Classification of speech disorders. Causes of speech disorders.
Based on materials from speech therapy literature, it was prepared by speech therapist V.N. Rychkova.
A child, when born, does not have an innate knowledge of the laws of the language he will speak. At a certain period of his development, he learns the norms and rules of the language spoken by the people around him. If for some reason language-speech-mental activity is not formed on time, then in the future this leads to disturbances in the child’s speech to one degree or another.
Classification of speech disorders
Psychological and pedagogical classification of speech disorders:
*Phonetic speech disorder or disorder of the pronunciation of individual sounds (NPOS). In this type, the phonetic side of speech (sound pronunciation, sound-syllabic structure of a word, prosody) as a whole or any individual components of the phonetic structure of speech (for example, only sound pronunciation or sound pronunciation and sound-syllabic structure of a word) are impaired.
*Phonological speech disorder (PSI ). This is the underdevelopment of phonemic processes (sound discrimination): phonemic perception, sound analysis and synthesis with normal sound pronunciation and the absence of agrammatisms.
*Phonetic-phonemic speech disorder (FFSD).
With FFND, along with a violation of the phonetic aspect of speech, there is also an underdevelopment of phonemic processes: phonemic perception (auditory differentiation of sounds), phonemic analysis and synthesis, phonemic representations.
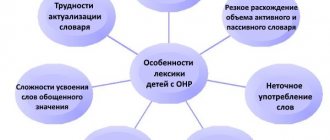
*Lexico-grammatical speech underdevelopment (LGSD). With LGNR, children have normal sound pronunciation, phonemic processes are relatively preserved (most often as a result of speech therapy), but there is a limited vocabulary and a violation of the grammatical structure of speech (agrammatism).
*General speech underdevelopment (GSD I , II and III ). With OHP in children, all components of the language (speech) system are impaired: the phonetic-phonemic side of speech (sound pronunciation and sound discrimination), vocabulary (limited vocabulary), grammatical structure.
Clinical and pedagogical classification —
reveals the mechanisms, forms and types of speech disorders. The following forms of speech disorders are taken into account: dyslalia, dysarthria or an erased form of dysarthria, rhinolalia, voice disorders; motor and sensory alalia; aphasia, delayed speech development (SDD), stuttering and others.
* Dislali I - a violation of sound pronunciation with normal hearing and intact innervation of the speech apparatus.
*Dysarthria is a disorder of the pronunciation aspect of speech caused by insufficient innervation of the speech apparatus (damage to the speech motor mechanisms of the central nervous system).
*Alalia (motor and sensory) – absence or underdevelopment of speech due to organic damage to the speech areas of the cerebral cortex in the prenatal or early period of a child’s development.
*Aphasia is a complete or partial loss of speech caused by local brain lesions.
*Speech development delay (SDD) is a slower than normal acquisition of the native language (sound pronunciation, vocabulary, grammatical structure) .
Causes of speech disorders.
Adverse internal factors affecting the brain during the period of its intensive development lead to a delay in the development of the child as a whole. These include: intrauterine pathology (intoxication, infectious diseases of the mother, toxicosis of pregnancy); injuries during childbirth (birth injuries, asphyxia, intracranial hemorrhage); hereditary factors (chromosomal disorders and genetic changes); compatibility of mother and fetus (Rh factor).
They lead to minimal organic brain damage in the infant, which is characterized by lack of attention, weakened memory, lag in motor development, disinhibition and, as a consequence, lag in speech development.
The use of alcohol, nicotine and drugs during pregnancy is especially harmful. This leads to disturbances in the physical and neuropsychic development of the fetus. Women who smoke, drink and use drugs give birth to children with low body weight and lagging behind in physical and mental development.
Unfavorable external factors : lack of an emotionally positive environment; individual characteristics of the mother (suspiciousness, anxiety, emotional coldness), insufficient attention to the child from adults, or, conversely, overprotection; raising a child in two houses, when the child alternately lives with divorced parents.
What is severe NRSH?
What is severe NRSH?
At 4-5 years old:
the child does not speak;
the child speaks only simple words (mom, dad, grandma);
The child has a phrase of 2 words with errors (“My ma”);.
NRSH is a systemic underdevelopment of speech in children with visual impairment, a complex disorder. There are 3 levels of NRSH. If a speech therapist says that your child has severe NRSH, this means that the child does not speak or barely speaks. Severe NSRS is the most severe level, but I would like to reassure parents a little. NDRS is not a medical diagnosis. He says that the child should be given a lot of work: a speech therapist or a speech therapist + a speech pathologist and parents at home and monitored by a neurologist
.
How can you tell if your child has severe NRSH?
If, according to the norms, a child should already begin to speak words or phrases, but they are not yet there, there is a neurological diagnosis, then I advise you to go for a consultation with a speech therapist, ask the neurologist to give a referral to a day hospital 5 DKB.
So, if a child at 2-3 years old does not speak in phrases, cannot say a whole word, or speaks only in onomatopoeia (av-av, mu-mu), then in this case the speech therapist will diagnose SRD (delayed speech development). You need to start studying with such children; you can also activate your speech on your own. But at 4-5 years old, a child with a simple phrase like “Ma, give me” will already be diagnosed with severe NRSH.
What to do next?
First, contact a speech therapist who works with toddlers or silent children. The speech therapist should conduct an examination and assume that what is wrong with the child (alalia, dyspraxia, speech auditory agnosia, dysarthria, anarthria - this is all the competence of a neurologist
, but the speech therapist can guess based on the examination).
Secondly, prepare for a long correction. That is, in a year the child most likely will not catch up with his 5-year-old peers.
Thirdly, you need to work with the child every day according to the recommendations of the speech therapist. The parent must be immersed in corrective work. Experts often recommend attending additional classes, for example, exercise therapy, dancing. You need to try to do everything.
You need to follow all the recommendations of the speech therapist, try to work with the child yourself. The main thing is not to turn a blind eye to the problem and think that it will go away on its own. Most likely it won't work. Unfortunately, children with severe NRSH cannot study in a comprehensive school.
How to get speech therapy help?
At the age of 3, all children must undergo an examination by a speech therapist in a clinic or sign up for a consultation with a speech therapist in a compensatory kindergarten. If a speech therapist diagnoses RRR, and the child has a neurological conclusion of PPCPNS, REP,.....: you can ask the neurologist for a referral to a neurologist at 5th Children's Clinical Hospital and undergo a comprehensive examination and treatment.
Speech therapy. Proficiency Test with Answers (2021) - Option 7
content .. 5 6 7 8 ..Question No. 1
If instead of the word “tomato” a child pronounces “bamidor”, this may indicate that he has 1) a softening defect 2) a voicing defect 3) a stunning defect (+)
4) there is no correct answer
Question No. 2
If a child pronounces “pulka” instead of the word “bun”, this may indicate that he has: 1) a defect in voicing; (+)
2) softening defect;
3) stunning defect; 4) there is no correct answer. Question No. 3
Carrying out work on differentiating sounds in pronunciation is not necessary for: 1) pararotacisms; 2) rotacisms; (+)
3) pararotacisms;
4) parasigmatisms. Question No. 4
Speech-auditory memory is impaired in the following type of aphasia: 1) afferent-motor; 2) acoustic-mnestic; (+)
3) acoustic-gnostic;
4) the same for all types of aphasia. Question No. 5
Violation of sound pronunciation with normal hearing and intact innervation of the speech apparatus is... a) rhinolalia b) alalia c) dyslalia (+)
Question No. 6
Child S. has a written speech disorder. Which of the mistakes made by the child when completing written assignments from the teacher indicate the presence of dysgraphia based on a violation of the processes of language analysis - synthesis? 1) replacement of letters 2) underwriting of elements (+)
3) omission of letters and syllables 4) spelling errors
Question No. 7
What is the unit of the phonological code of a language: -phoneme (+)
Question No. 8
The structure of a speech defect is understood as: a) a set of signs (manifestations) of a speech disorder; b) a set (composition) of speech and non-speech symptoms of a given speech disorder and the nature of their connections (+)
c) the nature of deviations in the functioning of processes and operations that determine the occurrence and development of speech disorders.
Question No. 9
A speech therapist teacher needs to create a task in the form of a sentence for a five-year-old child. Purpose of the task: the child reproduces the sentence. Which option matches the goal? 1) A plumber is fixing a water pipe 2) A policeman rides a motorcycle 3) The boys have built a snowman (+)
4) Hair is cut in a hairdresser
Question No. 10
What disorder causes paralysis or paresis of the speech muscles: 1) dyslalia; 2) dysarthria; (+)
3) stuttering.
Question No. 11
What sound attack is used when working on voice delivery with people who stutter: 1) hard, 2) aspirated, (+)
3) soft.
Question No. 12
Which of the researchers proposed to establish the levels of development of active speech (zero, situational, nominative, predicative, dissected)? 1) R.E. Levin 2) N.S. Zhukova (+)
3) G.V. Chirkina 4) T.B. Filicheva
Question No. 13
The features of the speech activity of students with moderate and severe mental retardation are (one correct answer): 1. lack of planned speech in preschool age, poor vocabulary, sentences in oral speech are often constructed incorrectly and are not complete; written language contains many specific errors; 2. speech with a poorly developed regulatory function, absence of adjectives and adverbs in speech, in most situations “the child’s speech is idling” (M.S. Pevzner); (+)
3. delayed mastery of the grammatical structure of speech, pronunciation defects, limited active vocabulary, difficulties in mastering written language;
4. pathologically slow rate of speech and rate of reading, inability to briefly retell the text, come up with a title for the story Question No. 14
What is the leading form of activity in preschool age? a) objective-action b) game (+)
c) emotionally positive communication with an adult
Question No. 15
What is meant by exogenous-organic causes of speech disorders? 1) incorrect speech of others; 2) bilingualism in the family; 3) traumatic brain injury.
(+)
Question No. 16
What is the unit of the phonological code of a language: 1) word; 2) phoneme; (+)
3) morpheme.
Question No. 17
A four-year-old child is in a lesson with a speech therapist. What word should the teacher choose to reproduce the sound-syllable structure for the child? 1) cabbage (+)
2) tomatoes 3) frying pan 4) medicine
Question No. 18
What does the child’s transition from physiological tongue-tiedness to dyslalia based on the type of distortions in the pronunciation of speech sounds indicate: 1) a lag in the formation of phonemic hearing; 2) about progress in the formation of phonemic hearing; (+)
3) about the primary inferiority of the organs of articulation.
Question No. 19
Disorders of the structural and semantic design of statements include: 1) alalia; (+)
2) rhinolalia;
3) dyslalia; 4) all answers are correct. Question No. 20
Restorative training is. a) a two-way controlled process, including the active cognitive activity of children in acquiring knowledge, skills and abilities and pedagogical guidance of this activity b) a process in which correction and compensation of the personal characteristics of persons with speech impairments are carried out (+)
c) a process that is aimed at restoring impaired speech and non-speech functions
Question No. 21
What is the cause of motor and oculomotor dysgraphia and dyslexia: 1) impaired phonemic hearing; 2) phonetic hearing impairment; 3) violation of hand, finger praxis or oculomotor functions
.
(+) Question No. 22
The inability to perform certain articulatory movements or switch from one movement to another with dysarthria is called 1) agnosia 2) amusia 3) apraxia (+)
4) ataxia
Question No. 23
If the structure of the organs of the articulatory apparatus is disturbed, a violation of sound pronunciation most often manifests itself in the form of 1) omission 2) replacement 3) confusion 4) distortion
(+)
Question No. 24
This type of dysarthria occurs when the subcortical nuclei are damaged 1) extrapyramidal (+)
2) pseudobulbar 3) bulbar 4) cortical
Question No. 25
Speech therapy is. a) the science of the psychophysical characteristics of the development of children with mental and (or) physical disabilities, the patterns of their education and upbringing b) the science of speech disorders, methods of their prevention, identification and elimination by means of special education and upbringing. Speech therapy studies the causes, mechanisms, symptoms, course, structure of speech disorders, and the system of correctional interventions. (+)
c) a branch of defectology that studies the problems of education and training of mentally retarded people and issues of their social rehabilitation.
Question No. 26
The subject of speech therapy as a science is: a) speech disorders and the process of training and education of persons with speech disorders (+)
b) a person (an individual suffering from a speech disorder; c) a pathological mechanism that determines the occurrence and development of speech disorders.
Question No. 27
One of the characteristics of general underdevelopment of speech of the third level (GSD-III level) according to R.E. Levina is (choose the correct answer option 1): 1. active vocabulary in a “rudimentary” state, consists mainly of sound pronunciations and babbling words ; 2. relatively detailed speech, the active vocabulary is dominated by nouns and verbs; (+)
3. enrichment of speech through the use of certain forms of inflection;
4. passive dictionary, no active understanding of speech Question No. 28
therapist teacher needs to select a specific task for a six-year-old child in order to study the state of phonemic analysis and synthesis. Which of the tasks corresponds to the goal? 1) task with highlighting a given sound from words (against the background of words) 2) task with highlighting the stressed vowel at the beginning of a word 3) task with highlighting the first consonant in a word 4) task with determining the sequence of sounds in a word
(+)
Question No. 29
The correct spelling of which sentence requires the assimilation and implementation of the phonetic principle of Russian spelling: 1) Here is my house. 2) Here is my parachute. 3) Here is my dog.
(+)
Question No. 30
Practical methods of speech therapy include: 1) games, exercises, modeling; (+)
2) observation, looking at drawings;
3) story, conversation, reading; 4) all answers are correct. Question No. 31
Speech disorders in students and pupils are characterized by the following features (exclude the incorrect answer option 1): 1. are stable and do not disappear on their own; 2. do not correspond to the age of the student or pupil; 3. are not dialecticisms, illiteracy of speech and a consequence of ignorance of the language; 4. are not associated with deviations in the functioning of the psychophysiological mechanisms of speech of the student or pupil
.
(+) Question No. 32
Check which of the listed symptoms of stuttering does not relate to psychopathological symptoms: 1) convulsions; 2) obsessive states; 3) asthenic syndrome.
(+)
Question No. 33
Erroneous reproduction of words, which consists in combining syllables belonging to different words into one word, is called: 1) perseveration; 2) anticipation; 3) contamination; (+)
4) accommodation.
Question No. 34
How many forms of speech disorders are identified in speech therapy (clinical and pedagogical classification? a) 9 6) 10 c) 11 (+)
Question No. 35
Which of the following tasks cannot be used to assess understanding of the meaning of what was read: 1) detailed retelling, 2) answering questions about what was read; 3) a brief retelling, 4) drawing up a plan for the text read.
(+)
Question No. 36
Continue the statement: “FFNR is...” 1) violation of the pronunciation aspect of speech; (+)
2) unformed lexical and grammatical categories;
3) violation of the syllabic structure of the word. Question No. 37
A change in the shade of voice timbre caused by a violation of the relationship between the nasal cavity and the oropharyngeal resonator during phonation is 1) aphonia 2) rhinophonia (+)
3) dysphonia 4) phonasthenia
Question No. 38
Which of the following areas is the most important in the initial stages of working with non-speaking children with motor disabilities according to the language approach: a) enrichment and activation of subject vocabulary; (+)
b) formation and development of articulatory motor skills;
c) development of auditory perception; d) enrichment and activation of the predicative vocabulary. Question No. 39
Determine the sequence of types of work to develop phonemic analysis: A. Determine the number of sounds in a word; B. Determine whether a given sound is in a word; B. Come up with a word with 4 sounds; D. Determine the place of the sound in the word (beginning, middle, end). 1) GBAV; 2) BGAV; 3) BAGV.
(+)
Question No. 40
What is not included in the main tasks of the preparatory stage for the formation of correct sound pronunciation a) development of auditory attention, auditory memory and phonemic perception b) elimination of insufficient development of speech motor skills, conducting preparatory speech exercises for the development of mobility of the organs of the peripheral speech apparatus c) elimination of incorrect sound pronunciation
(+)
Question No. 41
In which structural and functional block of the brain is the kinesthetic analysis of articulatory movements carried out: 1) Block I; 2) II block; (+)
3) III block.
Question No. 42
Which speech disorder primarily affects the fluency and rhythm of speech: 1) alalia; 2) stuttering; (+)
3) dyslalia.
Question No. 43
Clinical and pedagogical classification of speech disorders is based: 1) on a set of psychological and linguistic criteria; 2) on a set of psychological, linguistic and clinical criteria; (+)
3) on psychological criteria;
4) on linguistic criteria. Question No. 44
In accordance with the order of the Ministry of Education and Science dated December 24, 2010. No. 2075 “On the duration of working hours (standard hours of teaching work for the wage rate) of teaching staff” - the weekly workload of a speech therapist teacher in educational institutions is: (choose the correct answer) 1) a speech therapist teacher has an irregular work week 2) 20 hours per week week (+)
3) 24 hours a week 4) 36 hours a week
Question No. 45
This speech disorder is caused by anatomical and physiological defects of the speech apparatus: 1) dyslalia; 2) rhinolalia; (+)
3) stuttering;
4) alalia. Question No. 46
What type of dyslexia is caused by underdevelopment of the grammatical structure of speech, morphological and syntactic generalizations? 1) agrammatic dyslexia (+)
2) mnestic dyslexia 3) optical dyslexia 4) semantic dyslexia
Question No. 47
Bradylalia is. a) pathologically slow speech rate (+)
b) pathologically accelerated rate of speech c) a violation of the dark-rhythmic organization of speech caused by the convulsive state of the muscles of the speech apparatus
Question No. 48
Which speech disorder does not belong to the disorders of the means of communication identified within the framework of the psychological and pedagogical classification? 1) OHP, 2) stuttering, (+) 3) FFN,
Question No. 49
The semantic level of speech activity is: (choose the correct answer) 1) the ability to formulate speech in acts of articulate articulation (syntagmas) (+)
2) the ability to use familiar words 3) the ability to distinguish speech signals by ear 4) the ability to write a dictation without errors
Question No. 50
Working on speech with motor alalia involves (exclude unnecessary things) 1) normalization of breathing and voice formation; (+)
2) impact on the entire speech system;
3) the use of sign-symbolic activity; 4) use of subject-based practical activities. Question No. 51
Speech disorders are characterized by the following features: (exclude the wrong answer) a) They correspond to the age of the speaker (+)
b) Associated with deviations in the functioning of the psychophysiological mechanisms of speech c) Often have a negative impact on the further mental development of the child d) They are stable and do not disappear on their own
Question No. 52
What is the name of the phenomenon when a sound is pronounced as unusual in the phonetic system of the native language in its acoustic effect (abnormal reproduction of sounds due to incorrectly formed individual articulatory positions? a) distortion (+) b) confusion c) interchange
Question No. 53
At what stage of reading skill formation, identified by T.G. Egorov, there is a semantic guess at the level of the entire text: 1) the level of syllable-analytical reading; 2) the stage of development of synthetic reading techniques; 3) stage of synthetic reading.
(+)
Question No. 54
Which structural-functional block will you predict is unformed when you identify errors in replacement of paired consonants in written work: 1) block of regulation of tone and wakefulness; 2) block for receiving information processing and storage; (+)
3) programming, regulation and control unit.
Question No. 55
Phonemic perception is: 1) mental actions to analyze or synthesize the sound structure of a word; 2) special mental actions to differentiate phonemes and establish the sound structure of a word; (+)
3) subtle, systematized hearing, which has the ability to carry out operations of discrimination and recognition of phonemes that make up the sound shell of a word;
4) there is no correct answer. Question No. 56
What rate of speech is typical for stuttering: 1) intermittent; (+)
2) accelerated;
3) slow Question No. 57
The soft palate vibrates with the following type of rhotacism: 1) single-beat; 2) velar; (+)
3) uvular;
4) there is no correct answer. Question No. 58
For which of the listed types of speech disorders is “silent mode” used as the first stage of speech therapy work? 1) rhinophonia 2) alalia 3) bradyllalia 4) tachylalia (+)
Question No. 59
Choose the correct sequence of tasks for the development of spatial orientation: A. Determining the position of objects in relation to the right-left hand; B. Determination of spatial relationships between three objects; C. Orientation in one’s own body; D. Determination of spatial relationships between 2 objects. 1) SADB; (+)
2) ASBD;
3) DBAS. Question No. 60
The main areas of activity of a speech therapist include (exclude incorrect answer 1): 1. primary diagnosis of the child’s speech development; 2. psychological correction of personality traits; (+)
3. advisory activities;
4. speech therapy correction Question No. 61
Violation of the syllabic structure of a syllable in the form of likening one syllable to another (bicycle - “vevesiped”) is called 1) anticipation (+)
2) perseveration 3) contamination 4) elision
Question No. 62
The main areas of activity of a speech therapist teacher do not include: (choose the correct answer) 1) primary diagnosis of a child’s speech development 2) psychological correction of personality traits (+)
3) advisory activities 4) speech therapy correction
Question No. 63
Violation of the processes of formation of the pronunciation system of the native language in children with various speech disorders due to defects in the perception and pronunciation of phonemes is. a) general speech underdevelopment b) phonetic-phonemic speech underdevelopment (+) c) aphasia
Question No. 64
Disadvantages in the pronunciation of voiced consonants, expressed in the replacement of voiced consonants with paired voiceless sounds, are called a) voicing defects (+)
b) defects in softening c) defects in the pronunciation of palatal sounds
Question No. 65
What is the primary defect in optical dysgraphia, dyslexia: 1) impaired phonemic hearing: 2) impaired phonetic hearing; 3) violation of the generalized optical image of the letter
(+)
Question No. 66
On what sounds do stutterers most often experience cramps during speaking: 1) stop consonants; 2) vowels; (+)
3) fricative consonants.
Question No. 67
What causes articulatory-acoustic dysgraphia? 1) violation of various forms of language analysis and synthesis 2) underdevelopment of the grammatical structure of speech 3) underdevelopment of visual gnosis, analysis and synthesis, spatial representations 4) reflection of incorrect pronunciation in writing
(+)
Question No. 68
What is the outdated name for dyslalia? a) nasality b) muteness c) tongue-tied
(+)
Question No. 69
A form of dysarthria in which voluntary motor skills of the articulatory apparatus are impaired (in terms of manifestation in the sphere of sound pronunciation, it resembles motor alalia) a) bulbar b) cortical (+)
c) cerebellar
Question No. 70
Erased forms of pseudobulbar dysarthria are often confused with 1) alalia 2) dyslalia (+) 3) rhinolalia 4) all answers are correct
Question No. 71
Which of the following speech disorders belongs to disorders of the internal formulation of utterances? 1) bradyllia 2) aphasia (+)
3) dyslalia 4) dysphonia
Question No. 72
What form of stuttering is caused by psychogenic causes (psychotrauma): 1) neurosis-like; (+)
2) organic;
3) neurotic. Question No. 73
Who first formulated the principles of analysis of speech disorders? a) R. E. Levin (+)
b) F. F. Pay c) M. E. Khvattsev
Question No. 74
Work on the development of phonemic perception is carried out when eliminating: 1) semantic dyslexia; 2) mnestic dysgraphia; 3) acoustic dysgraphia; (+)
4) all answers are correct;
Question No. 75
Preventing the emergence of new speech disorders within an existing syndrome is the task of: 1) social prevention; 2) primary prevention; 3) secondary prevention; (+)
4) tertiary prevention.
Question No. 76
What is not one of the causes of functional dyslalia? a) pedagogical neglect b) underdevelopment of phonemic hearing c) shortened frenulum of the tongue
(+)
Question No. 77
What is the unit of the lexical code of a language: 1) word; (+)
2) phoneme;
3) offer. Question No. 78
A device for correcting a defect in the hard palate with clefts is called 1) orthodontics 2) synapse 3) obturator (+)
4) uranoplasty
Question No. 79
Corrective work for disorders of cognitive activity in children with speech pathology is aimed at: 1) solving problems of speech development and cognitive processes on the same speech material; (+)
2) solving problems of the development of cognitive processes;
3) on the formation of communicative and speech activity in the process of gaming or educational activities; 4) all answers are correct. Question No. 80
Which term characterizes congenital shortening of the frenulum of the tongue: 1) microglossia; 2) glossoptosis; 3) progeny; 4) ankyloglossia.
(+)
Question No. 81
What is the unit of the syntactic code of a language? 1) word; 2) morpheme; 3) offer. (+)
Question No. 82
Identify specific errors characteristic of phonemic dyslexia: 1) replacement of graphically similar letters; 2 violation of the sound-syllable structure of the word; (+)
3) changing the form and tense of verbs.
Question No. 83
With the help of what control is the feedback mechanism carried out in the speech functional system? 1) tactile, 2) visual, 3) kinesthetic
(+)
Question No. 84
Articulation disorders caused by any pathological changes in the language are called: 1) glossoplegia; 2) hypotension; 3) hyperemia; 4) glossolalia.
(+)
Question No. 85
Select the main biological factor in the occurrence of alalia: 1) organic damage to the speech zones of the left hemisphere; 2) left hemisphere organic damage to the central nervous system; 3) bilateral organic damage to the central nervous system.
(+)
Question No. 86
What is the unit of the syntactic code of a language? -suggestion (+)
Question No. 87
Which variant of incorrect writing of a sentence indicates that the child’s phonemic concepts are unformed: 1) There was a vase of roses on the table. (+)
2) There was a vasa with dew on the table.
3) On etol etoyala vaea e roeami. Question No. 88
Indicate what is an important prerequisite for successful literacy learning: 1) the idea of sound; 2) the idea of a grapheme; 3) idea of the phoneme.
(+)
Question No. 89
What term denotes persistent, repeated errors associated with difficulties in mastering and applying spelling rules: a) calligraphic; b) spelling; c) dysorthographic.
(+)
Question No. 90
On the basis of what documents is the speech therapy center of a general education institution staffed (exclude the incorrect answer 1): 1. PMPc extracts and statements from parents; 2. conclusions of the speech therapist and statements from parents; 3. conclusions of an otolaryngologist and statements from parents; 4. existing standards for the coverage of speech therapy correction for students and statements from parents
(+)
Question No. 91
Replacing sounds and words with similar ones in sound or meaning is called: 1) perseveration; 2) elision; 3) echolalia; 4) paraphasia.
(+)
Question No. 92
What is the name of the course of speech pathology in which there is an increase in symptoms of speech pathology: 1) regressive; 2) remitting; 3) stationary; 4) progressive.
(+)
Question No. 93
What is the unit of the lexical code of a language: - word (+)
Question No. 94
With what lack of pronunciation are whistling and hissing sounds pronounced like the sounds V and F: 1) predental sigmatism; 2) hissing sigmatism; 3) interdental sigmatism; 4) there is no correct answer.
(+)
Question No. 95
A defect in the pronunciation of the sounds [р] and [рь] is called. a) pararotacism b) rhotacism (+)
c) sigmatism
Question No. 96
What method is used to teach literacy to preschoolers with speech disorders: 1) the sound method; 2) sound-syllabic method; 3) sound analytical-synthetic method; (+)
4) it is not recommended to teach preschoolers with speech disorders to read and write.
Question No. 97
Who was one of the first in Europe to introduce the term “dyslalia” into scientific circulation? a) V. Oltushevsky b) R. Schulthess c) I. Frank (+)
Question No. 98
Which vocal register should be practiced in people who stutter at the initial stages of work on developing rational vocal skills: 1) head; 2) chest; (+)
3) average.
Question No. 99
What violations of sound pronunciation are an indicator of alalia in the differential diagnosis of it with dysarthria: 1) distortion; (+)
2) omissions;
3) replacements. Question No. 100
Which of the listed cranial nerves does not innervate the organs of the peripheral speech apparatus? 1) trigeminal; 2) olfactory; (+)
3) wandering.
content .. 5 6 7 8 ..