The NeuroSpectrum Center for Children's Speech Neurology and Rehabilitation has developed a method of helping children with speech, behavior, and intellectual disorders. It is based on identifying the causes that caused the problem and correcting them. For each child, an individual rehabilitation program is drawn up, which takes into account the characteristics of his nervous system. It consists of neurophysiological, pedagogical and hardware components. Therefore, if parents doubt their abilities in the fight against dysarthria, it is better to contact a qualified specialist. At the Center, an experienced speech therapist will perform the necessary procedure in a playful way to engage the child in the process as much as possible.
Treatment with speech therapy massage
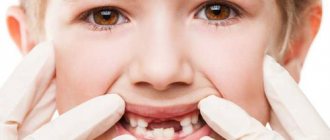
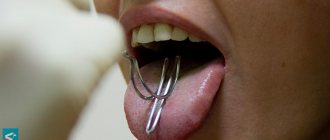
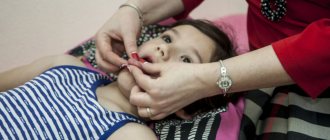
Speech therapy massage for a child with dysarthria is the most effective method of correcting developmental disorders of the speech apparatus, which can be carried out both by an experienced specialist at our Center and by parents at home. The priority is the child's peace and comfort during the procedure.
The first session lasts 5 minutes, gradually its duration increases. In some cases, the lesson can last up to half an hour. Parents are recommended to carry out the procedure independently, following the advice of a speech therapist. You can do a finger massage or use a toothbrush.
The advantage in this case is the possibility of carrying out the procedure at the most convenient time, when the child is full, in a good mood, and ready to interact. This ensures continuity of treatment, which directly affects its effectiveness.
Elena Arkhipova – Speech therapy massage for dysarthria
Elena Filippovna Arkhipova
Speech therapy massage for dysarthria
Introduction
Massage is a method of treatment and prevention, which is a set of techniques of mechanical influence on various areas of the surface of the human body. The mechanical effect changes the condition of the muscles, creates positive kinesthesia necessary for normalizing the pronunciation aspect of speech.
In a comprehensive system of corrective measures, speech therapy massage precedes articulation, breathing and voice exercises.
Massage in speech therapy practice is used to correct various disorders: dysarthria, rhinolalia, aphasia, stuttering, alalia. The correct selection of massage complexes helps to normalize the muscle tone of the organs of articulation, improves their motor skills, which contributes to the correction of the pronunciation side of speech.
The theoretical justification for the need for speech therapy massage in complex correctional work is found in the works of O.V. Pravdina, K.A. Semenova, E.M. Mastyukova, M.B. Eidinova.
In recent years, publications have appeared devoted to the description of speech therapy massage techniques, but the techniques have not yet been sufficiently introduced into speech therapy practice. At the same time, the advisability of speech therapy massage is recognized by all specialists who deal with such severe speech disorders as dysarthria, rhinolalia, stuttering, etc.
Speech therapy massage techniques are differentiated depending on the pathological symptoms in the muscular system for speech disorders.
The goal of speech therapy massage in eliminating dysarthria is to eliminate pathological symptoms in the peripheral part of the speech apparatus. The main objectives of speech therapy massage when correcting the pronunciation side of speech with dysarthria are:
– normalization of muscle tone, overcoming hypohypertonicity in facial and articulatory muscles;
– elimination of pathological symptoms such as hyperkinesis, synkinesis, deviation, etc.;
– stimulation of positive kinesthesia;
– improving the quality of articulatory movements (accuracy, volume, switchability, etc.);
– increase in the strength of muscle contractions;
– activation of subtle differentiated movements of the organs of articulation necessary for correcting sound pronunciation.
This manual presents the author's position on speech therapy massage. We consider speech therapy differentiated massage as a structural part of an individual speech therapy session conducted with a child with dysarthria. Speech therapy massage precedes articulation gymnastics.
The manual presents three sets of differentiated speech therapy massage, each of which offers exercises aimed at overcoming pathological symptoms.
I. a set of speech therapy massage exercises for rigid syndrome (high tone).
II. a set of speech therapy massage exercises for spastic-atactic-hyperkinetic syndrome (against the background of high tone, hyperkinesis, dystonia, and ataxia appear).
III. a set of speech therapy massage exercises for paretic syndrome (low tone).
The structure of an individual lesson includes 3 blocks.
I block, preparatory. It includes the following areas:
? Normalization of muscle tone of the organs of articulation. For this purpose, differentiated speech therapy massage is carried out, which revitalizes kinesthesia and creates positive kinesthesia.
? Normalization of motor skills of the organs of articulation and improvement of the qualities of the articulatory movements themselves (accuracy, rhythm, amplitude, switchability, strength of muscle contraction, subtle differentiated movements). For this purpose, we recommend performing articulatory gymnastics with functional load. Such articulatory gymnastics, based on new, precise kinesthesia, will help improve articulatory motor skills by creating strong proprioceptive sensations. This takes into account the principle of reverse afferentation (feedback), developed by P.K. Anokhin.
? Normalization of voice and voice modulations; for this purpose, voice gymnastics is recommended.
? Normalization of speech breathing. A strong, long, economical exhalation is formed. For this purpose, breathing exercises are performed.
? Normalization of prosody, i.e. intonation-expressive means and qualities of speech (tempo, timbre, intonation, voice modulation in pitch and strength, logical stress, pausing, speech breathing, etc.). To this end, in subgroup classes, students are first introduced to the emotional and expressive means of speech and develop auditory attention. They learn to differentiate the intonation and expressive qualities of speech by ear. In individual lessons, they achieve reflected reproduction of accessible emotional and expressive qualities of speech (tempo, voice modulation in pitch and strength, logical stress, intonation, etc.)
? Development of fine differentiated movements in the fingers. For this purpose, finger gymnastics is performed. In the works of Bernstein N., Koltsova M.M. indicates a direct relationship and correlation between the motor functions of the hands and the qualities of the pronunciation side of speech, since the same areas of the brain innervate the muscles of the organs of articulation and the muscles of the fingers.
II block, main. It includes the following areas:
? Determining the sequence of work on sounds (depends on the preparedness of certain articulation patterns).
? Practicing and automating the basic articulation patterns for sounds that need clarification or correction.
? Development of phonemic hearing. Auditory differentiation of phonemes in need of correction.
? Sound production using traditional methods in speech therapy.
? Automation of sound in syllables of different structures, in words of different syllabic structure and sound content, in sentences.
? Differentiation of delivered sounds with oppositional phonemes in syllables and words to prevent confusion of sounds in speech and dysgraphic errors at school age.
? Practicing words with a complex sound-syllable structure.
? Training of correct pronunciation skills in various speech situations with adequate prosodic design, using a variety of lexical and grammatical material.
III block, homework.
Includes material for consolidating knowledge, skills and abilities acquired in individual lessons. In addition, tasks from the psychological and pedagogical aspect of correctional influence are planned:
– development of stereogenesis (i.e. the ability to identify objects by touch without visual control by shape, size, texture);
– development of constructive praxis;
– formation of spatial representations;
– formation of graphomotor skills, etc.
Taking into account this organization and content of individual speech therapy classes in preschool educational institutions for children with severe speech impairment (SSD) or speech centers at preschool educational institutions and secondary schools, we propose to allocate 3–5 minutes for speech therapy massage. Depending on the age of the children and the type of institution where speech therapy work is carried out, the time allocated for individual lessons also changes. So with infants and young children, the duration of individual lessons is 20 minutes.
For preschool children, an individual speech therapy session lasts 15 minutes.
With school-age children – 20 minutes.
For teenagers and adults, individual speech therapy sessions on correcting the pronunciation aspect of speech with dysarthria are carried out for 30–45 minutes. Taking into account the regulations of individual classes, we propose to conduct speech therapy massage not in cycles (sessions), as many authors suggest, but to begin an individual lesson with a differentiated speech therapy massage. Individual speech therapy massage techniques (exercises) are selected taking into account the identified pathological symptoms. Adequate massage techniques create positive kinesthesia, which will help improve articulatory motor skills, as they will prepare the basis for better articulatory movements: accuracy, rhythm, switchability, amplitude, subtle differentiated movements and others. Thus, the goal of speech therapy massage, carried out at the beginning of an individual lesson before articulatory gymnastics, is to create and consolidate strong, positive kinesthesia, which creates the prerequisites (according to feedback laws) for improving articulatory motor skills in children with dysarthria.
The manual consists of 3 chapters. Chapter I discusses the structure of a speech defect in erased dysarthria, describing the pathological symptoms that determine the violation of sound pronunciation and prosody.
Contraindications to the appointment of logomassage
In addition to the patient’s well-being, it is necessary to take into account a number of factors, the presence of which significantly reduces the effectiveness of the procedure:
- respiratory diseases or viral infections;
- fungal infections of the skin;
- inflammation of the eyes or mouth;
- open wounds.
If there are circumstances that prevent a comfortable course of logomassage for children with dysarthria, it should be postponed or other treatment methods should be used. Also, from the age of 3 years, a complex of speech therapy massage for dysarthria may include kneading the muscles of the speech apparatus using a probe. This technique cannot be performed at home.
The center's methodology is based on a deep understanding of the physiology of the nervous system of children. Parents are required to provide support and exercise with their child at home. From the child himself - involvement and interest in classes, which will be ensured by experienced teachers.
The complex effect of sound pronunciation correction and speech therapy massage . Erased dysarthria as the main obstacle to normal speech. A consistent plan for working with speech therapy massage .
In recent years, the number of children with speech pathology, which is based on a violation of the innervation of the articulation organs, has sharply increased. In this regard, this problem is indisputable and is relevant today.
Currently, there are many publications devoted to the description of speech therapy massage , but they have not been sufficiently introduced speech therapy
Speech therapy work to eliminate violations of sound pronunciation is very labor-intensive , has a specific plan and is complex in nature , requiring comprehensive sessions with a speech therapist . One of the means of corrective action is speech therapy massage . Its purpose is not only to strengthen or relax articulatory muscles, but also to stimulate proprioceptive sensations, which contributes to the clarity of kinesthetic perception.
One of the most common speech defects in preschool is speech disorders in the erased form of dysarthria. Overcoming these disorders is one of the most pressing tasks of modern speech therapy science .
The term “erased” dysarthria was first proposed by O. A. Tokareva. She characterized its manifestations as mild manifestations of “pseudobulbar dysarthria.” In her opinion, in such cases, most isolated sounds are pronounced correctly , but in the speech stream they are poorly automated and differentiated. She draws attention to the unique nature of articulatory movement disorders, when, in the absence of
restrictions in the movements of the tongue and lips; inaccuracy of movements and lack of strength are observed [3].
Violations of the sound-pronunciation aspect of speech in such children are expressed in distortions, confusion, substitutions, and omissions of sounds . In this case, a characteristic feature is the simplification of articulation, when complex sounds are replaced by simpler ones in their articulatory-acoustic characteristics: fricative - plosive, voiced - voiceless, hissing - whistling, hard - soft, affricates are split into their constituent sound elements .
The ideas of O. V. Pravdina, E. V. Arkhipova speak of the need for speech therapy massage in correctional work [2 , 1]. Massage is a method of treatment and prevention, which is a set of techniques of mechanical influence on various areas of the surface of the human body. The mechanical effect changes the condition of the muscles, creates positive kinesthesia necessary for normalizing the pronunciation aspect of speech. In a comprehensive system of corrective measures, speech therapy massage precedes articulation, breathing and voice exercises. Massage in speech therapy practice is more often used in the correction of various disorders : dysarthria, rhinolalia, aphasia, stuttering, alalia. According to M.E. Khvattsev, “ massage of the articulatory apparatus and articulatory exercises not only improve the motor function of lagging brain systems, but also involve nearby brain systems in the work” [4].
The close relationship between the development of speech, sensory functions, motor skills and intelligence determines the need for correction of speech disorders in children in combination with stimulation of the development of all its aspects, sensory and mental functions, thereby realizing the formation of speech as an integral mental activity. The specificity of the work is a combination with differentiated articulation massage and gymnastics ,
speech therapy rhythm , and in some cases with general physical therapy, physiotherapy and drug treatment.
In this way, a long-term work plan can be drawn up.
1. Massage of facial and articulatory muscles, neck muscles. The goal is to activate muscles with flaccid paresis (paralysis, or relax muscles with spasticity.
2. Work on speech motor skills includes passive gymnastics (to activate the movements of the lips and tongue); active gymnastics (to activate the movements of the lips, tongue, soft palate, form voluntary breathing, increase the intensity and duration of exhalation.
3. Work on your voice.
4. Work on the prosodic coloring of speech.
5. Correction of the phonetic-phonemic aspect of speech.
6. Work on the lexical and grammatical side of speech.
Thus, we can say that in speech therapy practice , speech therapy massage is one of the most popular methods of working with children about correcting sound pronunciation . The correct selection of massage complexes helps to normalize the muscle tone of the organs of articulation, improves their motor skills, which contributes to the correction of the pronunciation side of speech.
Bibliography.
1. Arkhipova E. F. Correctional and speech therapy work to overcome erased dysarthria in children / E. F. Arkhipova. - M.: Astrel, 2008. - 257 p.
2. Pravdina O.V. Speech therapy . / Textbook manual for defectologist students. fact-tov ped. Inst. Ed. 2nd, add. and processed —— M.: Education, 1973. — 272 p.
3. Tokareva O. A. Dysarthria (speech disorder in children and adolescents). Ed. S. S. Lyapidevsky. - M.: Medicine, 1969. - P. 144.
4. Filicheva, T. B. Elimination of general speech underdevelopment in preschool children [Text] : practical work. Manual / T. B. Filicheva, G. V. Chirkina. — 4th ed. – M.: Iris Press, 2007.- 224 p. \Khvattsev M.E. Speech therapy . Book 1 - M.: Vlados, 2009. - 272 p.