Neurosis-like stuttering
Neurosis-like stuttering appears gradually and develops gradually, usually during the period of active formation of phrasal speech. The primary localization of seizures in the articulatory apparatus is typical: lips, tongue and soft palate. They appear more sharply when pronouncing such consonant sounds as “b”, “g”, “p”, “d”, “t” and “k”. Speech activity is usually increased, and tachylalia is characteristic. Often, neurosis-like stuttering appears against the background of severe dyslalia or existing in an erased form of dysarthria. In some cases, general speech underdevelopment is observed.
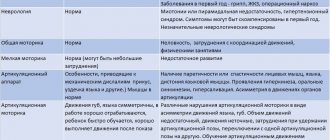
Typically, the speech movements of children with organic stuttering are insufficient in strength and volume, as a result of which their speech is monotonous and inexpressive, characterized by muffled pronunciation of sounds. Often such children accompany their speech with stereotypical movements (active gestures, sometimes antics). In parallel, as a rule, there is monotony and some stiffness of movements, insufficient fine motor skills, poor facial expressions, elements of dysgraphia and dyslexia. Synkinesis is detected. Insufficient speed and dexterity when performing motor acts makes the child clumsy and sluggish. In the mental sphere, there is impulsiveness, inertia, euphoria, difficulty switching, exhaustion and fatigue. Fixation on one’s own speech defect is not typical; there is no logophobia. At the same time, the child does not have any particular desire to get rid of the speech defect. In addition, overcoming stuttering is hampered by immaturity of the emotional-volitional sphere.
Neurosis-like stuttering is characterized by a relative constancy of the intensity of speech disorders. Its strength does not depend on external psycho-emotional factors, and there is no increase in stuttering characteristic of a neurosis-like form in an unfamiliar environment or when in contact with unfamiliar people. Neurosis-like stuttering increases due to psychomotor agitation and heavy speech load. Some deterioration in speech may be observed with overwork and after suffering from somatic (acute gastritis, cystitis, glomerulonephritis, etc.) or infectious (measles, chicken pox, ARVI, influenza, tonsillitis, etc.) diseases.
At the age of 12-15 years, neurotic symptoms may develop in the form of anxiety and logophobia in the presence of strangers. There is a decrease in speech activity, and a fixation on difficult-to-pronounce sounds appears. An increase in stuttering is detected in a psychologically uncomfortable atmosphere, but it is not permanent. Stuttering takes on a wave-like course, since it depends on the mental and physiological state of the child.
basic information
Modern science defines two types of stuttering: neurotic and neurosis-like. In the first case, the disease is associated with psychological trauma and can appear in a person of any age category.
The second type appears due to disturbances in the functioning of cerebral structures; for this reason, practicing neurologists characterize it as organic. Typically, this variety develops at the stage of active formation of speech functions - this occurs at the age of 3-4 years.
If we talk about older age, then symptoms associated with the presence of a speech defect may also develop. Such a case would be more typical for logoneurosis. For this reason, a number of authors define neurosis-like stuttering with neurotic layers as a separate type of disease, calling it mixed stuttering.
Diagnosis of the disease
An examination of the child by a neurologist determines symptoms of diffuse residual neurological type, signs of cerebrasthenic syndrome and various motor disorders. Characterized by a weak sense of rhythm and inconsistency of movements.
The examination of speech for diagnostic purposes includes the diagnosis of oral speech and auditory-verbal memory, the study of written speech (school-age children). To identify this pathology, instrumental examinations are necessary.
To identify signs of hydrocephalus, an X-ray of the skull is performed, an Echo-EG is performed to identify intracranial hypertension, and an ECG is performed to identify disorders that will indicate the presence of organic changes. A CT scan or MRI of the brain is also performed to rule out a number of diseases that may also cause the development of this disease.
Differential diagnosis
Neurosis-like stuttering is manifested by neurotic symptoms, and neurotic stuttering can be characterized by signs of microorganisms.
Thanks to a neurological examination, it is possible to distinguish organic stuttering from those speech disorders that act as syndromes of other diseases, when a disorder in fluency of speech is associated with disturbances in the functioning of the articulatory muscles.
Sometimes there is a need to distinguish neurosis-like stuttering from the so-called stumbling, which is characterized by unclear and accelerated speech, in which some sounds and syllables are skipped or rearranged. The second situation is often observed in children with hyperactivity disorder.
The pathognomonic feature of stumbling is that speech becomes better when reading an unfamiliar text, and vice versa, it worsens when reading a familiar one.
Treatment of the disease
Neurosis-like stuttering is an interdisciplinary disease, for the treatment of which it is necessary to be observed by several specialists of different profiles (neurologist, speech therapist, psychologist). Treatment is carried out with the help of nootropics, as well as metabolic and absorbable drugs. To reduce intracranial pressure, diuretics and magnesium sulfate solution are usually prescribed. If complex therapy is carried out, then the use of homeopathic remedies is allowed.
To reduce the intensity of speech defects, constant sessions with a speech therapist are necessary, aimed at correcting dysarthria and dyslalia. Classes with a psychologist should not be relegated to the background, since they also play a significant role in the therapy process.
Classes with a psychologist should be aimed at the psychomotor development of the child. If the disease is of a mixed nature, psychotherapy methods are used. If necessary, psychotherapy can be supplemented with the use of sedatives and antidepressants.
Is it possible to cure stuttering in a child?
Treatment of stuttering, especially the neurosis-like type, is a long process. Usually it takes about a year, but in the future it requires constant dynamic monitoring by a neurologist and taking prescribed pharmacological medications.
Timely consultation with a doctor and careful adherence to all his recommendations provide a favorable prognosis for the treatment of stuttering.
However, according to WHO, in 1% of children the pathology may persist, despite the efforts of doctors and parents. In this situation, the help of a psychologist will be effective, helping to establish communication and manage the emotional state.
What is stuttering in children?
Stuttering is a speech disorder that occurs due to genetic or neurological dysfunction of the child’s nervous system.
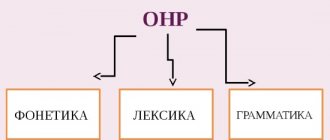
According to the nature of the disorders, experts distinguish two main types of logoneurosis, namely:
- tonic, accompanied by pauses in speech or prolongation of a certain sound;
- clonic, manifested as repetition of sounds, syllables or words;
- mixed.
Depending on the etiology, the following forms of stuttering are distinguished:
- neurosis-like, including difficulty articulating (impaired pronunciation of words, reading and writing);
- neurotic, in which the appearance and severity of pronunciation difficulties are associated with a stressful situation.
Speech neurosis can be caused by any deviations from the norms of child speech development, such as delayed speech development or an excess of new words.
What to do if your child stutters?
When the first signs of stuttering appear in a child, you should consult a doctor and undergo a comprehensive diagnosis. Based on the results obtained, the pediatrician will refer you for treatment to a specialized specialist.
If the speech disorder is of a neurotic nature, then the leading specialists in therapy are a child psychologist and a neurologist.
In case of neurosis-like stuttering, the main doctor will be a speech therapist-defectologist, often with additional help from a neurologist.
Since the correction of stuttering is complex, in addition to classes with doctors, the help of parents occupies a significant place in the treatment of pathology.
Effective ways to help parents overcome their child’s stuttering are:
- creating a comfortable and friendly atmosphere at home;
- adherence to a daily routine with a mandatory 10-hour sleep;
- measured pace of study;
- healing and hardening of the child (vitamins, gymnastics that improve coordination, breathing and functioning of the cardiovascular system);
- clear, calm, unhurried speech of parents;
- absence of sharp gestures and raising the voice of parents;
- support with tactile contact, praise;
- the child’s ability to speak at a pace that is comfortable for him, etc.
Speech classes are also performed at home with the child. In these classes, it is necessary to use material (books, films, games, crafts), on the basis of which the subsequent conversation is conducted. During the conversation, parents gently correct speech, without focusing on its defects.
Speech classes are built on the principle of “constantly, as much as possible and gradually,” that is, from a simple statement to a detailed answer. It is extremely important to conduct classes regularly for 3-4 months, overcoming the fear of speaking.
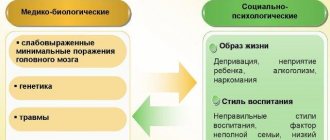
Causes of the disease
Neurosis-like stuttering differs from neurotic stuttering in that it is in no way connected with any situation traumatic to the psyche. It is explained by functional changes in the central nervous system that appear due to some organic pathology of the brain. It can be triggered by negative influences on the developing child’s body in the antenatal period, birth trauma, and various diseases in the postnatal period. At the time of stuttering, organic changes in cerebral structures, as a rule, are residual or residual in nature.
Triggers that can influence the appearance of such a disease include serious illnesses suffered by parents (most often these are infectious or neuropsychiatric diseases), harmful effects on the body of a pregnant woman (there may be occupational factors, smoking, substance abuse, drug addiction, exposure to medications ), complications during pregnancy and childbirth.
An important role is played by hereditary indicators, which become the basis for the tendency to stutter at the genetic level. Scientists note that children suffering from neurosis-like stuttering have relatives with speech disorders.
When does stuttering go away in children?
According to the observations of specialists, signs of pathology increase with fatigue, especially in the autumn-winter period of the year. The severity of stuttering directly depends on the environment in which the child is currently located. So, in the morning and in a comfortable situation, speech impairment may not appear, but in the company of peers it increases significantly.
It is known that children do not stutter when they are alone, reading poetry and singing songs.
If a child’s speech neurosis was provoked by a temporary factor (a quarrel between parents, a sudden sharp sound, etc.), then it is possible that he will eliminate himself within a month. In some cases, a relapse of stuttering is possible, which subsequently also disappears.
However, when the speech reproduction disorder does not go away on its own, it is necessary to seek professional help from a doctor.
Signs indicating the need to make an appointment with a pediatric speech therapist or neurologist are:
- speech disorders in a child over 4 years of age;
- the duration of the disorder of fluency and continuity of speech is more than 3 months (it is important to keep a calendar of the appearance/disappearance of disorders, where each relapse serves as a new starting point);
- facial nervous tic when talking;
- hereditary factor for stuttering.
How is stuttering in children treated?
Numerous therapeutic techniques are used to treat logoneurosis in children. The selection of treatment tactics is carried out by a doctor, based on the characteristics of the speech pathology and psyche of the child.
The most popular methods of normalizing speech for stuttering are:
- silence mode (4-6 day period of speechless communication using special signals. It is effective for stopping spasms of the speech apparatus, stimulating new spasms);
- Speech therapy rhythm is a correctional combination of music, speech and movement, which involves repeated repetition of developed motor skills;
- breathing and articulation gymnastics for training the articulatory organs and developing speech breathing;
- improving fine motor skills as a way to stimulate nerve centers in the brain (areas responsible for speech and movement are located very close);
- massage;
- voice exercises to normalize speech motor skills, etc.
To relieve muscular and mental tension during stuttering, relaxation techniques are used to promote emotional stability and concentration. Medications that calm the nervous system and relax the muscles of the speech apparatus structures are often prescribed.