Work on the correction and development of speech in children with general speech impairment (GSD) is labor-intensive and painstaking work, designed to last more than one year and affecting all aspects of speech. To achieve the best results, it is necessary that all participants in this fascinating process: a speech therapist, a neuropsychologist, a child and his parents form a strong union of like-minded people, the main task of which is the formation of speech-thinking activity, competent speech of a beloved child, as a ticket to life in the big world of adults.
Like any process, speech formation occurs gradually, step by step, from simple to complex. In parallel, working on the formation of all language levels: sound, verbal and word-formation, grammatical and syntactic.
In order to express his thoughts most correctly, completely and accurately, a child must have a sufficient vocabulary. Therefore, work on the correction and development of oral speech begins with expanding and improving the vocabulary. In this case, the word is considered as a lexical unit of the language and as a grammatical and syntactic unit of a sentence. By introducing children to the concepts of “a word denoting an object” and “a word denoting an action of an object,” they thereby prepare a platform for working on a sentence. By giving the concept of “a word denoting a characteristic of an object,” material is accumulated for spreading the sentence by definition.
After children have formed an idea of the words denoting an object and the action of an object, children are brought to the concept of a sentence and begin to work on the structure and grammatical design of the sentence.
After children learn to compose a common sentence and form it grammatically correctly, they move on to working on coherent speech.
First, we teach children to retell short stories based on the sequence of actions occurring in the story. then move on to descriptive stories. After which they move on to teaching children short, selective and creative retelling.
Having taught children retelling, they move on to developing in children the skill of composing short stories based on a series of pictures, a plot picture and a series of subject pictures.
Work on the syllabic composition of a word precedes work on the sound-letter composition of the word. By dividing words into syllables, children learn to recognize and isolate vowel sounds, which are the sound basis of a word. This is important considering that omitting vowels in words is one of the most common mistakes children make when writing.
After children learn to isolate vowel sounds from a word, they move on to work on isolating consonant sounds. First, children are taught to hear and distinguish between hard and soft consonants.
Work on the sound-letter composition of the word has actually already begun in the early stages. By this time, children already have an idea that words consist of sounds (letters); they are able to isolate vowel sounds from words, hear the presence of hard and soft consonant sounds in words, and identify the letters that indicate these sounds in a word. By completing tasks, children learn to listen and read words, to feel each subsequent sound in a word. Work on children’s assimilation of the sound-letter composition of words is carried out using the material of monosyllabic words. As practice shows, if a child learns to correctly perform sound-letter analysis of a monosyllabic word, then he can easily analyze and correctly write words of any syllabic structure, even the most complex.
At the same time, from the very first stage to the last, work is underway on sound production, automation of practiced sounds and their introduction into spontaneous speech.
Article by children's speech therapist Natalia Tsvetkova.
Methodology for correcting sound pronunciation
Education and training in general and speech in particular are carried out through classes. Their organization, structure, and use of methodological techniques depend on the diagnosis established by specialists, on the level of impaired psychomotor functions of the child, and largely on the professional level of the speech therapist.
The main principle of work on developing pronunciation skills in children, used by a speech therapist , is the principle of an individual approach. At the same time, a subgroup form of organizing classes is not excluded, especially at the stage of preparing the articulatory apparatus and automating sound in coherent speech.
The second important principle is the use of the child’s compensatory capabilities, relying on intact links (connection of visual, auditory and tactile analyzers).
The third principle is the rational selection of material used in correctional classes. Each lesson should be emotional, developmental and, if possible, educational in nature, and be optimally intense. Not only speech, but also intelligence should develop.
The effectiveness of correctional work depends on the use of various forms and methods of work. The main methods of correctional work of a speech therapist are:
1. Specific (motor-kinesthetic, auditory-visual-kinesthetic) methods. The motor-kinesthetic method involves establishing a connection between the movement of articulatory muscles and their sensation. For example, if a child cannot expose his upper teeth on his own, the speech therapist lifts the child’s upper lip with his index finger. This creates a new sensation - raising the upper lip.
The use of the auditory-visual-kinesthetic method consists in establishing connections between the perception of sound by ear, the visual image of the articulatory pattern and the motor sensation during its pronunciation. To form an auditory-visual image of a sound, the speech therapist demonstrates to the child an articulatory pattern, shows the position of the articulatory structure with the help of his hands, while simultaneously pronouncing the sound. For example, when making the sound [sh], the child is asked to cup his palm and tongue, pronounce the sound and at the same time hold the palm of his hand in the shape of a cup.
2. Didactic methods: - visual; - verbal methods based on visualization; — verbal methods without relying on visualization; - practical methods that should be playful in nature.
Methods and techniques of correctional education should not only correspond to the interests of children and their needs in play, but also ensure the intellectual development of the child, training his thoughts and mind.
Visual techniques - showing toys, pictures, illustrations in books, actions - contribute to the formation of elementary concepts, expanding knowledge about the world around us and developing the ability to generalize.
In correctional work, the principle of multiple presentation of the same subject and speech material in variations should be observed. These could be toys, large pictures, printed board games, illustrations in books. The variety of material will contribute to the formation of generalized ideas about objects. The same visual and verbal material can be used to automate sound in words, then in sentences, phrases, riddles, to compose a descriptive story, etc.
In speech therapy practice, the technique of simultaneous pronunciation of a sound and writing the letter denoting this sound is used (writing and speaking). Children who cannot write are encouraged to pronounce sounds and perform simple actions. For example, pronounce the sound [zh] and move your fingers (“a bug flies, buzzes and flaps its wings”), pronounce the sound [r] and quickly drum your fingers on the table (this is how our tongue hits the “tubercles”), combine the pronunciation of the sound [w] with the movement of a bent palm (“a snake crawls and hisses”).
The following verbal techniques can be distinguished: - verbal sample; - simultaneous pronunciation of sounds by the child and the speech therapist; - repetition; — explanation; - indication; - verbal exercises; - a question as a stimulus for a child’s speech activity; — assessment of children's speech .
Gaming techniques are implemented in the use of various characters, fairy-tale plots, theatricalization, staging (uttering phrases on behalf of characters or animals), inverted words, intentional mistakes, and in the emotional presentation of the material. Children love to correct “mistakes” made by the teacher or character present in the lesson, teach fairy tale guests, and act in some role.
Classes should contain a maximum of information that helps enrich children's memory with images and ideas. A variety of tasks and a fast pace of classes prevent fatigue, develop switching attention and allow children to maintain interest throughout the entire lesson. Structure of individual and subgroup lessons
Individual and subgroup lessons for correcting sound pronunciation at all stages of work may have one general structure, but depending on the stage of work on sound, changes are made to it.
In the preparatory period and at the stage of sound production, more attention is paid to the development of articulatory motor skills, speech-auditory attention, the formation of speech breathing, voice correction, and the development of cognitive processes, while at the stage of sound automation the main thing is the development of the child’s speech activity and the formation of phonemic analysis and synthesis skills.
The proposed structure of classes is based on specific and didactic principles adopted in speech therapy. The structure of individual classes is determined by each speech therapist, based on the individual characteristics of the child, the level of development of articulatory motor skills, speech skills and cognitive processes. For example, articulatory gymnastics and exercises for the development of breathing and voice at the stage of automating sounds in coherent speech are not necessary and are carried out only with those children who need them.
It should be understood that the proposed structure of classes is advisory in nature. It all depends on the situation, and even the mood of the child. For example, when working on a word, it is possible to supplement a sentence with words, jointly compose sentences or a short dialogue, or compose pure proverbs. A speech therapy session is aimed at developing speech and psychomotor functions and consists of several interrelated parts. The sequence of these parts or the structure of classes contributes to the gradual involvement of all brain structures in the work and is the most effective. Let us reveal the essence of each part of the lesson and the variability of the tasks used.
Lesson structure 1. Organizational moment. Relaxation exercises. Plastic studies. Formation of spatial representations. Development of auditory perception. 2. Development of fine motor skills of the fingers. Coordination of movements with speech. 3. Massage or self-massage. 4. Mimic exercises. 5. Articulation gymnastics. Development of fine articulatory movements. Formation of correct articulatory patterns of the lips and tongue. Development of switchability of the organs of the articulatory apparatus. 6. Exercises to develop speech breathing and voice. Coordination of speech with movement. Overcoming violations of syllable structure. 7. Sound production. Development of phonemic awareness. Formation of phonemic analysis and synthesis skills. Development of attention and memory. 8. Automation of sound in syllables. 9. Automation of sound in words. 10. Automation of sound in phrases. 11. Automation of sound in sentences. 12. Automation of sound in pure tongues. 13. Automation of sound in riddles and poems. 14. Automation of sound in independent speech. 15. Teaching storytelling. Development of imagination. 16. Development of cognitive processes (thinking and imagination). 17. Preparing for literacy . Working with letters.
Each part of the lesson provides variability in the tasks used.
Modern approaches to the development and correction of speech of preschool children
Klavdia Trizno
Modern approaches to the development and correction of speech of preschool children
Formation of correct speech in children is one of the main tasks of modern preschool education . Currently, serious changes are taking place in the organization of speech correction work in kindergartens. However, the number of preschoolers with speech disorders, unfortunately, is not decreasing. I can note this fact as a teacher who has been working in a speech therapy group for many years. Today, figurative speech, rich in synonyms, additions and descriptions, in preschool is a rare phenomenon. The reasons for this phenomenon are varied and numerous. Therefore, the task of timely formation of children’s speech , prevention and correction of various speech disorders is still urgent.
In order to achieve sustainable results in the prevention and overcoming of speech , it is important to understand that overcoming speech disorders in preschoolers is a task not only for the speech therapist teacher, but for all interested adults. A decisive role is played by high-quality interaction and cooperation between educators, specialists and parents. It is an integrated approach to the correction of speech disorders , as well as a combination of the best traditional methods with modern approaches and forms of work, that allows us to achieve the best results and creates the necessary starting conditions for the child to move to the next stage of education and successfully master the primary school program.
interaction in the development and correction of a child’s speech as a system that solves three blocks of problems:
Block I - creation of a unified correctional and educational space ;
Block II - organization of a correctional and developmental educational environment;
Block III - correction of speech underdevelopment through a multidimensional impact on speech and extra-speech processes, stimulating the cognitive activity of children.
The goal of teachers’ work on the development and correction of speech of preschool children is the development of the child’s initial communicative competence. According to the federal state educational standard for preschool education , “speech development includes mastery of speech as a means of communication and culture; enrichment of the active vocabulary; development of coherent , grammatically correct dialogue and monologue speech ; development of speech creativity ; development of sound and intonation culture of speech , phonemic hearing; acquaintance with book culture, children's literature, listening comprehension of texts of various genres of children's literature; formation of sound analytical-synthetic activity as a prerequisite for learning to read and write.”
To achieve these targets, educational work is planned and carried out in four main areas (direct educational activities, educational activities in special situations, creating conditions for independent activities of children and interaction with parents and social partners).
1. As in any kindergarten, work begins with planning. In August, educators and specialists jointly develop work programs. Individual educational routes are developed for children with disabilities and they are accompanied throughout the year by specialists from the psychological, medical and pedagogical council of the preschool educational institution, and dynamic monitoring is carried out. development of children is assessed . This is a very important area of work at the present stage, requiring rethinking and bringing it into line with modern requirements . Our kindergarten is participating in experimental work in this area with the Novosibirsk Pedagogical College No. 1 named after. A. S. Makarenko, and our group is a pilot group.
2. In direct educational activities we actively use information and communication technologies. It's no secret that for today's preschoolers , born in the digital age, this is simply necessary. The inclusion of ICT in the educational process arouses interest, increases the involvement and activity of children and allows them to successfully solve many correctional problems . We use specialized technologies in our work (for example, the speech therapy correction program “Games for Tigers”
etc., as well as independently developed media presentations and
developmental tasks using an interactive whiteboard. A positive emotional background, which is also important for high-quality correctional work , is helped to create “Speech therapy chants”
by G. S. Ovchinnikova and
“Speech therapy songs”
by E. Zheleznova.
3. Recently, quest technologies or educational quests have become widespread and very popular. We are happy to join this movement and conduct speech therapy quests both in the group and in the fresh air. This is truly a very interesting and effective form of work that arouses great interest and activity among children, thanks to the combination of an extraordinary organization of educational activities and an exciting plot. We also use gaming innovative lapbook technology and are currently planning work on creating a large speech therapy lapbook as the final product of the year’s work.
4. To ensure the child’s initiative and implement such a principle of the Federal State Educational Standard for Education as individualization of the educational process, we actively use project activities. This form also allows us to solve another important task of correctional work , namely, the inclusion of parents in the educational process. Several projects were successfully implemented this academic year: the environmental project “Feed the birds in winter”
, a children's thematic project
"Healthy lifestyle and professions"
as part of the festival-competition
"Nutrition and Health"
. The children went on numerous excursions: to the fire department,
"Children's Auto City"
, educational
, to their parents' work. Work on the project requires involvement in communication with adults and peers and high speech activity. The product of the project was children's mini-presentations and author's little books "My Future Profession"
. Our project was among the winners of the regional competition, and now we, together with parents, are preparing a creative presentation for the city stage.
Another project - “Writers of Novosibirsk for Children”
.
Its implementation allows us to solve the very important task of introducing children to fiction. We all know that fiction serves as an effective means of mental, moral and aesthetic education and has a huge impact on the development and enrichment of a child’s speech . Various genres of literary and folklore works allow you to work on all aspects of speech (phonetic, lexical, grammatical)
.
But today, most parents not only do not see the importance of reading in teaching and raising children, but they themselves do not read or read little. This is what the survey of parents and the survey of children in the group, which was conducted in September 2015, showed. Very few parents and children could name writers from their native land. “Writers of Novosibirsk for Children”
project is to create conditions for
the development of children’s speech by introducing children and parents to reading fiction;
acquaintance with the works of writers of Siberia and Novosibirsk. In the process of implementing the project, children and parents became acquainted with the works of Taisya Pyankova, Yuri Magalif, Vladimir Shamov, Nelly Zakusina, and Elizabeth Stewart. A literary salon took place with the participation of Novosibirsk poetess Elena Nikolaevna Zinovatnaya. Children were able not only to listen and recite poems, but also to communicate with the author, ask questions that interested them, and receive autographed books. Thematic exhibitions were arranged in the book corner, and a variety of productive and creative children's activities were organized. The most interesting form of cooperation with parents was parent readings, when in the afternoon fathers and mothers read works of art for children. 5. A very effective form for introducing children to the world of fiction and for the development of speech in general is our network interaction with the N. Ostrovsky Library, which is carried out on the basis of an agreement and a joint plan for educational work. We offer excursions monthly. In cold weather or ice, when we cannot take the children out, library specialists come to our kindergarten. “There’s a Library Next Door” were organized for children in a fun and accessible way for children.
,
“Tumbling, running, skipping”
,
“My native district of Dzerzhinsky”
,
“The winter forest is full of fairy tales and miracles”
,
“Safety rules”
,
“Mom is a dear word”
,
“The good world of Korney Chukovsky”
, etc. We also successfully cooperate with schools.
For example, in addition to excursions to schools, for several years we have been collaborating with the literary and theater club “Fairy Tales”
of school No. 57. This year, students in grades 3 and 4 prepared and conducted for us the program “Fairy Tale Carousel for Our Little Friends.”
It was especially pleasant to see among the young actors already grown-up graduates of our kindergarten! We enjoyed watching the mini-plays “The Monkey’s House” (based on the fairy tale by Boris Zakhoder)
and “The Invisible Guest”
(Romanian fairy tale)
. This is important for motivating our children because they see that what they participate in in kindergarten will be useful to them in school.
6. We not only watch the theater, but also, of course, participate in theatrical activities. “Tales of Childhood” has been operating in our kindergarten for 6 years now.
The creative group of the studio consists of teachers from our institution: senior teacher, educators, music director.
6 performances were staged, they were awarded diplomas of laureates of the international festival of children's and youth theatrical creativity “Times are the connecting thread”
.
The performances “The Princess and the Pea”
and
“The Little Flower of Seven Flowers”
were shown on the small stage of the
Globus
.
This year our children took part in the play “The Wizard of the Emerald City”
. A total of 52 children took part in it. It is difficult to overestimate the importance of theatrical activities. During the production of the play, we see a huge increase in motivation and noticeable progress in the children’s conscious attitude towards working on their own speech.
subject-spatial environment plays a huge role in successfully overcoming speech disorders For correctional and developmental work, not only a separate speech therapy room is used, but also a speech center in the group, which is a specially equipped space for individual games or games in small subgroups, as well as for joint activities of an adult and a child. When designing the speech center, we took into account the principles reflected in the Federal State Educational Standard for Education, and also provided a variety of materials; compliance with the age and individual characteristics of children, the structure of speech disorders; design aesthetics. The speech center is located next to the library and theater center. The leading toy, the “mistress”
of the correctional center, is the multifunctional toy Kvakusha, made by the mother of our pupil. The basis of the speech center includes gaming and didactic material in the following sections: sound pronunciation, development of fine motor skills, phonemic hearing and consolidation of acquired skills in teaching literacy, vocabulary, grammatical structure of speech and development of coherent speech , enrichment of vocabulary, formation of higher mental processes. Children have access not only to purchased educational games and equipment , but also to manuals made by parents and teachers. The most interesting of them were presented at the exhibition of pedagogical ideas “Mosaic of Childhood”
, as part of the scientific and practical conference of
preschool education workers in the Novosibirsk region in September 2016.
8. The group has been operating a mini-museum “Russian Izba”
, which is used both for independent activities of children and for the implementation of the author’s technology
“Introducing
preschool children to the origins of their native culture .
Patriotic, spiritual and moral education of children is a popular, relevant direction in preschool pedagogy . I think this is very important and correct. It is difficult to overestimate the importance of our cultural heritage for the development of a child , including the formation of beautiful, correct speech . Throughout the year, together with parents, we hold various ritual and folklore holidays: “Cabbage Gatherings”
,
Carols”
,
“Heroic Fun”
,
“Svetlaya
Easter" and others.
Our children participated in the concert program of the folklore ensemble “Rozhdestvo” under the direction of O. Gurina “Come, guests, to us!”
at the Novosibirsk State Philharmonic.
The guys performed the dance “Timonya”
.
9. I would like to say a few words about one more effective direction in correcting children’s speech - motor activity. The influence of motor activity on the functional state of the brain, and in particular, on the development of the sensory and motor aspects of speech , has been proven in experimental studies conducted under the leadership of M. M. Koltsova preschool children with complex types of speech disorders have psychomotor deficiencies development , coordination is often impaired. “Sudarushka” helps us solve this problem.
.
In the process of choreographic activity, arbitrariness of movements and switchability from one movement to another
develops The sequence of movements, their accuracy, proportionality and smoothness are formed. Our children not only dance wonderfully at the holidays, but also successfully participate in various competitions. 10. Participation in competitions of various types has a positive impact on children’s motivation, contributes to the formation of their social competence, and is a significant factor for parents. This year our children successfully participated in All-Russian, regional, and city competitions.
11. And the last thing I want to say is the importance of parents’ direct participation in the process of development and correction of children’s speech . This is often not easy. But our kindergarten and group have accumulated sufficient experience in constructive cooperation with the parents of pupils. And being a city innovation platform in this area, we use many modern , interesting forms of cooperation. We have already talked about some. We would like to add that, based on our experience, the following forms of interaction are effective: questionnaires and surveys with the obligatory presentation of results at parent meetings and subsequent joint planning and holding of events of various types (themed leisure and entertainment , family competitions, exhibitions, etc., holding discussions, clubs on interests, evenings of questions and answers with the involvement of specialists, as well as the presentation of positive parental experience, holding Understudy Day and Days of meetings with interesting people, organizing platforms for interactive communication with a pedagogical focus (we have a closed VKontakte group: we practice posting recommendations, links to interesting webinars, video materials, literary texts and works, recommendations from a speech therapist for home exercises to consolidate sounds, etc.) The main thing is that the information is regularly updated.
This approach allows us to successfully solve the assigned tasks, obtain the expected results in our work and positive dynamics in the speech development of children .
Correction of general speech underdevelopment in preschool children
Lyubov Gorshkova
Correction of general speech underdevelopment in preschool children
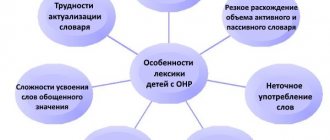
General speech underdevelopment is a variety of complex speech disorders in which children have impaired formation of all components of the speech system related to its sound and semantic side, with normal hearing and intelligence.
General underdevelopment of speech can be observed in the most complex forms of childhood speech pathology: alalia, aphasia, as well as rhinolalia, dysarthria - in cases where insufficient vocabulary , grammatical structure and gaps in phonetic-phonemic development are simultaneously detected.
For the first time, a theoretical justification for general speech underdevelopment was formulated as a result of multidimensional studies of various forms of speech pathology in children of preschool and school age , conducted by R. E. Levina and a team of researchers at the Research Institute of Defectology (N. A. Nikashina, G. A. Kashe, L. F. Spirova, G.I. Zharenkova, etc.) in the 50-60s of the XX century.
T. B. Filicheva, G. V. Chirkina under general speech underdevelopment in children (with normal hearing and primarily intact intelligence)
understand a form of speech anomaly in which the formation of each of the components of the speech system is disrupted;
vocabulary, grammatical structure, sound pronunciation. In this case, there is a violation of both the semantic and pronunciation aspects of speech . The group with OHP includes children with various nosological forms of speech disorders (dysarthria, alalia, rhinolalia, aphasia)
in cases where there is a unity of pathological manifestations in the three indicated components.
Currently, in speech therapy there are two traditional classifications of speech : clinical-pedagogical and psychological-pedagogical. These classifications consider speech disorders in various aspects. But at the same time, the data of one and the other classification complement each other and serve common tasks: recruiting groups of children with speech pathology and implementing systemic, differentiated speech therapy, taking into account the symptoms and mechanisms of speech .
The clinical and pedagogical classification is not strictly correlated with clinical syndromes. She focuses on those disorders that should be the object of medical, psychological and speech therapy intervention.
In the process of making a speech therapy report, medical data and clinical characteristics are necessary, which make it possible to clarify a particular speech therapy diagnosis. Clinical characteristics are focused primarily on explaining the causes of speech disorders and treating the child, and not on a correction .
The clinical and pedagogical classification reveals the etiology, mechanisms, forms and types of speech disorders. This classification identifies the following forms of speech disorders: dyslalia, dysarthria or erased dysarthria, rhinolalia, voice disorders, motor, sensory alalia, childhood aphasia, adult aphasia, delayed speech development (ZRR, stuttering, tachylalia, stumbling (polturn)
.
The psychological and pedagogical classification is focused on identifying, first of all, speech symptoms (symptological level)
.
The symptomological level of analysis of speech disorders makes it possible to describe the external symptoms of language underdevelopment ( speech) , which serves as the basis for sending children to certain kindergarten groups or to a certain type of school.
The psychological and pedagogical classification was developed by R. E. Levina and employees of the speech therapy sector of the Institute of Defectology. This classification is based on linguistic and psychological criteria.The most significant among them is the identification of impaired components of speech systems (phonetic-phonemic aspect of speech , lexical-grammatical structure of speech ).
In accordance with the specified criteria, this classification distinguishes two groups of speech disorders:
Group 1 - violation of means of communication .
Group 2 - disorders in the use of means of verbal communication (stuttering)
.
The first group of speech disorders, according to R. E. Levina, includes phonetic-phonemic underdevelopment and general speech underdevelopment (GSD)
.
Phonetic-phonemic underdevelopment is a violation of the formation of the pronunciation system of the language due to insufficient phonemic perception and articulation of speech .
General underdevelopment of speech is characterized by a violation of the formation of all components of the speech system in their unity (sound aspect of speech , phonemic processes, vocabulary, grammatical structure of speech ) in children with normal hearing and relatively intact intelligence.
General underdevelopment of speech can be observed in various forms of speech pathology (according to clinical and pedagogical classification)
: motor, sensory alalia, childhood aphasia, dysarthria, including erased dysarthria.
In the etiology of general underdevelopment of speech, various factors of both a biological and social nature are identified. Biological factors include: infections or intoxication of the mother during pregnancy, incompatibility of the mother and fetus according to the Rh factor or group affiliation, pathology of the natal period, postnatal diseases of the central nervous systems and brain injury in the first years of a child’s life, etc.
At the same time, general underdevelopment of speech may be due to unfavorable conditions of upbringing and training, and may be associated with mental deprivation during sensitive periods of speech . In many cases, general underdevelopment of speech is a consequence of the complex influence of various factors, for example, hereditary predisposition, organic failure of the central nervous system (sometimes easily expressed, unfavorable social environment.
The most complex and persistent option is general speech underdevelopment , caused by early organic brain damage.
E. M. Mastyukova attaches particular importance in the etiology of ONR to perinatal encephalopathy, which can be hypoxic (due to intrauterine hypoxia and asphyxia during childbirth, traumatic (due to mechanical birth trauma, bilirubin (due to incompatibility of the blood of the mother and fetus according to the Rh factor or group affiliation) .
Typical for the entire OHP group is: late appearance of speech , a sharply limited vocabulary, pronounced agrammatism, defects in pronunciation and phoneme formation, characteristic violations of the syllabic structure of words. Speech underdevelopment in preschool children can be expressed to varying degrees: from the complete absence of speech means of communication to extensive speech with elements of lexico-grammatical and phonetic disorders.
Clinical types of general speech underdevelopment are varied . In the classification of E. M. Mastyukova, three groups of children with OHP .
Group I is an uncomplicated variant of OHP, characterized by the presence of only signs of general speech underdevelopment . In children with this variant of OHP, local lesions of the central nervous system are not detected. In the anamnesis of these children, there is most often no indication of a pathological course of pregnancy and childbirth, only sometimes mild toxicosis of the second half of pregnancy or prolonged asphyxia is observed. In the postnatal period, these children may experience somatic weakness, frequent infectious and colds. From a psychological point of view, these children show general emotional and volitional immaturity and lack of formation of regulation of voluntary activity.
In children of the first group, there is a lack of fine differentiated movements of the fingers and difficulties in the dynamic organization of movements.
In the second group of children, a complicated variant of OCD of central organic origin is detected. In children of this group, OHP is characterized by more complex symptoms and pathogenesis. Impaired speech development is combined with neurological and psychopathological symptoms. Severe neurological symptoms in these children indicate not only the immaturity of the central nervous system, but also gross damage to certain brain structures.
In this group, according to E. M. Mastyukova, the most common syndromes are:
1. Hypertension-hydrocephalic syndrome, which is characterized by increased intracranial pressure, an increase in head size, and expansion of the venous network in the temple area. Children syndrome experience rapid exhaustion, increased excitability, disinhibition, irritability, frequent headaches, and dizziness.
2. Cerebrasthenic syndrome is characterized by increased neuropsychic exhaustion, emotional instability, impaired attention and memory. Cerebrasthenic syndrome in some cases manifests itself against the background of emotional and motor anxiety, in others it is accompanied by lethargy, lethargy, and passivity.
3. Movement disorder syndromes manifest themselves in changes in muscle tone, in impaired coordination of movements, in the immaturity of general , fine manual, and articulatory motor skills, which in turn manifests itself in the form of tremor, synkinesis, violent movements, mild paresis, spasticity, characterizing erased dysarthria .
In general, children the second group are characterized by insufficiency of gnosis , praxis, and gnosispraxis.
The immaturity of the emotional-volitional sphere is manifested in these children in emotional lability, in the superficiality of emotions, in the insufficiency of volitional processes .
Children with group III OHP have alalia (mainly motor alalia)
.
Currently, the etiology of alalia is correlated with damage to the speech zones of both the left and right hemispheres. Children with motor alalia have complex dysontogenetic disorders; encephalographic studies show that children with motor alalia have not only local lesions of the cerebral cortex, but also lesions of the subcortical structures of the brain .
Despite the variability in the clinical characteristics of children with OSD , what they have in common is systemic speech underdevelopment . of speech is especially complex and persistent .
Speech underdevelopment in children can be expressed to varying degrees: from complete absence of speech to minor developmental deviations. Taking into account the degree of unformed speech of R. E. Levina identified three levels of her underdevelopment .
Thus, general speech underdevelopment is one of the complex speech disorders, characterized by pathology of all speech .
Innovative methods for correcting speech disorders article on speech therapy on the topic
Prepared
teacher of State Educational Institution SO Yeshi No. 13
Ekaterinburg
Belyakova Irina Anatolevna
Interactive Metronome
A program created by Interactive Metronome (USA) to overcome speech, attention and behavior disorders associated with timing and movement planning.
Purpose
- children with ADHD,
- autism spectrum disorders (early childhood autism (ECA), Asperger syndrome, autistic conditions),
- mental retardation,
- cerebral palsy,
- speech tempo disturbances,
- children after traumatic brain injuries, spinal cord injuries.
Principle of operation
The Interactive Metronome device (IM - Interactive Metronome) allows you to activate (stimulate) areas of the brain, resulting in improved coordination, attention, memory, perception (including phonemic), cognitive functions, sensory processing, regulation of emotional states and self-regulation. Improves motor functions, rhythm, behavior, reading and writing skills.
IM is an interactive therapeutic computer program. The work is carried out through a touch glove (put on the hand) or a touch panel (step with your foot, moving forward, or with your heel, moving backward). The child must tap the rhythm (clap) with one hand, two hands, or step with one (two) feet, or alternately changing hands and feet. During the session, the child listens to the original metronome ri included in the program. Thus, a deep rhythm is formed, auditory-motor coordination is trained, and a priori the basis is prepared for correcting violations of the syllabic structure of words.
The interactive metronome stimulates brain activity, which is necessary to process sensory information coming from outside. This contributes to the development of the ability to plan one’s activities and stabilizes behavioral reactions. The work is based on the “feedback” principle. The child should clap their hands or stomp their feet in accordance with the rhythmic beeps of the metronome. A sensory glove or sensory mat allows you to evaluate the child’s accuracy in completing a task.
You can start training at the age of 4-5 years.
Tomatis method
The Tomatis Method is a system of auditory training. The goal of the method is to improve the brain's ability to perceive and process auditory information. With the help of training according to the Tomatis method, the listening process is reprogrammed, which, in turn, has a positive effect on understanding spoken language and concentration.
Purpose
- children with autism spectrum disorders (early childhood autism (ECA), Asperger syndrome, autistic conditions),
- attention deficit hyperactivity disorder,
- delays in speech and psychomotor development,
- impairments of written speech (dysgraphia, dyslexia)
- disorders of balance function.
Principle of operation
Many children with completely normal hearing have very poor perception and assimilation of what they hear. It seems that while listening, they are thinking about something of their own, do not delve into the words, are inattentive to what is happening, they have to repeat the same thing many times, they give the impression of being inattentive. In noisy environments (for example, at school or kindergarten), these difficulties are exacerbated. The inability to process and analyze information heard leads to problems in learning and inhibits the development of social skills. Audio-vocal training using the A. Tomatis method allows you to teach the brain to correctly perceive surrounding sounds, identify the most important ones among them, process and analyze even those that the child has not “heard” before.
The operating principle of the Tomatis method is sensory sound stimulation. Sound is transmitted in two ways: bone conduction, caused by vibration in the top of the skull, and air conduction, which transmits sound vibrations through the outer ear. TOMATIS devices are designed to create a unique perceptual sound contrast. This effect causes the muscles of the inner ear to contract and relax. This back-and-forth movement is caused by a sudden transition from low frequencies, which do not require any special training from the hearing aid, to high frequencies, which, on the contrary, require special effort from the hearing system. This action is similar to gymnastics for the ear muscles, since through repeated repetition and progressive mobilization of the muscles, the transmission of sensory sound messages to the brain improves.
The use of this method is possible thanks to a special complex device called the Electronic Ear. During the lesson, the child listens to Mozart's music or Gregorian chants through headphones. At the same time, the ECHO filters the music in a certain way, causing the auditory system to work more efficiently. During training, the child can play, draw or engage in any quiet activity. Electronic Ear filters are adjusted individually for each child.
Contraindications?
- epileptic activity
- acute period of any disease
- severe arterial hypertension
- tumor diseases.
An electroencephalogram is required before the appointment. Classes can begin at 3-4 years of age. Auditory training must be long-term, since the brain learns only after 40-45 hours.
FastForWord
Fast ForWord is a computer correction technique developed by leading American scientists in the field of speech disorders, employees of Scintific Learning.
This is a special computer method for correcting disorders of speech development, auditory perception, understanding and awareness of spoken language. With the help of this program, the language center of the cerebral cortex is trained, subcortical pathways are optimized, which helps improve attention and memory development.
Purpose
- children with disorders of oral and written speech, speech (phonetic-phonemic underdevelopment of speech, general underdevelopment of speech (and when leaving alalia), dysgraphia and dyslexia)
- with pathologies of auditory perception and underdevelopment of the functions of phonemic analysis and synthesis,
- children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
- mental development delays,
- attention disorders,
- autism spectrum disorders (ADD, Asperger's syndrome).
Principle of operation
Human speech is a sequence of rapidly changing sound signals, which, entering the brain through the auditory organs, undergo multi-stage processing by various parts of the central nervous system. If the speed of information processing is lower than the speed of its receipt, the child simply does not have the ability to perceive speech by ear. In most cases, he learns to recognize only a certain number of “slow” sounds, and all the “fast” ones that the brain does not have time to process are eliminated by his subconscious. Incorrect perception of speech in the general case leads not only to disturbances in its understanding, but also to corresponding distortions in the reproduction of words. The child tries to speak as he hears, but what he initially hears is the wrong set of phonemes.
In the 70s of the 20th century, American psychologist Paola Tallal conducted a study in which she found that if the speed of presentation of sounds is slowed down, then children with hearing and speech impairments can assimilate them. Special programs were developed that were individually adjusted to the speed of perception of phonemes of each child with subsequent acceleration to the age norm. Experts immediately noted a positive effect: patients learned new words faster and their diction improved significantly. The result looked truly fantastic. This is how the Fast ForWord technique appeared
The name of the program translates as “Running for the Word” or “Quick Word”. This program does not teach the child to speak. Moreover, it is in English. But this does not at all hinder the effectiveness of its use in different countries. This program trains the auditory perception system, that is, it creates the foundation for speech formation.
How does this happen? In many countries, children who begin to speak different languages use typical combinations of vowels and consonants in their babble, such as “da-da-da” and “ba-ba-ba.” The first words that children utter also usually consist of the following combinations: “dad”, “mom”, “baba”.
For a child with speech problems, distinguishing between these similar sounds remains a big problem for a long time. These children's hearing cannot process typical combinations of consonants and vowels that are pronounced quickly. Children do not have time to hear the beginning of a syllable or how sounds change within a syllable.
This inability to cope with a basic task disrupts all aspects of the child’s language development. The child spends a lot of effort and time trying to distinguish sounds and understand which word was spoken. This causes problems with understanding speech, the pronunciation side of speech, reading and writing. But the problem can be solved with the help of special training.
The Fast ForWord program consists of several series of exercises that train the basic brain functions associated with language skills.
The program is designed like a computer game. The child listens to sounds through headphones and completes tasks from the characters. For example, in one of the tasks the child learns to distinguish between “ba” and “da”. But not in the same way as it could happen in regular classes with a speech therapist! First, the computer artificially slows down the speed of these sounds. A person, unlike a computer, cannot do this. For example, the sound A can be pronounced quickly or slowly, but this cannot be done with the sound B.
First, the child’s brain is trained on slow sounds, then the program gradually increases their speed, bringing them closer to the speed of “fast parts of speech.”
When a child completes a task correctly, something fun happens on the screen. Positive emotions contribute to the production of special substances - neurotransmitters, which help the brain consolidate acquired skills. Therefore, the results of training last for a long time.
Fast ForWord results
- normalizes brain function in children. Researchers from Standsford University scanned the brains of children with dyslexia before and after the Fast ForWord course. It showed that after the course, the brain function of all subjects returned to normal. Before training, children with dyslexia did not use the same areas of the brain when reading that typical children did.
- Children's attention and ability to concentrate improves
- The Fast ForWord program improves not only phonemic awareness, but also the brain’s overall ability to process information. The program also trains the brain's ability to manage time. This leads to an improvement in the child’s performance in all school subjects.
- helps children with autism. Many children with autism have problems with speech development. As a result of working with the program, the children began not only to speak more, but also became more sociable.
Forbrain
FORBRAIN® (“For the Brain”) is a special device that allows you to train the brain’s processing of auditory information. For training, the child’s own voice and the teacher’s voice are used. FORBRAIN was developed by specialists from Hong Kong.
Purpose
- children with various speech and communication problems (developmental disorders of the autism spectrum, alalia, stuttering, dysarthria, etc.)
- learning difficulties at school.
Principle of operation
FORBRAIN is designed to enable all aspects of audio signal transmission and processing. For this, a vibrating device is used to enhance bone conduction (which is much faster than air conduction) and a special dynamic filter that enriches the sound of speech with high frequencies.
Using FORBRAIN allows you to become a more attentive listener, as well as improve the quality of your voice and speech: the child hears his own voice in an adjusted form, and the brain is forced to rebuild its work in response to these changes.
Contraindications
It is not recommended to use FORBRAIN while taking Tomatis or inTime courses.
InTime
This is a method of harmonizing the work of the brain, based on listening to rhythmic music, developed by a multidisciplinary team of experts from Advanced Brain Technologies (USA).
Individualized training involves not only listening to music, but also a variety of motor-rhythmic exercises using your own body, voice, drums and other noise musical instruments. These exercises help maintain an internal sense of rhythm and make rhythm an integral part of life.
It combines two important aspects for brain development: stimulation with sounds of certain frequencies and stimulation with rhythm.
Purpose
- children with attention disorders (ADHD, hyperactivity),
- disturbances in the tempo and rhythm of speech (stuttering),
- various disorders of written and oral speech (dysgraphia, dyslalia, dysarthria, alalia),
- developmental disorders of the autism spectrum.
Principle of operation
The functioning of the nervous system is a complex, rhythmic activity involving synchronized interaction between different areas of the brain. In a child with developmental disorders, as a rule, the brain does not work rhythmically enough. Exercises aimed at solving this problem have a beneficial effect on all areas of functioning.
Interaction with rhythmic music inTime stimulates the development of a sense of rhythm, attention, resistance to stress, and the ability to organize one’s thoughts and movements in time. All these abilities develop due to the fact that the training process provides stimulation that improves the quality of the functioning of the brain and the quality of its connections with the body.
inTime training involves listening to musical modules lasting 9 minutes several times a day with motor-rhythmic exercises (bodily percussion and drum exercises). Psychoacoustically modified music is listened to using the Waves™ multisensory audio system and special headphones that provide, in addition to air conduction, sound - bone.
Device “Spectrum” – phototherapy
A physiotherapeutic method of treatment using low-intensity light and laser radiation from different parts of the optical spectrum. It is carried out using the Spectr apparatus (St. Petersburg).
Purpose
- violation of muscle tone in the articulatory apparatus and more.
- immunocorrective,
- vasodilator
- anti-inflammatory effect
Operating principle
Many children with speech disorders have one or another problem with the regulation of muscle tone. Muscle tone may be increased or decreased. Sometimes these problems affect the muscles of the speech apparatus only, and in some cases the entire body. Dysregulation of muscle tone in the cervical-collar area is especially common.
Red radiation improves the functioning of nerve tissue and is used in cases where it is necessary to activate muscle function. Green radiation, on the contrary, has a calming effect and is used in cases where it is necessary to reduce muscle tone. These procedures are a good addition to speech therapy and physical therapy classes.
The procedures are absolutely painless and easily tolerated by the child. During treatment, the specialist applies the LED tips of the green or red matrix of the device to reflexogenic zones on the body or face. Depending on the goals of therapy, continuous or pulsed operating mode of the device can be used
Audio-visual stimulation
This is a program for developing a child's intellectual abilities and increasing learning ability.
Purpose
- attention disorders
- behavioral disorders
Principle of operation
Each anatomical structure of our body has its own rhythm. There is a common rhythm for the nerve centers responsible for behavior and learning. In children with attention and behavior disorders, this rhythm can be changed. The technique of audio-visual stimulation not only sets the correct rhythm, but also trains the body to reproduce it itself. This rhythm is characteristic of normal learning, control of emotions and behavior.
Stimulation of two channels at once is used: auditory and visual. This helps form a bond between them. This connection is extremely important, for example, for mastering competent reading and writing.
Auditory stimulation - the child listens to a series of rhythmic sounds through headphones for 7-10 minutes. Visual stimulation - the child sits for 7-10 minutes with his eyes closed in special glasses through which rhythmic flashes of light are given.
You can start classes from about 5 years old (it is important that the child is able to sit for 7-10 minutes with his eyes closed)
Bioacoustic correction
Correction of the state of the brain using classroom feedback. The method was developed by the State Research Institute of Experimental Medicine of the Northwestern Branch of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences, Physiological Department named after. I.P. Pavlova (from 1992 to 2008), St. Petersburg.
Purpose
- Mental development disorders (mental retardation, mental retardation, autistic syndrome).
- Speech development disorders (dysarthria, dyslalia, OHP, alalia, dysgraphia, dyslexia).
- Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder.
- Neurosis-like disorders (tics, enuresis).
- Tension headaches. Migraine.
- Consequences of stroke, organic brain damage, traumatic brain injury.
- Hypoxemic-ischemic lesions of the central nervous system of perinatal origin
- Adaptation to school and preschool institutions.
- General health improvement and psychoprophylaxis
- Increasing and supporting the optimal level of the body’s adaptive capabilities and the process of self-regulation.
Principle of operation
Some children with neurological disorders have abnormal brain wave activity. It can be normalized through training on a special device.
Restoration of self-regulation processes is carried out by acoustic stimulation consistent with the current bioelectrical activity of the brain. The presentation of music-like sounds, the parameters of which are consistent with the indicators of the frequency structure of the EEG and synchronous with the events of bioelectrical activity of the brain, creates unique conditions for adaptive stimulation
Sensors are attached to the child's head and record the bioelectrical activity of the brain - EEG. In real time, brain waves are converted into sound signals reminiscent of organ music. The child listens to this “music of his brain” through headphones. We can say about this method in a simplified version: the better the brain activity, the better the music will be.
The method activates the body's natural self-regulation processes. The child’s emotional state and speech improve, the child becomes more sociable and sociable.
Significant EEG improvements are observed.
Contraindications.
- Acute postoperative period
- Hypertensive crisis
- High body temperature
- Early stage after TBI
- Psychotic state
- With caution: epilepsy
Logo trampoline
A technique for training brain functions involved in reading and writing. The training was developed by specialists based on visual-vestibular exercises proposed by Samantha Zlotnik, a doctor of optometry from New York.
Purpose
- children with reading and writing disorders (dyslexia, dysgraphia),
- children with attention disorders.
- children learning to read
- children with stuttering.
Principle of operation
Many children with speech, reading, and writing disorders have difficulty processing visual information. Often these difficulties are associated with impaired interaction between the senses (sensory integration disorder). In other words: the child’s brain does not have time to effectively process information from different channels. For example, a child cannot simultaneously listen to the teacher’s instructions and take notes in a notebook, or complete a task and quickly respond to the teacher’s remarks. When reading, he often loses a line, does not understand the meaning of the words he read, and misses letters while writing.
These workouts help synchronize the functioning of the visual, auditory and vestibular systems. Trampoline jumping combined with reading aloud promotes the development of rhythm and timing, which are essential for successful reading, writing and other learning activities. These trainings are multi-level stimulation of all sensory systems involved in the formation of speech, reading and writing. Exercises also help develop saccadic movements of the eyeballs and increase the field of vision. This is very important reading.
During training, the child rhythmically jumps on a small trampoline and reads out loud the letters (syllables, words) that appear on the screen. Gradually, the reading material becomes more complex. Additionally, exercises are provided to develop spatial orientation and visual perception.
Cerebellar stimulation
A series of rehabilitation techniques aimed at stimulating the functioning of the brain stem and cerebellum.
Purpose
- clumsiness, imbalance and coordination of movements (signs of disorders of the brain stem and cerebellum). They are often diagnosed in children with delayed speech and mental development, autism spectrum disorders (early childhood autism (ECA), Asperger's syndrome, autistic conditions), behavioral and attention disorders, and ADHD.
Principle of operation
The cerebellar stimulation program normalizes the functioning of the brain stem and cerebellum. The technique improves:
- perception of oral and written speech
- rote reading skills
- math skills
- all types of memory
- sports skills
The results quickly manifest themselves in improved behavior, attention, speech of the child, and academic success. Cerebellar stimulation significantly increases the effectiveness of any correctional classes (with a speech therapist, psychologist, speech pathologist).
A cerebellar stimulation program may include the following techniques:
- exercises on the Posturograph - a device from Neurocom (USA), created to assess and train balance, coordination of movements, and muscle sense.
- Learning Breakthrough is Dr. Bilgo's balance board exercise system.
- exercises on the Wii Fit interactive platform.
Rhythmic transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS)
A method of treating diseases of the nervous system using short magnetic pulses. Indications
- delayed speech development,
- attention deficit hyperactivity disorder,
- autism,
- spasticity in cerebral palsy,
- some forms of epilepsy.
Principle of operation
There are two main modes of rTMS: low frequency and high frequency. With low-frequency magnetic stimulation (5 Hz) – an increase. Low frequency mode is used to treat some forms of epilepsy. Such stimulation of the epileptic focus reduces the frequency of seizures.
The high-frequency mode is used in cases where it is necessary to activate the functioning of certain cortical or subcortical areas of the brain and/or connections between them. When rTMS is performed in high-frequency mode, new functional connections are formed in the brain. The areas of the brain responsible for speech development are exposed to mild stimulation, which activates the activity of these areas, normalizes speech development, and also normalizes the development of cognitive processes (memory and attention).
In addition, the following positive changes are observed:
- the severity of neurotic symptoms decreases;
- tension, anxiety and fear are relieved;
- positive emotions arise;
- regeneration occurs faster in places where the pathways of the nervous system have been disrupted;
- vegetative instability decreases;
- blood pressure is normalized;
- improves sleep and mood; anxiety decreases;
- the feeling of fear and muscle tension decreases;
- resistance to stress increases.
The rTMS method is a painless and easily tolerated procedure that is performed by a neurologist or neurosurgeon.
Contraindications
The procedure is not performed if the patient has large metal objects in the body, a pacemaker or electronic implants, aneurysmal disease, or in the acute period of any disease.
Transcranial Micropolarization (TCMP)
The therapeutic effect of constant microcurrents on nerve cells of the brain.
Purpose
- children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)
- attention deficit
- patients with neuroses and neurosis-like conditions
- delays in mental and speech development
- behavioral and speech problems
- autism
- treatment of children with cerebral palsy
- as a rehabilitation therapy to eliminate the consequences of injuries and neuroinfectious diseases of the brain and spinal cord
Principle of operation
This is an effective method of “point” impact on individual areas of the brain that work “wrongly” or are unbalanced. A weak direct electric current of very small magnitude using small electrodes stimulates the work of individual parts of the brain, promotes the development of nervous tissue and the creation of new connections between nerve cells.
Since the effect is carried out locally, it is aimed only at those brain structures in which disturbances are observed, and does not affect healthy areas. Stimulation of brain cells using a weak electric current promotes the formation of new interneuron connections and the overall development of nervous tissue - which is why this method is successfully used in the treatment of the consequences of traumatic brain injuries and neuroinfectious diseases.
An individual treatment protocol is drawn up by a neurologist after examining the child and conducting functional diagnostics. During the procedure, a cap with wires is placed on the child’s head; the child does not experience any sensations and can do something: play, watch a cartoon, read a book, draw, etc.
Contraindications
- acute period of any disease.
Neurodynamic gymnastics (sensory integration)
About forty years ago, Jane Ayres, a speech therapist and psychologist from Oklahoma (USA), in the process of practical work came to the creation of a theory of dysfunction of sensory systems - the theory of sensory integration dysfunction. More than 70% of children who have any deviations in the development of speech, motor and emotional spheres, problems with learning, behavior, communication, have a disruption of the sensory systems.
No part of the central nervous system works on its own: information is transferred from one part to another. Touch helps to see, vision helps to maintain balance, balance helps to feel the position of the body in space and move, movement helps to learn.
Sufficient stimulation leads to an increase in the number of connections between brain cells.
From birth, children develop only if they are constantly stimulated by sensations from their own body and the environment.
This is a system of physical exercises and outdoor games aimed at developing sensorimotor integration - the brain’s ability to combine and process information coming from the senses.
Purpose
These activities are useful for almost all children, since sensorimotor integration is a mandatory stage in the mental development of every child.
Principle of operation
The formation of sensorimotor integration begins in the prenatal period of life on the basis of three basic systems: vestibular, proprioceptive (sensation of the relative position of body parts and their movement - the feeling of one’s body) and tactile.
Normally, this process should be completed at about 4 years of age, but for many children it occurs much later.
Modern children experience a deficit of motor activity, so their brain does not receive sufficient information about the position of the body in space. The process of formation of sensorimotor integration is disrupted. This interferes with the development of higher mental functions.
Classes are held in a special room where the child can receive various sensations necessary for the maturation of the nervous system.
Neurodynamic gymnastics are outdoor games using special equipment: swings of different shapes and sizes, roller boards, slides, trampolines and many other devices.
These are exercises to develop balance, tactile sensitivity, awareness of space and boundaries of your body, development of bilateral coordination, and proper breathing.
It is very important that the child is active during such activities, since sensorimotor integration is formed only during intentional movements.
This semi-structured interaction with an adult is very important for the development of emotions, thinking and brain-body connections.