- motor alalia, when the child understands speech addressed to him; but he cannot repeat it arbitrarily, according to a model, and as he gets older and realizes his defect, he complicates the problem by the fact that he does not want to try;
- sensory alalia, when there is a gap between meaning and sound, the child hears a certain sound okroshka, which does not assign their verbal meaning to objects, actions, the world that surrounds him, which leads to a secondary impairment of intelligence. This division is conditional, and in practice Combinations of the two forms are often found.
Many children have preserved visual perception, which must be taken into account in correctional work. Children with alalia are characterized by neurotic reactions to the defect, rapid fatigue, decreased attention and performance. Both sensory and motor alalia require the supervision of a neurologist.
FFN (phonetic-phonemic disorders)
Most speech therapy diagnoses are related to speech reproduction, that is, with HOW and WHAT we say, but before speaking, the child must hear and perceive correctly.” Your child has a phonemic hearing disorder,” says the specialist.” “My child hears well,” the mother is perplexed, but agrees that the baby has what is characteristic of this diagnosis:
replacement of some sounds with others (remember, in Deniska’s stories: fyfka, hykhka, syska); rearrangement of sounds and syllables (kopa instead of poka); simplification of the syllabic structure of the word (chaschik instead of watchmaker). Such children do not distinguish sounds that are similar in sound. Without visual support and without context, the child does not immediately understand what we are talking about - a white braid or a white goat, a hairstyle or an animal? The sound changes and the meaning changes. What a tremendous power the phoneme has - a sound and meaning distinguisher.
And if a child misunderstands something from the flow of information, then, as a consequence, secondary disorders occur: FFSD (phonetic-phonemic underdevelopment of speech), dysgraphia (impaired written speech).
For specialists, we recommend the material of our colleagues Natalya Vareshina and Elena Ermilova “The system of work of a speech therapist teacher on the formation of phonemic hearing”
Rhinolalia
The interpretation of this diagnosis is different in different medical and speech therapy sources; the only common one is nasal speech timbre syndrome. Nasality is how this diagnosis sounds in defectological dictionaries of old. Or maybe someone suffers from chronic rhinitis, but at the same time he has the correct pronunciation of sounds - is this diagnosis then made? Let's try to clarify it and isolate it from others. Rhinolalia is a violation of the timbre of the voice and sound pronunciation in the presence of organic defects in the anatomy and physiology of the speech apparatus: congenital clefts of the hard, soft palate, upper lip - what is popularly called “cleft palate”, “cleft lip” . Due to the fact that the oral and nasal cavities are combined (OPEN form), in the very first hours of a child’s life, eating becomes a problem and he requires early surgical intervention. In the future, operations are indicated depending on the size and shape of the defect; adenoid growths, curvature of the nasal septum, fusion of the nasal passages - what belongs to the CLOSED form
Speech therapy classes with such children should begin as early as possible, because the results of work on eliminating nasal connotation and correct sound pronunciation usually decrease after the next operation, but if the child already has experience, then his speech is restored faster. Mechanical dyslalia, which is often confused with this diagnosis, it is distinguished by the preservation of vowel sounds, and with rhinophony, although the same nasal timbre is observed (chronic rhinitis?), the child’s pronunciation of sounds is correct.
General speech underdevelopment (GSD)
A child does not immediately speak a good literary language; first he masters his native speech through the experience of adults, then goes through his own path of trial and error (see Chukovsky “From 2 to 5”). Many children love to “distort” words - some of the masterpieces forever fit into the family chronicle. Then in what cases are errors in speech a symptom of a diagnosis? OPD is, first of all, a SYSTEMIC disorder when all components of speech are impaired: vocabulary, grammar, and phrasal speech. At the same time, physical hearing and intelligence remain normal. Children with ODD are distinguished from children with intellectual disabilities by a sufficient passive vocabulary for their age and a sufficient level of performance of non-verbal tasks.
There are 3 levels of OHP, although practice shows that there are no clear boundaries between the levels. The main thing is that the division (according to Levina) is based on the level of development of phrasal speech. A short digression about the importance of the verb in a child’s speech. The phrase contains an action, and the action is indicated by a verb, without it there is no conclusion, cause-and-effect relationships are not provided, and thinking suffers.
Level 1.
"Speechless" children
- Babbling words, onomatopoeia. One word can denote different concepts, actions and objects; to clarify, the child widely uses facial expressions and gestures. “Ma” - behind this appeal to mom there is a desire to cuddle, and “I want to eat,” and “let’s go for a walk,” and “turn on the TV” (while bringing the remote control); and the pleasure of riding a slide.
— The words are not grammatically formed.
- There is no phrase.
Level 2
— The vocabulary is larger, but the words contain omissions of syllables, rearrangements, and incorrect forms are often used. “Goose.” Drowning. "- in the picture there is a duck diving into the water.
— Gross grammatical errors, lack of agreement in words. “Two apples” - two apples.
— Phrasal speech is primitive, although the sentence already contains 2-3 words.
Level 3
- A good dictionary of everyday words, but abstract concepts are poorly absorbed: names of seasons, generalizing concepts (cucumber, tomato, cabbage - the child points and names, but cannot name “vegetables” in one word), the replacement of words with nearby words is typical: he calls a baby dog a little dog .
- The grammar is characterized by simplification of prepositions, in the diminutive form - incorrect use of suffixes, and when counting - errors in the endings of words.
— The conversational phrase is detailed, but composing a story based on a series of plot pictures and retelling due to a lack of speech planning causes difficulty.
Some children also experience a violation of the sound design of speech; in such cases, it is important to clarify the integrity or impairment of phonemic perception during diagnosis. In the second case, we can talk about OHP against the background of phonemic deficiency, and corrective work should begin with the primary violation. Underdevelopment of speech also affects the development of cognitive processes: children with ODD experience unstable attention, decreased memory, and weak verbal and logical thinking.
Exercises to develop cognitive functions are perfect for children with ODD.
Dysgraphia
Dysgraphia is a disorder of written speech.
General speech underdevelopment
This is a complex of various speech pathologies, expressed by the following characteristic features:
- undeveloped coherent speech;
- violation of pronunciation and differentiation of sounds;
- vocabulary is poor and not age appropriate;
- word formation and inflection are difficult.
With general underdevelopment of speech, all components of the system suffer: phonetics, vocabulary, grammar. Such children start speaking late. They understand the speech of others, but cannot formulate the statement themselves.
There are three levels of OHP:
- There are individual elements of speech, babbling words, one-word sentences, abbreviations of complex words.
- Speech consists of short phrases consisting of 2-3 distorted words, with syllables rearranged and inconsistent with each other.
- The use of prepositions, endings, and the syllabic structure of complex words is impaired.
The main causes of such speech therapy problems in children are the pathological course of pregnancy and birth trauma. They can also be the causes of the following speech pathology.
Delayed speech development - symptoms and treatment
Classes with a speech therapist. The speech therapist conducts special lessons with the child on the initiation and development of speech, and helps to construct sentences correctly. Such techniques include articulatory gymnastics, sound production exercises, and play techniques, such as finger puppet theater. If a child understands phrases, his intelligence is preserved, and his speech is delayed by six months to a year, then speech therapy classes are sufficient [1][8].
Classes with a speech pathologist-defectologist differ from regular speech therapy classes. For example, a speech pathologist is able to work with children who have difficulty understanding speech and severe developmental delays. During classes, the child learns basic concepts (big/small, color, shape, size), does exercises to improve fine motor skills, and learns the names of objects to form a passive vocabulary. After mastering basic knowledge, the speech therapist-defectologist begins to develop expressive speech [7][12][15].
Comprehensive medical and pedagogical rehabilitation for delayed psycho-speech development. If a child does not understand speech well, is excitable, and has not developed social and everyday skills, then comprehensive rehabilitation may be required. In such cases, speech significantly lags behind the age norm, diction is grossly impaired, and other neurological symptoms are expressed [2]. To develop speech, neurologists prescribe nootropic drugs: Cortexin, Cogitum, Ceraxon. According to the manufacturers, the drugs activate neurons, improve the transmission of nerve impulses and eliminate the effects of hypoxia - lack of oxygen. (The effectiveness of these drugs for delayed speech development has not been proven in studies, and in the new Russian clinical guidelines for the treatment of autism, a group of experts has already described nootropics as an ineffective method of treating the disorder - editor's note at ProBolesny). B vitamins will also help normalize the functioning of the nervous system. However, it is important to remember that only a pediatric neurologist prescribes medications, taking into account the characteristics of the child, since medications can cause overexcitation and allergic reactions [2][16].
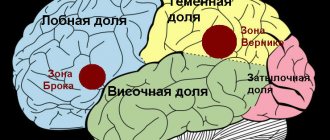
Microcurrent reflexology is a method of treating children with speech delays, approved and recommended by the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation. It consists of selective activation of speech areas of the brain:
- Wernicke's area (responsible for speech understanding);
- Broca's area (associated with active vocabulary and the desire to talk);
In addition, influencing the frontal lobes will help develop logical thinking and form everyday skills. Treatment is carried out under the control of electroencephalography (EEG) [6][13][14].
Speech therapy massage is an effect on articulatory muscles: muscles of the face, tongue, lips, soft palate. Manipulations are carried out with sterile probes. The purpose of the massage is to normalize the tone of the muscles of the tongue, orbicularis oris muscle, and improve blood supply to the organs of articulation. The method is necessary for children with excessive drooling and impaired diction. The procedure is also prescribed to non-speaking patients, since speech may be absent due to inability to control the organs of articulation [10][13].
Disorders of tempo and rhythm of speech
These speech therapy problems in children are noticeable even to non-specialists. Among them:
- Tahilalia - accelerated pronunciation of words and sentences;
- Bradylalia - slow pronunciation, accompanied by the same internal speech (such a child also thinks slowly);
- Stumbling - stops in speech of a non-convulsive nature;
- Stuttering is one of the most difficult speech pathologies to correct, caused by convulsions of all parts of the speech apparatus. The cause of stuttering is improper speech education, mental trauma.