Examination of children with rhinolalia
If a child has a congenital cleft palate, then a systematic approach is used in the treatment of rhinolalia. In addition to a thorough study of the structure and operation of the articulatory apparatus, respiratory and vocal function, a speech therapy study of the state of sound pronunciation, phonemic perception, and the development of vocabulary and grammar is mandatory.
Stage 1 – instrumental methods
At the 1st stage, the examination is carried out by doctors who use special methods. Radiography
is necessary to establish the anatomical and physiological structure of the child’s speech apparatus, the mobility of the soft palate, the characteristics of the velopharyngeal closure, and the activity of the pharyngeal muscles.
The study of timbre and pitch of the voice reveals spectral analysis. The X-ray tomography
method studies the position of the speech organs, the degree of mouth opening, and the direction of tongue movements.
The spirometry
method provides data on respiratory function and lung capacity.
Using rhinoscopy,
the structure and growth in the nasal cavity are studied.
A phonendoscope
examines the presence of submycotic clefts (Gutsman test). Using syllable tables, speech intelligibility is studied (audit analysis method). Only after a medical examination is a diagnosis made: open, closed or mixed rhinolalia.
Stage 2 – psychological examination
The second stage is a psychological examination. Specialists examine the state of memory, attention, thinking, emotional-volitional sphere, communication skills, features of the child’s mental development, leading activities, level of sensory development, general and fine motor skills.
Doctor's reportAt the final stage, the verdict is made by a speech therapist, who must determine which components of speech have suffered due to the defect, what is the severity of speech disorders, what is primary and what is secondary. Speech therapy examination includes:
|
Schoolchildren are examined in reading and writing.
The speech therapist makes a conclusion: FN (phonetic disorder), FFN (phonetic-phonemic disorder), GSD (general speech underdevelopment).
Up
Staging sounds
Almost all sounds when diagnosed with rhinolalia sound approximate. And therefore, work on staging sound pronunciation can last a long time.
It is important to follow the sequence of sounds in rhinolalics. When correcting each sound, the child must learn to distinguish it from others.
With this diagnosis, vowels are the first to be processed. The first is processed by A, then E, O, U, I. The child must learn to pronounce sounds correctly and in isolation from other sounds. Next, he must gradually combine these sounds with each other. To do this you need to do the following exercises:
- The child should pronounce the vowel letter while exhaling.
- Next you need to complicate the task. It is necessary that the child repeat one vowel as many times as possible in one exhalation.
- Next, the child must pronounce the already mastered vowels, connecting them.
- The next level of difficulty: the child should try to pronounce vowels in different voice timbres. First low, like a bear, then high, like a bird.
After the work has been successfully done, the speech therapist moves on to the production of consonant sounds. Correction of consonant sounds in rhinolalia can be carried out from any sound or adhere to a certain pattern. Often the first sound for production is f. Next in line are various types of consonant sounds. Their order is determined by the speech therapist. It depends on the individual case. You shouldn't practice according to a certain pattern.
These exercises should be based on the principle of simple to complex and based on already learned sounds, so that it is not difficult for the child to practice. But any lesson should be preceded by a speech therapy examination of children with rhinolalia.
Singing can be considered a good workout.
Correction of open rhinolalia
The structure of correctional work depends on the form of rhinolalia. There are several original approaches to eliminating open rhinolalia, including the works of famous scientists G. Gutsman and M.Yu. Khvattseva. Correction of open rhinolalia is divided into two stages: preoperative and postoperative. A.G. Ippolitova was one of the first to offer classes with children in the preoperative period. Her method is based on the fact that the child’s attention is directed not to the phoneme, but to the article. Speech therapist N.I. Serebrova and doctor L.V. Dmitriev first developed an effective technique after studying radiography, based on the production of oral and nasal breathing. T.N. Vorontsova suggests development in the postoperative period, which boils down to singing sounds. Modern speech therapy is based on the step-by-step methodology of I.I. Ermakova in the preoperative and postoperative periods.
Preoperative period
The preoperative period begins with the birth of the child.
| Stage 1. Prevention of asthenic syndrome. Rhinolalic children are born weak, so from the first days of life it is important to work on hardening and stimulate physical development (swimming pool, bicycle, skiing). Sick children are delayed in crawling and walking, so it is necessary to stimulate motor activity - moving a toy away, etc. The use of walkers is not recommended, since the crawling stage is very important for speech development. |
| Stage 2. Correcting and preventing incorrect tongue fixation . Avoid placing the child on his back so that the root of the tongue does not move posteriorly. It is preferable to lay on your stomach or side. From birth, encourage the baby to do some tongue exercises to imitate an adult: “Delicious jam” (lick the upper lip), “Swing” (raise the tip of the tongue up and down), “Clock” (swing the tongue from side to side), “Snake” (stretch your tongue back and forth), “Turkey” (quickly run your tongue along your upper lip). |
| Stage 3. Prevention of breathing problems. From 1.5-2 years old, play exercises are carried out: “steep the tea” (hold your lip at the level of the cup), blow into a straw, “smell a flower” - small cups from Kinder Surprise are filled with flower petals, inhale through the nose. You can play the harmonica, blow fluff from your palm, blow up balloons (without tension), soap bubbles, play with an airball, helping to pinch your nose. |
| Stage 4 . |
| Stage 5 . |
| Stage 6 . |
| Stage 7 . |
| Stage 8 . |
| Stage 9 . |
| Stage 10 . |
| Stage 11 . |
| Stage 12 . |
| Stage 13 . |
Up
Postoperative period
1 step.
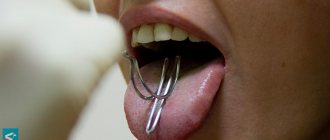
It begins with the stage of setting vowel sounds and eliminating excessive nasal resonance. If the child received speech therapy before surgery, this period is short (2-3 weeks). If no assistance was provided, the period is delayed by 3-6 months. During this period, the velum palate can be stretched to its maximum, so it is important not to miss the moment. After surgery, a long period of silence is inevitable, so speech deteriorates. The soft palate is swollen, the child feels pain, avoids correct articulation of sounds, and speaks through the nose. It is necessary to include the operated palate into phonation as quickly as possible, this facilitates the acquisition of the skill of oral vowel resonance. The operated organ for the child receives its intended purpose. Speech therapy work must be started on the second day after obturation or 15-20 days after uranoplasty. In six months, when the scarring process is over, the work will be meaningless.
With special exercises and massage, you can stretch the edge of the soft palate by 1-3 cm. Massage is carried out with a probe, spatula or pacifier. Carefully move the instrument back and forth along the hard palate, without touching the seams, while the muscles of the pharynx and soft palate reflexively contract. When pronouncing the sound “A”, apply light pressure on the soft palate with a probe or finger (activation of the gag reflex). The child does self-massage and strokes the stitches with his tongue. Massage is performed at least 2 times a day for a year, two hours before or after meals. Gymnastics for the palate are also performed: swallowing in small portions, coughing with the tongue hanging out, yawning with the mouth closed and open. Articulatory gymnastics includes stretching the lips (“Smile” - “Tube” in dynamics), additionally – vibration of the lips (coachman’s “tpprrrr”, stop the “horse”), for the cheeks – drawing the cheeks into the oral cavity. Voice exercises in the same order, starting with the vowels “A”, “E”. At the same stage, work on breathing is carried out. Inhale-exhale through the nose, inhale-exhale through the mouth, inhale through the nose, exhale through the mouth.
Step 2
– stage of sound pronunciation correction. We start with vowel sounds. The order of consonants is as follows: first “P”, “F”, then “Py”, “F”, “V-V”, “T-T”, “K-K”, “X-H”, “S-” Sj”, “G-G”, “L-L”, “B-B”, “D-D”, “Z-Z”, “Sh”, “R-R”, the last ones – “Zh”, “ Shch", "Ch", "C". At the same time, they develop the prosodic side of speech.
Step 3
– automation of new skills. Features of the work depend on the age of the child. At the same time, they develop the lexical and grammatical structure of speech. The work with breathing does not stop, they use airballs, blowing on a basin of water, on sand, on a toy. Classes are conducted in a playful way, sounds are reinforced in short rhymes.
Up
Exercises to increase the mobility of the soft palate and velum
There are also exercises to train the mobility of the muscles of the soft palate. To develop this part of the child’s body, it is necessary to use exercises such as imitation of gargling, imitation of coughing, yawning, and swallowing small drops of any liquid. This could be juice, water, cool tea, etc.
For the last exercise, you need to use a pipette, and it is better to have a doctor do it. You need to place a small drop on the root of your tongue. The child must try to swallow this very drop.
Children over 3-4 years old can do the first exercises, namely, rinsing with and without sound helps the development of the muscles of the soft palate. While rinsing, the child should pull Y, but not push the lower jaw back, you should also throw back your head.
Also, the child may try to yawn first with his mouth open and then with his mouth closed.
Exercises to develop phonemic awareness
In order to train with such exercises, the child must know all the instruments that he is asked to guess. And the first exercise: “Who’s here?” — The child must close his eyes and recognize the musical melody being produced by ear.
The second exercise - the speech therapist asks the child to repeat after him the stresses in words. First, he puts stress in words only on the first syllable, then only on the second, and so on.
The third exercise is for the teacher to deliberately pronounce a sentence with an obvious error, and the child must name this error.
In this situation, exercises are also selected individually. It is worth noting that breathing exercises for rhinolalia should not be performed simultaneously in one session.
Conclusion
In order to undergo a rehabilitation course for children with rhinoplasty, a sufficient amount of time is needed. Parents should be patient. It is necessary to choose a well-qualified speech therapist and you cannot self-medicate in this case; all actions must be coordinated with the doctor.
Related posts:
- What is "War and Peace" about? Summary of the novel “War and Peace” by chapters. All answers...
- Logorhythmic classes and correctional means By various means, speech therapy classes contribute to the effective correction of speech in children...
- Forms of rhinolalia Forms of rhinolalia differ both in the causes of occurrence and in ...
- What do we know about rhinolalia? Rhinolalia in children is diagnosed quite simply. Also her methods...