4.1
Average rating: 4.1
Total ratings received: 2824.
4.1
Average rating: 4.1
Total ratings received: 2824.
Texts in Russian vary significantly in the choice of words and in their information content. How the text will look and what impression it will make depends on what style of speech we have chosen. We'll talk about speech styles.
The material was prepared jointly with a teacher of the highest category, Kuchmina Nadezhda Vladimirovna.
Experience as a teacher of Russian language and literature - 27 years.
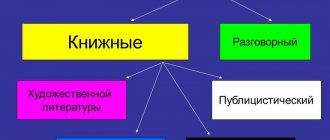
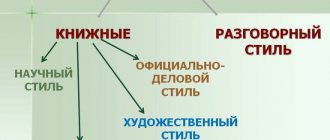
Formal business style
Document style. It is also used in writing. Approximate and abstract reasoning is unacceptable in it. This is the most regulated style.
The writer knows where and what to write, and such a clear structure is necessary to make it easier for people working with documents to navigate the multitude of papers, and also to avoid the possibility of double understanding and interpretation. A standard form, language clichés, etc. are used.
An example of a text in a formal business style would be a statement or memo.
The essence and types of communication
Definition 1
Communication is a complex, multifaceted process of establishing and developing contacts between individuals or groups of people, generated by their needs for joint activities and including three components: communication, interaction and perception.
Within the framework of communication, scientists identify three interconnected parties:
- Communication side (exchange of information between individuals);
- Interactive side (organization of interaction between individuals);
- The perceptual side (communication partners’ perception of each other, the formation of mutual understanding on this basis).
In the specialized literature one can see many different approaches to the classification of types of communication. In particular, based on the position of those communicating in communication, the following are distinguished:
Are you an expert in this subject area? We invite you to become the author of the Directory Working Conditions
- business conversation,
- formal or role communication,
- primitive communication,
- interpersonal communication,
- manipulative communication,
- secular communication.
Journalistic style
Newspaper style. He is characterized by special agitation. Its purpose is to influence the reader or listener. Expressive vocabulary and rhetorical figures (questions, exclamations, appeals, etc.) are used. Texts of public speeches, articles “on the topic of the day,” etc. are created in this style. Anyone who uses a journalistic style seeks to convince us of something, to shape public opinion. This is a rather expressive style; harsh statements, generalizations, puns, assessments, etc. are appropriate.
Conversational style
Conversation style. It uses a lot of colloquial words (but not curse words, etc., since this is a style of literary language, and slang and obscene language are outside its boundaries). The topics of the conversational style are the most ordinary, the sentences are short and expressive, the vocabulary is relaxed, succinct and colorful. We find the conversational style mainly in oral speech, its favorite form is dialogue. Signs of a conversational style include the significant role of non-linguistic means of expression: facial expressions, intonation, and the like.
The style of fiction can include, depending on the author's intention, elements of any style, or several styles, or even non-literary words (for example, slang).
Functional and semantic types of speech
Speech types are often mistakenly confused with speech styles. However, a functional speech style is a set of speech elements (words and ways of constructing sentences that are special for each speech style).
And the type of speech is the way of presentation, the construction of words and sentences in a logical order. Depending on the content of the text, the following types of speech are distinguished: narration, description, reasoning.
Let's consider the features of each type of speech.
A narrative is a story about an event that occurs in a certain period of time. The actions reflected in the event are sequential and logically related to each other. The narration can come from both the third person and the first, and it is characterized by such elements as the beginning (the beginning of the event), the development of the action and the denouement (the outcome of the event being described).
Since the narrative is an event text, its speech feature is a large number of verbs and a chain development of action. The text answers the questions “what? Where? When?" - What's happened? where and with whom did it happen? when did it happen?
The narration can be pictorial (the emphasis is on changing images that “show” the event) and informative (the text not only talks about the event, but also explains it and includes interesting facts).
Example of a narrative text:
“At night a strong wind rose and it started to rain. It quietly drummed on the roof and flowed down the glass, turning the world outside the window into a blur. Streams of water washed away dust from trees and sidewalks, gurgled in gutters, and cooled the city scorching from the summer heat. And those who were not sleeping opened the windows, inhaled the damp coolness and exposed their faces to the icy drops. The city had been waiting for rain for two months, and now that it came, people smiled silently, blessing the crying sky...”
An example text - a visual narrative - answers the following questions:
- What's happened? – it started to rain in the city;
- where and with whom did it happen? – city residents waited for the rain;
- when did it happen? - It started to rain in the summer.
Description is a verbal image of an object, phenomenon, event. The description lists and reveals the main features of the selected item. The goal is to present the reader of the text with an image that is easy to imagine in color. The unity of time and place of manifestation of signs is important.
The description text consists of the following parts:
- general characteristics of the item, general impression;
- signs, details;
- overall assessment of the subject.
For example, the description can be portrait, landscape; the object of writing can be anything - a person, his emotional state, an animal, a plant, a place (city, hotel house, park, village), and the weather. Speech feature – predominance of nouns, adjectives, adverbs, minimum action and static text.
Descriptive text answers the questions “which one?” which?" (what object is being described? what does it look like? what are its qualities and properties?).
Example of descriptive text:
“It rained for the third day. Gray, small and harmful. Unpredictable, like a low gray sky. Endless. Endless. He restlessly knocked on the windows and quietly rustled on the roof. Sullen and carefree. Annoying. Bored.”
Sample text answers descriptive questions:
- what object is being described? - rain;
- what is the subject? – gray, small, harmful, unpredictable, endless, etc.
Reasoning is the development and confirmation of thought, the explanation of a phenomenon (properties of an object) and the expression of one’s own opinion. Reasoning answers the questions “why?” For what?".
The reasoning consists of the following parts:
- thesis - an idea that needs to be proven;
- justification of the thesis, supporting argumentation with examples, evidence;
- summary – results, conclusions.
The text of the argument is aimed at convincing, explaining, proving. Reasoning is characterized by the active use of rhetorical questions and introductory words - connectives: firstly... secondly... thirdly... therefore (thus accordingly); meanwhile, because, so.
The reasoning is as follows:
- reasoning-proof (why is this and not otherwise? What follows from this?);
- reasoning-explanation (what is it? where did it come from? Why is the subject exactly like that?);
- reasoning-reflection (what to do? To be or not to be? What to do?).
An example of a reasoning text:
“So, the night will pass, and the rain will stop making noise, the thunder will die down. So, what is next? Again – the sweltering heat of a stuffy summer? Again – hot asphalt? Again - a city choking in dust? Or will the weather have mercy on tired city dwellers and give at least a week of coolness? Since the weather forecasters' predictions are vague and vague, we can only wait and watch.”
An example text – reasoning-reflection – answers the following questions:
- Why? – because the rain will stop and the heat that everyone is tired of will return;
- For what? - to imagine what to expect from the capricious nature.
Types of speech are methods of presentation that solve the following author’s tasks:
- narration – dynamically reflects reality, tells about its events; narration is a clip, a movie, a change of frames;
- description – depicts a static reality, studies the object of interest from all sides; the description is a photograph, a frozen frame;
- reasoning – looks for cause-and-effect relationships between events and phenomena, expresses the author’s opinion, “because...”; This is a diagram with blocks of theses and evidence and arrows - logical questions.
Reminder: Do not confuse functional speech styles with speech types. After all, for example, a newspaper article in a journalistic style of speech can be narrative (a report from the scene), and descriptive (a note about a missing person; an advertisement for a new building), and reasoning (an analytical article).
How to determine text style
Speech styles are studied by a special branch of linguistics - stylistics.
- To determine the style of speech in Russian, you need to pay attention to several signs: the purpose of the statement;
- vocabulary;
- form and genre;
- is it oral or written;
- who is the recipient of the text?
In addition, each style has some characteristics.
The table below shows speech styles and their features.
| Speech style | target | peculiarities | where is it used |
| Official business | Convey official, business information | Significant unification; special words - clerical words | document |
| Scientific | Provide scientific information | Exact numbers, a lot of information, terms | encyclopedia, textbook |
| Colloquial | Communication, transfer of ordinary information | Colloquial vocabulary, short sentences, simple syntax | oral speech |
| Journalistic | Convince the reader of something | Rhetorical figures, expressive vocabulary | newspaper, oral presentation |
| Art | Excite feelings and imagination with artistic images | Expressive means of language | literary work |
Diagnostics
Anyone can adjust their communication style in the right direction in order to establish harmonious relationships in a family or team. The beginning of such work is psychological testing, which helps to establish the individual’s real attitude towards others, his innate abilities and inclinations. There are many tests to determine personal communication style.
The most popular of them are:
- Test of interpersonal relationships by American psychologist Timothy Leary, created in 1950, adapted for the Russian-speaking environment by Lyudmila Sobchik. The purpose of the test is to determine the personal image of oneself and the predominance of the type of communication. The test consists of 2 parts and contains 128 statements about a person’s character. How he sees himself ideally and in the present period. The test can be used for personal assessment and for assessing a person “from the outside.” It is also possible to determine the degree of objectivity of self-assessment.
- The Persistence-Acquiescence Test is one of a series of interpersonal tests created by Hans Eysenck and Glen Wilson. The 210 questions have "yes" and "no" answer options. Using the test, the basic characteristics of an individual’s communication are determined: aggressiveness or flexibility, the ability to manipulate, the desire for leadership or subordination.
- “Diagnostics of communicative aggression” is a technique developed by Russian psychologist Viktor Boyko. The test allows you to determine the degree of aggressiveness in a relationship and the ability to switch. The “Aggression Index” is based on 11 parameters.
- “Diagnostics of the type of communicative attitude” was created under the leadership of Viktor Boyko to determine the presence and magnitude of the manifestation of negative attitudes in communication. The test consists of 25 questions that have “yes” and “no” answer options.
- The Interpersonal Relations Questionnaire by the American psychologist William Schutz is designed to determine the communicative characteristics of a person.
- The SMIL test was developed according to the basic method of L. Sobchik creates a complete psychological portrait of a person, including his communication styles. To get complete information about yourself you need to spend time and answer 567 questions. But there is also a shortened version of 65 questions.
Nowadays, you can take many tests and get results within a few minutes on the Internet online for free. The disadvantage of such studies is that a person who is not a specialist in the field of psychology cannot always objectively evaluate the test results. For serious research, it is better to contact a professional consultation center.
Psychological centers often conduct diagnostics of styles and other components of communication in the business sphere. Such services can be ordered by companies to assess the level of employees, or by individuals. The cost of services depends on the choice of specialist and the range of studies. The approximate initial cost of one test with comments from a psychologist is about 1,500 rubles.