Subject to normal speech development, a five-year-old child has full command of detailed speech, skillfully uses a variety of constructions of complex, long sentences and phrases, and has a sufficient vocabulary necessary for the correct expression of thoughts and desires. If such processes are disrupted, systemic underdevelopment of speech may occur.
Systemic speech underdevelopment (SSD) represents a whole complex of disorders of the speech apparatus, which are accompanied by dysfunction of the most important language components - grammar, phonemics, vocabulary, as well as the sound part of the lexicon. In some situations, systemic underdevelopment of speech in a child may be a symptom of a more severe and dangerous condition - a pathology of psycho-emotional development.
general information
Speech is a complex skill in which it is customary to distinguish several functional elements:
- grammar, which implies knowledge of the rules for the formation of sentences and words, including their agreement with each other by gender, case and number;
- vocabulary, characterized by vocabulary, the vocabulary gradually increases as the child grows up;
- phonetics - correct pronunciation of sounds and their combinations.
SDN in speech therapy is a speech defect that affects all three components of speech in children over 5 years of age. If similar disorders are detected before this age, then speech therapists and pediatricians talk about delayed speech development.
Only a speech therapist can make a diagnosis of SNR after a comprehensive examination of the child and speech therapy analysis.
Signs
How can you understand that a child is falling behind and suspect that there is a delay in mental, speech or intellectual development before the child turns five?
- The first alarm bells can be observed in the first year of life. What should alert you: in response to words and sounds uttered by adults, the baby does not try to reproduce something of its own.
- At the age of one to one and a half years, the child learns to imitate the sounds pronounced by loved ones, as well as point to objects at the mother’s request. If this does not happen, you need to think about it.
- The next milestone is 2 years. Here the child must be able to speak words or phrases of his own free will, that is, spontaneously.
- At three years old, adults should understand approximately two-thirds of what the child says, and at four years old, the meaning of absolutely all words. If this does not happen, you should consult a specialist.
- At the age of five, when we are already talking about such a diagnosis as SSD, the signs may be as follows: speech remains slurred and difficult to understand; there is no consistency between impressive and expressive speech - the child understands everything, but cannot speak out himself.
Possible reasons
Systemic speech disorders are observed in patients with organic changes in the structure of the brain. Doctors identify the following possible causes:
- Hypoxic damage to the central nervous system in the prenatal period. Hypoxia can develop due to pathology of the placenta, the presence of diseases of the mother’s internal organs, including infectious ones.
- Chronic intoxication of the fetus due to alcoholism, drug addiction or smoking of a pregnant woman.
- Birth injury or brain damage as a result of traumatic exposure in the first 3 years of life.
In addition, systemic underdevelopment of speech is observed in mental retardation, cerebral palsy and genetic abnormalities (Down syndrome, etc.).
Syndromes combined with different degrees of MR
Down syndrome is the most common genetic cause of intellectual disability. It is caused by a chromosomal abnormality - if normally there are 46 of them, then in this case there is an unpaired 47th chromosome. People with this syndrome can be identified by an abnormally short skull, flat face, short arms and legs, short stature, and small mouth. They process the information received poorly and remember it, they lack the concept of time and space, and their speech is poor. Moreover, such individuals adapt well to society.
Martin-Bell syndrome (fragile X chromosome). The second most common genetic cause of mental retardation. It is recognized by the following external features: increased mobility of joints, an elongated face, an enlarged chin, a high forehead, large, protruding ears. They start talking late, but poorly, or don’t speak at all. They are very shy, hyperactive, inattentive, constantly moving their hands and biting them. Men have more cognitive impairment in this category than women.
Williams syndrome (“elf face”). It occurs as a result of hereditary chromosomal rearrangement, the loss of genes in one of them. The patients have a very interesting appearance: the face is narrow and long, blue eyes, flat nose, large lips. Usually suffer from cardiovascular diseases. Rich vocabulary, good memory, excellent musical abilities, and social interaction skills. But there are problems with psychomotor skills.
Angelman syndrome (happy doll or Parsley). Caused by a change in chromosome 15. Very light eyes with characteristic spots on the iris and hair, the head is small, the chin is pushed forward, the mouth is large, the teeth are sparse and long. Severe delay in psychomotor development, significant impairment of speech and movement (poor balance, walks on stiff legs). He often smiles and even laughs for no reason.
Prader-Willi syndrome . It is characterized by the absence of a paternal copy of chromosome 15 and a number of other disorders. He is short in stature, has small arms and legs, suffers from compulsive overeating, and, as a result, obesity. Problems with short-term memory, speech, information processing.
Lejeune's syndrome (cry of the cat or 5p syndrome). A very rare and serious disease caused by the absence of the short arm of chromosome 5. The head is small, the face is round, the lower jaw is underdeveloped and the bridge of the nose is wide, so the eyes are located far from each other. The feet are turned out, the hands are small. The larynx is underdeveloped, there are vision problems, in particular, strabismus. She often cries and makes a sound similar to a kitten meowing. Motor development is delayed, and the ability to pay attention is limited.
In addition to the syndromes mentioned, intellectual disability can coexist with cerebral palsy, deafness and blindness, autistic disorders, epilepsy and other somatic and mental illnesses.
Clinical manifestations
Symptoms of the pathology and their severity depend on the severity of the disease. In speech therapy, there are three degrees of systemic speech underdevelopment:
- With a mild illness, the pace of conversation remains at a normal level or may even be accelerated. The child clearly pronounces individual sounds. Difficulty occurs when trying to pronounce a complex sentence or phrase. Due to underdevelopment of speech, he poorly understands cause-and-effect relationships. The vocabulary is limited, which leads to the use of the same words in conversation, without the possibility of selecting synonyms for them.
- Underdevelopment of moderate severity is associated with a violation of the process of articulation, that is, the pronunciation of sounds. The intonation of such a child is monotonous. If you ask him to quickly talk about something, the patient mixes sounds or replaces them with others. There are grammatical errors in the sentences. Poorly understands what is said, especially if the words have a figurative or hidden meaning. Schoolchildren are passive in communication - they prefer to answer questions rather than ask them themselves. When retelling a story, elements of the story are omitted or the general meaning is distorted. The vocabulary is limited. As a result of speech impairment, students demonstrate dyslexia and dysgraphia.
- In severe cases, articulation disturbances are pronounced. Speech is slow and monotonous. At the same time, it is fuzzy and indistinct, which is associated with distortion of sounds. There are a large number of grammatical errors, including the appearance of non-existent words and statements. Such children poorly understand speech addressed to them. When trying to communicate independently, they speak in separate simple phrases, rarely containing more than 3-4 words. Communication is accompanied by pronounced gestures and facial expressions. Characterized by a significant decrease in vocabulary. As a result of impaired fine motor skills of the hands, writing skills are absent or at a minimal level.
Systemic speech underdevelopment is a diagnosis that is given to children over the age of five. To confirm this, the child is examined by a speech therapist, psychiatrist and neurologist. With concomitant mental retardation or emotional disturbances, a diagnosis of “mental retardation” may be made.
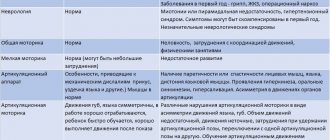
Norms of speech development in a child
There are certain criteria that will help parents suspect disorders in their child and go to the hospital:
| Period | Description |
| 1-8 months | During this period, the child makes sounds and syllables. Baby talk gradually appears. The baby plays with vocal sounds. Can name certain objects and people with whom he most often communicates. Articulation and intonation are also formed. |
| 1-2 years | The child begins to pronounce verbs, but parents mistake this step for the first words. At this stage, everything depends on the mental development of the child. In some situations, only those close to him who spend the most time with him understand him. By the age of 2, the baby can already pronounce several words or phrases. Vocabulary is gradually increasing. |
| 2-3 years | The number of words gradually increases. The kid tries to make sentences based on the main word, as a result of which a grammatical connection is formed. At this stage, the child begins to master changing endings in words. He learns to mentally think about words and constructions, and gradually master his native language. |
| 3-5 years | At this stage, the child pronounces complete phrases, fragments of oral speech with a general meaning. He learns to maintain communication with his interlocutor. During the same period, the vocabulary of his language was formed. |
| 5-7 years | The child masters coherent speech. Learns to express his thoughts by composing whole sentences. At the same time, he adheres to a certain sequence. He develops conversational logical thinking. |
The division of speech development into levels occurs individually in each case. It all depends on the child’s psycho-emotional state, his physical health and individual characteristics.
Diagnostic measures
A speech therapist diagnoses speech disorders. The examination plan includes mandatory familiarization with the child’s medical documentation. If necessary, the speech therapist consults with a pediatrician, child neurologist or psychiatrist. It is also necessary to find out the duration and nature of the development of speech disorders in parents.
In the process of communicating with a child, a speech therapist identifies the degree of formation of individual components of speech: vocabulary, phonetics and grammar. Diagnosis begins with an assessment of coherent speech. The child is asked to create a story based on the pictures, retell a simple text, or create a story about his own memory. During this exercise, the specialist gives a description of speech literacy. While working on exercises to assess the coherence of speech, vocabulary is studied.
The second part of the diagnostic examination is the study of speech phonetics. The speech therapist evaluates the functional integrity of articulation, the features of sound pronunciation and the sound content of speech. The child’s hearing must be assessed, since speech defects may be due to the fact that the process of assimilation of speech structures is disrupted.
Children with intellectual disabilities
Society must be tolerant of people with mental retardation; a special approach and teachers are needed who know the specifics of the work, who can give intellectual disabilities an education and help them realize their potential.
Children with disabilities need the support of others, especially parents, who must provide such children with psychological comfort, development, and improve their quality of life.
In infants, it is quite difficult to identify mental retardation, especially its mild form, since they are almost no different from others. But their activity is impaired: they begin to hold their heads up late, babble, sit, and crawl.
But as the child grows up, when he begins to go to kindergarten, it becomes noticeable that he has difficulty maintaining a daily routine, communicating with peers, and mastering new skills. For example, a three-year-old child cannot assemble a pyramid on his own, although he repeated this many times with the teacher. My classmates succeeded after 1-2 lessons.
Oligophrenic children are not inquisitive; they cannot sit in one place for a long time, but they get tired very quickly. Their speech is poor, they confuse letters (especially consonants). Since their phonemic hearing and analysis are poorly developed, they pronounce words incorrectly, and then write incorrectly. The development of auditory discrimination and the articulatory speech apparatus lags behind - hence slurred speech.
Gross and fine motor skills suffer as the central nervous system develops abnormally. The baby's movements are uncertain and sluggish, he manipulates objects chaotically. For a long time he cannot determine the “main” hand; he moves both of them inconsistently.
Difficulties with the “pinch” and “tweezer” grip do not allow the child to hold a pencil and pen correctly and learn to write. Underdevelopment of fine motor skills also makes it difficult to care for oneself.
The child cannot concentrate and remember something. This negatively affects cognitive activity and mental activity. The baby does not see or hear what is said to him due to attention problems.
Studying is difficult for such children: they learn the material slowly because they do not remember it and cannot reproduce the information received. They cannot apply the skill or knowledge they have learned after repeated repetitions and quickly forget it.
The child is not able to express feelings verbally, because he has poor speech, but he expresses emotions through facial expressions, touches, and gestures. He is incapable of empathy. His will is weak, so he is trusting of any person, easily suggestible, and this is very dangerous.
Contact a specialist (neurologist) without delay if your child behaves unusually or you do not understand what is happening to him. The benefit of this is double - in the best case, all doubts about the adequacy of your child will be dispelled, and in the worst case (which, however, is also not bad) - early diagnosis will allow you to immediately take measures to solve the problem. This will allow such a child to be better socialized and adapted to life.
The doctor will examine the little patient, ask the parents about the symptoms, when they appeared, about the child’s practical and social skills, adaptive behavior, etc. An intelligence test is required to find out how teachable the child is, how he can solve problems and think abstractly. An IQ below 70 may indicate the presence of intellectual disability and its level.
Tips for parents
The following recommendations can be given to mothers and fathers of special children:
- Of course, hearing such a diagnosis for your child is a terrible blow, causing negative thoughts. There is a feeling of guilt, resentment at fate, anger, despair, melancholy. But you still have to accept this fact, come to terms with it, and communication with other parents who have a similar problem can be a good support. It’s also a good idea to visit a psychologist.
- You need to clearly separate your capabilities from what is impossible to do and, without giving up, look for ways to solve problems and means.
- Consult with specialists. It is also advisable to collect as much information as possible from serious sources about mental retardation, how and how you can help the child, what exactly should be done, where to go. The experience of families with an oligophrenic child is invaluable, communicate with them.
- Learn about and take advantage of government and community services for families with children with mental retardation.
- Think not about limitations, but about your child’s capabilities, what he can do and what he needs, how to please him. It is in your power to help him become independent and socialize as much as possible.
- Under no circumstances isolate your child from other people, neither children nor adults.
- Despite the fact that the level of development of your child at certain stages is lower than that of his peers, you need to communicate with him not as with a baby, but in accordance with his age.
- It is necessary to regularly conduct developmental and training sessions. The goal of education is social adaptation, that is, the child must master speech, writing, and everyday independence.
Don’t expect anything special from all your efforts, some super-result, be happy with the smallest progress. But we shouldn’t stop there either. Even if you understand your child by individual words, this is not enough for communication with others and social adaptation. Move on, don't give up and don't indulge your child's laziness.
To reduce the likelihood of having a mentally retarded child, a pregnant woman should:
- DO NOT drink, smoke or take drugs;
- take folic acid;
- visit a doctor regularly;
- Eat a diet containing fruits and vegetables, whole grains, and foods low in saturated fat.
After the baby is born:
- carry out screening of the baby - this will identify diseases that can provoke mental retardation;
- visit your pediatrician regularly;
- do all scheduled vaccinations;
- allow him to ride a bicycle only with a helmet, and to ride in a car until the required age only in a car seat;
- Avoid contact of your child with household chemicals and lead-based paints.
Support by specialists
A child with an intellectual disability needs comprehensive support throughout childhood from the following specialists:
- child psychologist and psychiatrist;
- speech therapist;
- neurologist;
- speech pathologist.
If there are other disorders (blindness, deafness, cerebral palsy, autism spectrum disorder), then a rehabilitation specialist, an ophthalmologist, a massage therapist, and a physical therapy teacher are added to the above-mentioned professionals.
Corrective measures
The speech therapy program depends on the severity of systemic speech underdevelopment. Children with stage 1 SDD are given various exercises to activate independent thinking and speech activity. To this end, the speech therapist and parents must actively communicate with the child, stimulating the development of free speech and vocabulary. If such disorders occur in a child due to underdeveloped hearing, then he needs to buy a hearing aid. This allows him to actively learn speech structures and language grammar from conversations with adults and other children.
With systemic speech underdevelopment of moderate severity, speech activity and speech understanding are comprehensively developed. Separately, they work to improve the lexical and grammatical foundations of the language and expressive communication. Additional exercises to correct the pronunciation of sounds and their combinations are shown to each child.
Severe speech disorders require complex and long-term speech therapy assistance. Such children are educated in special schools for children with severe speech defects. In addition to exercises on phonetics, grammar and vocabulary, corrective classes are conducted to improve speech perception and develop minimal writing and reading skills.
Any speech disorders in children of preschool and school age should be eliminated with the help of a speech therapist. Independent attempts at treatment can lead to the progression of speech defects.
Levels of speech underdevelopment
The level of speech development depends on the severity of the disorders present.
In medicine, the following stages of manifestation of disorders are distinguished:
| Name | Description |
| I level | The child uses babbling words, onomatopoeia, gestures and facial expressions in conversation. |
| Level II | There are some rudiments of common speech. The child communicates primitively, his words are distorted. There are also elementary grammatical forms and constructions. |
| Level III | The child’s speech is developed, but there are elements of lexico-grammatical and phonetic-phonemic underdevelopment of speech. |
| IV level | All components of speech change slightly. |
At any level, speech underdevelopment will prevent a child from mastering new skills and gaining knowledge. Limited thinking will affect writing and meaningful communication with other people. A timely consultation with a specialist will help correct the situation.
Forecast
The speech correction and development program continues for several years. With its early onset against a background of mild SNR and preserved hearing, speech therapists are able to achieve complete normalization of speech function, writing and reading skills within 1-2 years. For children with severe articulation disorders due to mental retardation, the effectiveness of speech therapy is limited. They must study in specialized educational institutions, where the entire learning process is aimed at developing speech and related skills. In these cases, the symptoms of the disease cannot be completely eliminated.
Systemic speech underdevelopment is a serious disorder that occurs in children as a result of brain damage before the age of three. The disorder is characterized by incorrect pronunciation of sounds, low literacy and a poor vocabulary. An examination by a speech therapist allows you to assess the severity of the disorder and select corrective measures, including exercises for the development of speech, writing and reading. If there are concomitant changes in thinking or memory, children may also be prescribed medications that improve the condition of nervous tissue - nootropics, antioxidants, etc.
Features of childhood dementia
Preschool age only forms a personality, which is characterized by many factors: developmental characteristics, temperament, individuality.
Only after the child goes to school can parents identify a developmental disorder. Such children practically do not master the program. It is not possible to attract the attention of oligophrenics and fix it on something. Difficulties arise with memorization and retelling—children suffering from ID are unable to retain received information in memory for a long time.
A “special” student usually does not understand the essence of the task and does not grasp the connections between things and phenomena. It is very easy to intimidate him in such a situation: you just have to shout, and the psychological trauma that follows the stress is inevitable.
Depending on the environment, such a child can develop into two completely different personality types:
- kind and sympathetic, ready to help at any moment, vulnerable and warm-hearted;
- embittered and aggressive, who, having no desires and feelings of their own, are subject to the negative influence of others.
A practicing psychotherapist shared the story of a boy who was doomed to mental illness while still in utero development. A dysfunctional mother carried a child in violation of all acceptable rules: she smoked, drank alcoholic beverages, and took psychotropic drugs. After the birth of the child, he was deprived of proper attention.
After some time, the visiting nurse noticed some mental underdevelopment of the baby: he could not hold his head up on his own and did not make any sounds. Thanks to the prompt and coordinated work of medical workers, the boy was saved. And at the moment it has practically adapted to modern living conditions.
A predisposition to mental illness or unacceptable behavior of a pregnant woman is a reason to warn her about the possible dementia of the unborn child.
However, a loving and caring mother who leads a healthy lifestyle and has absolutely no prerequisites for the occurrence of mental pathologies can also face the problem of dementia in her child.
Having noticed the first alarm bells, which are a definite reason for consultation, you must immediately contact a qualified specialist. This will give you the opportunity to deeply adapt your baby to society before the moment of his socialization.
Diagnostics
Mental development disorders are difficult to detect at an early stage. However, such diagnosis is extremely necessary for early correction and compensation of the detected defect.
The diagnosis of “mental retardation” is made on the basis of special methods that allow assessing the intellectual level of an individual. Sometimes specialists use neuropsychological diagnostics, which allows us to determine the level of development of higher mental functions, as well as assess the child’s potential.
A correctly made diagnosis makes it possible to timely develop corrective methods to eliminate the pathology and treat it. In this case, the doctor must make sure that the little patient does not have signs of progression of underdevelopment or signs of more serious mental illnesses (schizophrenia, schizoaffective disorder, etc.).
It is also important to determine that the patient’s condition is not pedagogical neglect. This often happens to children who have lost their parents and were sent to an orphanage. There they can be subjected to harsh treatment, bullying, violence, etc. But if the child changes the situation for a better one - he is adopted, he lives and is raised in a normal family, then his condition returns to normal.