Preparation of the articulatory apparatus
Doing various speech gymnastics is very important for a child. Examples of articulation exercises that are recommended to be performed in front of a mirror:
- make a fence of teeth and smile;
- blow on soap bubbles, cotton balls, fluff, floating toys in the water;
- whistle into sticks;
- make a “spatula”: the tongue lies in a wide position on the lower lip (hold for a few seconds);
- “tube” exercise: open your mouth and curl your tongue into a tube, then blow into it for a long time.
In the Russian language, there are 42 speech sounds, or, to use another term, 42 phonemes (from the Greek word phonema, which means “speech sound”).
According to the mechanism of formation, phonemes are divided primarily into vowels and consonants (6 vowels and 36 consonants).
All vowels are characterized by phonation (voice formation), caused by vibration of the vocal cords, and the free passage of exhaled air through the oral cavity.
Consonants are characterized by the formation in the oral cavity of barriers to the path of exhaled air, either in the form of a stop of certain speech organs, or in the form of more or less narrow slits and passages formed by them, or, finally, in the form of a sequential connection of a stop with a gap. When some consonant phonemes are formed, these barriers are combined with phonation; when others are formed, phonation is absent.
The articulatory classification of vowels is built taking into account:
1) participation or non-participation of the lips. In the articulation of the vowels o and u, in addition to the tongue, the lips take an active part, which move forward and round when pronouncing these phonemes. Therefore, the vowels o, u are called labialized (from the Latin labia - lips), and all other vowels are called non-labialized;
2) the degree of elevation of the tongue to the palate (upper, middle and lower elevation);
3) places where the tongue rises (front, middle and back row).
There are six vowel sounds in modern Russian: [a], [o], [u], [e], [i], [s]. The different quality of vowels, which we perceive by ear as different sounds, depends on the volume and shape of the oral cavity during the formation of vowels. The volume and shape of the oral cavity are determined by the movement of the tongue and lips - the active organs of pronunciation. Depending on the movement of the tongue in the horizontal direction (back and forth), vowels are divided into: 1) front vowels [i], [e] (when pronounced, the tongue moves forward, and its tip rests on the lower teeth); 2) middle vowels [ы], [а] (when pronouncing them, the tongue moves slightly back); 3) back vowels [у], [о] (when pronouncing them, the tongue moves back to a greater extent).
Depending on the degree of elevation of the tongue to the palate, i.e., vertical movement of the tongue, the following are distinguished: 1) vowels of the upper rise [i], [s], [y] (when they are formed, the tongue is raised to the palate to the greatest extent); 2) vowels of medium rise [e], [o] (when they are formed, the tongue rises less high to the palate); 3) lower vowels, which include only [a] (when it is formed, the tongue is not raised or raised to a minimal extent, the lower jaw is lowered and the mouth is wide open).
VOWEL CLASSIFICATION
| Participation of lips | Unrounded | Ruined | ||
| Row | Front | Average | Rear | |
| Climb | Upper | AND | Y | U |
| Average | E | ABOUT | ||
| Lower | A |
The articulatory classification of consonants is based on five main features:
1) the presence or absence of vibration of the vocal folds;
2) method of articulation;
3) place of articulation;
4) the presence or absence of additional elevation of the back of the tongue to the hard palate;
5) place of resonance.
Based on the first sign (the presence or absence of vibration of the vocal folds), consonants are divided into:
1) voiced, in the formation of which the tone of the voice is combined with a pronounced noise: b, b', d, d', g, g', c, c', z, z', g, g';
2) sonorous (from the Latin sono - sound), in the formation of which there is almost no noise and the tone of the voice predominates: l, l', p, p', m, m', n, n', and (j),
3) deaf, in the formation of which only noise is involved: p, p', t, t', k.k', f, f', s, s', x, c, ch', sh, shch.
According to the second criterion (according to the method of articulation), consonants are divided into:
1) stops - stop-plosives: b, b', p, p', d, d', t, t', g, g', k, k' and stop-plosives: m, m', n, n ',l,l';
2) fricatives (fricatives): v,v', f,f', z,z', s,s', sh, zh, shch, x,x', and (j),
3) affricates: c, h';
4) trembling: p, p'.
According to the third criterion (place of articulation), consonants are divided into:
1) labial - labiolabial: m, m', p, p', b, b' and labiodental: f, f', v, v'.
2) lingual - lingual-dental: t, t', d, d", n, n', s, s', z, z', c; lingual-alveolar: l,l', p,p'; lingual-anteropalatal: w, g, h, sch; lingual-mid-palatal: k', g', x', 'th (j); posterior lingual (back palatal): g, k, x.
According to the fourth characteristic (by the presence or absence of elevation of the back of the tongue), consonants are divided into:
1) hard: hard pairs of all consonants, except h, sch;
2) soft: soft pairs of all consonants, except sh, zh, c.
According to the fifth criterion (according to the place of resonance), consonants are divided into:
1) nasals: m, m', n, n';
2) oral: all other consonants.
CLASSIFICATION OF CONSONANTS
| Oral or nasal resonating | Degree of voice and noise involvement | Place of education Method of education | Labial | lingual | |||||||||||||
| Labiolabial | Labiodental | Lingual-dental | Lingual-alveolar | Lingual-anteropalatal | Lingual-mid-palatal | Lingual-posterior palatal | |||||||||||
| TV | m | TV | m | TV | m | TV | m | TV | m | TV | m | TV | m | ||||
| Oral Nasal | Noise | Call | Occlusive | B | B' | — | — | D | D' | — | — | — | — | — | G' | G | — |
| Deaf | |||||||||||||||||
| P | P' | — | — | T | T' | — | — | — | — | — | TO' | TO | — | ||||
| Call | Slotted | — | — | IN | IN' | Z | Z' | — | — | AND | — | — | Y | — | — | ||
| Deaf | |||||||||||||||||
| — | — | F | F' | WITH | WITH' | — | — | Sh | SCH | — | X' | X | — | ||||
| Call | Occlusion-slit | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||
| Deaf | — | — | — | — | C | — | — | — | — | H' | — | — | — | — | |||
| Sonora | Trembling | — | — | — | — | — | — | R | R' | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||
| Connectively-passing | — | — | — | — | — | — | L | L' | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||
| Sonora | Connectively-passing | M | M' | — | — | N | N' | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
Sound production technique C
You can make the sound “C” in different ways:
- imitating;
- mechanically;
- with the help of articulatory gymnastics;
- using other sounds.
In order to make the sound “C” by imitation, you need to practice in front of a mirror and show your baby the correct position of the tongue and lips. The child should feel the cool exhaled air while pronouncing a consonant - put his palm to his mouth.
The mechanical method involves the use of auxiliary devices: a probe, a spatula. At home, a mild toothpick or ice cream stick is suitable for use.
Procedure:
- The object must be placed along the tongue, fixing its correct position for pronunciation.
- The child should smile and place the edge of the tongue on the lower incisors. You need to blow through the resulting gap.
- Pressing the object along the tongue forms a groove along which a stream of air flows. A whistle should be heard.
- The tongue should be hidden behind the teeth, and the teeth should be brought together.
- The child continues to whistle, and the parent (speech therapist) adjusts the pressure, achieving the correct and clear sound pronunciation of “C”.
- As soon as the sound begins to sound clearly, remove the mechanical object.
After several such trainings, the child can independently control his tongue, positioning it correctly in the oral cavity, and whistle.
When setting “C”, you can use other sounds.
- When pronouncing the soft “Сь”, it is necessary to press with a mechanical device on the front part of the tongue to form a groove - the hard sound “C” is pronounced. This option is practiced several times until the tongue learns to lie correctly;
- you need to say “T” for a long time, while smiling, stretching your lips. To make the “C” sound clear, you need to smile wider;
- when the baby pronounces “Sh” correctly, you need to hiss for a long time, while moving your tongue towards the front teeth (the sound “S” will be heard);
- ask the child to pull “I”, then start blowing, releasing a stream of air along the groove that has formed (the tongue is in the same place).
profiles
Diagram 1. Sound
And buKVE A
Features of articulation. The mouth is wide open. The lips are calm (not tense or rounded). The tip of the tongue is located at the lower teeth, the tongue is flat. The exhaled air does not meet any obstacles in the mouth. The vocal cords are working, the throat is trembling (there is a voice). Characteristic. The sound [A] is a vowel.
Letter color designation. The letter is colored red.
Scheme 2. Sound I letter O
Features of articulation.
The lips are rounded and pushed forward.
The tip of the tongue moves slightly away from the lower teeth, the back of the tongue is raised. The exhaled air does not meet any obstacles in the mouth. The vocal cords are working, the throat is trembling (there is a voice). Characteristic.
The sound [O] is a vowel.
Letter color designation.
The letter is colored red.
Diagram 3. Sound
And buKVE
U
Features of articulation. The lips are rounded and strongly pushed forward. The tip of the tongue extends from the lower teeth, the back of the tongue is curved. The exhaled air does not meet any obstacles in the mouth. The vocal cords are working, the throat is trembling (there is a voice). Characteristic. The sound [U] is a vowel.
Letter color designation. The letter is colored red.
Scheme 4. Sound I letter Y
Features of articulation. The lips are slightly stretched. The teeth are visible. The tip of the tongue extends from the lower teeth, the back of the tongue is strongly arched. The exhaled air does not meet any obstacles in the mouth. The vocal cords are working, the throat is trembling (there is a voice). Characteristics Sound [Y] - vowel.
Letter color designation. The letter is colored red.
Diagram 6. Sound
And
the letter
P
Features of articulation. The lips are closed and open under the pressure of exhaled air. The tip of the tongue extends slightly from the lower teeth. The tongue is flat.
The vocal cords are resting, the throat is not trembling (no voice). Characteristic. The sound [P] is a hard, voiceless consonant. Letter color designation. The letter is colored blue.
Diagram 7. Sound I letter B
Features of articulation.
The lips are closed and open under the pressure of exhaled air.
The tip of the tongue extends slightly from the lower teeth. The tongue is flat. The vocal cords are working, the throat is trembling (there is a voice). Characteristic.
The sound [B] is a hard voiced consonant.
Letter color designation.
The letter is colored blue.
Diagram 8. Sound I letter T
Features of articulation. The tip of the tongue is pressed against the upper teeth, the back of the tongue is lowered. Under the pressure of exhaled air, the tongue comes off the teeth. The vocal cords are resting, the throat is not trembling (no voice). Characteristics The sound [T] is a hard, voiceless consonant. Letter color designation. The letter is colored blue.
Diagram 9. Sound
And
the letter D
Features of articulation.
The tip of the tongue is pressed against the upper teeth, the back of the tongue is lowered.
Under the pressure of exhaled air, the tongue comes off the teeth. The vocal cords are working, the throat is trembling (there is a voice). Characteristic.
The sound [D] is a hard voiced consonant.
Letter color designation.
The letter is colored blue.
Diagram 10. Sound
And
the letter C
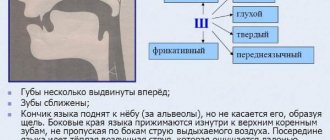
Features of articulation.
The teeth are close together.
The lips are slightly stretched. The tip of the tongue rests on the lower teeth, the back is arched. The vocal cords are resting, the throat is not trembling (no voice). Characteristic.
The sound [S] is a hard, voiceless consonant.
Letter color designation.
The letter is colored blue.
Scheme 11. Sound AND letter 3
Features of articulation.
The teeth are close together.
The lips are slightly stretched. The tip of the tongue rests on the lower teeth, the back is arched. The vocal cords are working, the throat is trembling (there is a voice). Characteristic.
Sound [3] is a hard voiced consonant.
Letter color designation.
The letter is colored blue.
Diagram
12. Sound I letter
K
Features of articulation.
The tip of the tongue extends slightly from the lower teeth, the back of the tongue is curved steeply and touches the palate.
Under the pressure of exhaled air, the back of the tongue comes off the palate. The vocal cords are resting, the throat is not trembling (no voice). Characteristic.
The sound [K] is a hard, voiceless consonant.
Letter color designation.
The letter is colored blue.
Diagram 13. Sound
And
the letter G
Features of articulation
The tip of the tongue extends slightly from the lower teeth, the back of the tongue is curved steeply and touches the palate.
Under the pressure of exhaled air, the back of the tongue comes off the palate. The vocal cords are working, the throat is trembling (there is a voice). Characteristic.
The sound [G] is a hard voiced consonant.
Letter color designation.
The letter is colored blue.
Diagram 14. Sound I letter F
Features of articulation.
The lower lip is slightly retracted and pressed against the upper teeth, the upper lip is slightly raised. The upper teeth are visible. The tip of the tongue extends slightly from the lower teeth, the tongue is flat. The exhaled air breaks into the gap between the upper teeth and lower lip. The vocal cords are resting, the throat is not trembling (no voice).
Characteristic.
The sound [F] is a hard, voiceless consonant.
Letter color designation.
The letter is colored blue.
Diagram 15. Sound
And
the letter B
Features of articulation. The lower lip is slightly retracted and pressed against the upper teeth, the upper lip is slightly raised. The upper teeth are visible. The exhaled air breaks into the gap between the upper teeth and lower lip. The vocal cords are working, the throat is trembling (there is a voice). Characteristic. The sound [B] is a hard voiced consonant. Letter color designation. The letter is colored blue.
Diagram 16. Sound
And the letter Ш
Features of articulation.
The lips are pushed forward and rounded. The tip of the tongue is raised towards the front of the palate, but does not touch it. The lateral edges of the tongue are pressed against the upper molars. The back of the tongue is raised. The shape of the tongue resembles a cup.
The vocal cords are resting, the throat is not trembling (no voice). Characteristic.
The sound [Ш] is always a hard, voiceless consonant.
Letter color designation.
The letter is colored blue.
Diagram 17. Sound
And
the letter Z
Features of articulation. The lips are pushed forward and rounded. The tip of the tongue is raised towards the front of the palate, but does not touch it. The lateral edges of the tongue are pressed against the upper molars. The back of the tongue is raised. The shape of the tongue resembles a cup.
The vocal cords are working, the throat is trembling (there is a voice). Characteristic. The sound [Zh] is always a hard voiced consonant. Letter color designation. The letter is colored blue.
Diagram 18. Sound I letter Ch
Features of articulation.
The lips are slightly pushed forward and rounded. The tip of the tongue touches the palate (behind the tubercles). The lateral edges of the tongue are pressed tightly against the upper molars. The back of the tongue is raised. Under the pressure of exhaled air, the tip of the tongue comes off the palate. The vocal cords are resting, the throat is not trembling (no voice).
Characteristic.
The sound [H] is always a soft, dull consonant.
Letter color designation.
The letter is colored green.
Diagram 19. Sound I letter Ш
Features of articulation.
The lips are slightly pushed forward and rounded. The tip of the tongue is raised to the cusps behind the upper teeth. The lateral edges of the tongue are pressed tightly against the upper molars. The back of the tongue is raised. The tongue is tense. The vocal cords are resting, the throat is not trembling (no voice).
Characteristic.
The sound [Ш] is always a soft, voiceless consonant.
Letter color designation.
The letter is colored green.
Diagram 20. Sound I letter C
Features of articulation.
Initially, the back of the tongue is sharply curved and touches the tubercles behind the upper teeth, the tip of the tongue rests on the lower teeth.
Then the back of the tongue lowers to the position occupied when pronouncing the sound [C], and the tip of the tongue remains in place. The vocal cords are resting, the throat is not trembling (no voice). Characteristic.
The sound [Ц] is always a hard, voiceless consonant.
Letter color designation.
The letter is colored blue.
Diagram 21. Sound I letter M
Features of articulation. The lips are closed and do not open, the exhaled air passes through the nose. The tip of the tongue extends slightly from the lower teeth, the tongue is flat.
The vocal cords are working, the throat is trembling (there is a voice). Characteristic. The sound [M] is a hard voiced consonant. Letter color designation. The letter is colored blue.
Diagram 22. Sound I letter N
Features of articulation.
The tip of the tongue is pressed against the upper teeth, the back of the tongue is lowered.
The exhaled air passes through the nose. The vocal cords are working, the throat is trembling (there is a voice). Characteristic.
Sound (Н] - a hard voiced consonant.
Letter designation by color.
The letter is colored blue.
Diagram 23. Sound
And buKVE X
Features of articulation.
The tip of the tongue moves slightly away from the lower teeth, the back of the tongue is curved steeply.
The vocal cords are resting, the throat is not trembling (no voice). Characteristic.
The sound [X] is a hard voiceless consonant.
Letter color designation.
The letter is colored blue.
Diagram 24. Sound
And the letter L
Features of articulation.
The tip of the tongue rests on the upper teeth or on the cusps behind the upper teeth. The middle part of the back of the tongue is lowered, the back of the back of the tongue is raised, the lateral edges of the tongue are lowered. The shape of the tongue resembles a saddle. The exhaled air passes along the sides of the tongue. The vocal cords are working, the throat is trembling (there is a voice).
Characteristic.
The sound [L] is a hard voiced consonant.
Letter color designation.
The letter is colored blue.
Diagram 25. Sound
And
the letter P
Features of articulation.
The tip of the tongue touches the cusps behind the upper teeth.
The lateral edges of the tongue are pressed against the upper molars. The shape of the tongue resembles a spoon. The tip of the tongue trembles under the pressure of exhaled air. The vocal cords are working, the throat is trembling (there is a voice). Characteristic.
The sound
[R]
is a hard voiced consonant.
Letter color designation.
The letter is colored blue.
Diagram 26. Sound [YA]
And
the letter I
Features of sound articulation
[Y]. The lips are stretched into a smile. The teeth are visible. The tip of the tongue is pressed against the lower teeth, the back of the tongue is curved steeply.
The vocal cords are working, the throat is trembling (there is a voice).
Features of sound articulation [A].
The mouth is wide open. The lips are calm (not tense or rounded). The tip of the tongue is located at the lower teeth, the tongue is flat.
The exhaled air does not meet any obstacles in the mouth. The vocal cords are working, the throat is trembling (there is a voice).
Characteristic.
The sound [YA] is a vowel.
Letter color designation.
The letter is colored red.
Diagram 27. Sound [YO]
And buKVE E
Features of sound articulation
[Y]. The lips are stretched into a smile. The teeth are visible. The tip of the tongue is pressed against the lower teeth, the back of the tongue is curved steeply. The vocal cords are working, the throat is trembling (there is a voice).
Features of sound articulation [O].
The lips are rounded and pushed forward. The tip of the tongue moves slightly away from the lower teeth, the back of the tongue is raised. The exhaled air does not meet any obstacles in the mouth. Vocal cords work, throat trembles (there is a voice)
Characteristic.
The sound [YO] is a vowel.
Letter color designation.
The letter is colored red.
Diagram 28. Sound [YU] AND letter
Features of sound articulation
[Y]. The lips are stretched into a smile. The teeth are visible. The tip of the tongue is pressed against the lower teeth, the back of the tongue is curved steeply.
The vocal cords are working, the throat is trembling (there is a voice).
Features of sound articulation [U].
The lips are rounded and strongly pushed forward. The tip of the tongue extends from the lower teeth, the back of the tongue is curved.
The exhaled air does not meet any obstacles in the mouth. The vocal cords are working, the throat is trembling (there is a voice).
Characteristic.
The sound [YU] is a vowel.
Letter color designation.
The letter is colored red.
Diagram 29. Sound
And
the letter I
Features of articulation.
The lips are stretched into a smile.
The teeth are visible. The tip of the tongue is pressed against the lower teeth, the back of the tongue is strongly arched. The exhaled air does not meet any obstacles in the mouth. The vocal cords are working, the throat is trembling (there is a voice). Characteristic.
The sound [I] is a vowel.
Letter color designation.
The letter is colored red.
Scheme zo. Sound [Y E] and letter E
Features of sound articulation
[Y]. The lips are stretched into a smile. The teeth are visible. The tip of the tongue is pressed against the lower teeth, the back of the tongue is curved steeply.
The vocal cords are working, the throat is trembling (there is a voice).
Features of sound articulation [E].
The lips are stretched into a smile. The tip of the tongue is located at the lower teeth, the back of the tongue is raised.
The exhaled air does not meet any obstacles in the mouth. The vocal cords are working, the throat is trembling (there is a voice).
Characteristic.
The sound [YE] is a vowel.
Letter color designation.
The letter is colored red.
Diagram 31. Sound [P']
Features of articulation.
The lips are closed and open under the pressure of exhaled air. The tip of the tongue is pressed against the lower teeth, the back of the tongue is arched. The vocal cords are resting, the throat is not trembling (no voice).
Characteristic.
The sound [P'] is a soft, voiceless consonant.
Letter color designation.
The letter is colored green.
Diagram 32. Sound
[B ' ]
Features of articulation.
The lips are closed and open under the pressure of exhaled air.
The tip of the tongue is pressed against the lower teeth, the back of the tongue is arched. The vocal cords are working, the throat is trembling (there is a voice). Characteristic.
The sound [B'] is a soft voiced consonant.
Letter color designation.
The letter is colored green.
Diagram 33. Sound [T']
Features of articulation. The tip of the tongue rests on the lower teeth, the back of the tongue is curved into a steep hill and is pressed with the front part against the tubercles behind the upper teeth. Under the pressure of exhaled air, the front part of the tongue comes off the tubercles.
The vocal cords are resting, the throat is not trembling (no voice). Characteristic. The sound [G] is a soft, dull consonant. Letter color designation. The letter is colored green.
Features of articulation.
The tip of the tongue rests on the lower teeth, the back of the tongue is curved into a steep hill and is pressed with the front part against the tubercles behind the upper teeth. Under the pressure of exhaled air, the front part of the tongue comes off the tubercles.
The vocal cords are working, the throat is trembling (there is a voice). Characteristic.
The sound [D'] is a soft voiced consonant.
Diagram 34. Sound
[D'] Letter color designation.
The letter is colored green.
Diagram 35. Sound
[С']
Features of articulation.
The teeth are close together.
The lips are stretched into a smile. The tip of the tongue rests on the lower teeth, the back of the tongue is arched. The vocal cords are resting, the throat is not trembling (no voice). Characteristic.
The sound [С'] is a soft, voiceless consonant.
Letter color designation.
The letter is colored green.
Diagram 36. Sound [3′]
Features of articulation.
The teeth are close together.
The lips are stretched into a smile. The tip of the tongue rests on the lower teeth, the back of the tongue is arched. The vocal cords are working, the throat is trembling (there is a voice). Characteristic.
The sound [3′] is a soft voiced consonant.
Letter color designation.
The letter is colored green.
Diagram 37. Sound
[K']
Features of articulation.
The tip of the tongue is pressed against the lower teeth. The back of the tongue is curved steeply and touches the palate. Under the pressure of exhaled air, the back of the tongue comes off the palate.
The vocal cords are resting, the throat is not trembling (no voice). Characteristic.
The sound [K'] is a soft, voiceless consonant.
Letter color designation.
The letter is colored green.
Diagram 38. Sound
[G']
Features of articulation.
The tip of the tongue is pressed against the lower teeth.
The back of the tongue is curved steeply and touches the palate. Under the pressure of exhaled air, the back of the tongue comes off the palate. The vocal cords are working, the throat is trembling (there is a voice). Characteristic.
The sound [G'] is a soft voiced consonant.
Letter color designation.
The letter is colored green.
Diagram 39. Sound
[F']
Features of articulation.
The lower lip is slightly retracted and pressed against the upper teeth, the upper lip is slightly raised. The upper teeth are visible. The tip of the tongue is pressed against the lower teeth, the back of the tongue is arched. The exhaled air breaks into the gap between the upper teeth and lower lip. The vocal cords are resting, the throat is not trembling (no voice).
Characteristic.
The sound [F'] is a soft, voiceless consonant.
Letter color designation.
The letter is colored green.
Diagram 40. Sound [B']
Features of articulation. The lower lip is slightly retracted and pressed against the upper teeth, the upper lip is slightly raised. The upper teeth are visible. The tip of the tongue is pressed against the lower teeth, the back of the tongue is arched. The exhaled air breaks into the gap between the upper teeth and lower lip. The vocal cords are working, the throat is trembling (there is a voice).
Characteristics Sound [B'] is a soft voiced consonant.
Letter color designation. The letter is colored green.
Diagram 41. Sound
[ M ' ]
Features of articulation. The lips are closed and do not open, the exhaled air passes through the nose. The tip of the tongue is pressed against the lower teeth, the back of the tongue is arched. The vocal cords are working, the throat is trembling (there is a voice).
Characteristic. The sound [M'] is a soft voiced consonant. Letter color designation. The letter is colored green.
Diagram 42. Sound [Н' ]
Features of articulation. The tip of the tongue rests on the lower teeth, the back of the tongue is curved into a steep hill and is pressed with the front part against the tubercles behind the upper teeth. The exhaled air passes through the nose. The vocal cords are working, the throat is trembling (there is a voice). Characteristics The sound [Н'] is a soft voiced consonant. Letter color designation. The letter is colored green.
Diagram 43. Sound [L']
Features of articulation.
The lips are stretched into a smile. The front of the tongue touches the cusps behind the upper teeth. The middle part of the back of the tongue is raised. The back of the back of the tongue is lowered. The tongue is tense. The exhaled air passes along the sides of the tongue.
Automation C in syllables
After exercises to train the articulatory apparatus (with regular practice), syllables with the sound “C” are given (repeated 3 times): -sa, -so, -su, -sy, -as, -ys, -os, -us, -is, -es, -es, -yus, -yas.
Then the syllables are combined with each other:
- -sy-sa-so;
- -sa-sy-su;
- -sa-sy-sa;
- -sy-sa-sy;
- -sa-sa-sy-sy.
The exercises are gradually complicated by other consonants:
| SK CM ST JV CH NE | A - ska, sma, sta, spa, sleep, sva |
| U - sku, smu, stu, spu, snu, swo | |
| O - sko, smo, hundred, spo, sno, svo | |
| Y - skis, smas, sts, spas, dreams, svy | |
| And - ski, media, sti, sleep, sleep, swee |
Taking this criterion into account, the following types of dysgraphia can be distinguished:
1. Articulatory-acoustic dysgraphia is a form of dysgraphia associated with a disorder of oral speech.
The mechanism of this type of dysgraphia is the incorrect pronunciation of sounds, which is reflected in writing: the child writes words the way he pronounces them.
Pronunciation deficiencies are reflected in writing only if they are accompanied by impaired auditory differentiation and unformed phonemic representations.
Articulatory-acoustic dysgraphia manifests itself in mixtures, substitutions, and omissions of letters, which correspond to mixtures, substitutions, and absence of sounds in oral speech.
2. Dysgraphia against the background of impaired phoneme recognition (phoneme differentiation) - acoustic dysgraphia .
This type of dysgraphia manifests itself in substitutions, omissions of letters denoting phonetically similar sounds, in violation of the designation of soft consonants in writing, more often in writing letters denoting whistling and hissing, voiced and voiceless, affricates and components included in their composition are mixed (B-P, D-T, S-Z, and others, CH-TH, CH-SH, C-T, C-S, S-SH, Z-Zh, as well as the vowels O-U, E-I).
The mechanism of acoustic dysgraphia is associated with inaccurate auditory differentiation of sounds. At the same time, children's pronunciation is normal. Inaccuracy of kinesthetic images of sounds, which prevents the correct choice of phoneme and its correlation with the letter.
3. Dysgraphia due to impairment of language analysis and synthesis.
The mechanism of dysgraphia due to a violation of language analysis and synthesis is a violation of the following forms of language analysis and synthesis:
- dividing sentences into words,
- syllabic and phonemic analysis and synthesis.
The lack of structure in the analysis of sentences into words is revealed in the continuous spelling of words, especially prepositions, and in the separate spelling of words, especially prefixes and roots.
Distortions of the sound-letter structure of a word due to the immaturity of phonemic analysis and synthesis, which is the most complex form of language analysis.
4. Agrammatic dysgraphia.
This type manifests itself in agrammatisms in writing, due to the immaturity of the lexico-grammatical structure of speech. Agrammatisms in writing manifest themselves at the level of words, phrases, sentences and text.
5. Optical dysgraphia.
It is caused by the immaturity of visual-spatial functions: visual gnosis, visual analysis and synthesis, spatial representations.
With optical dysgraphia, the following types of writing disorders are observed: distorted reproduction of letters in writing, replacement and mixing of graphically similar letters, most often letters that differ in one element are mixed (P-T, L-M, I-Sh,) or letters consisting of identical or similar elements, but differently located in space (V-D, E-S), mirror writing of letters, writing from right to left.
I offer you, from my work experience, a lesson summary on the topic: “Automation of the sound “C” and the letter “C”. The lesson can be used in speech therapy classes for the correction of reading and writing in primary schoolchildren who have articulatory-acoustic dysgraphia with elements of dysgraphia due to a violation of language analysis and synthesis.
Automation C at the beginning of a word
The adult says and the child repeats the following words:
- Savva, kindergarten, saga, barn, glanders, soot, saury, lard, centimeter, carp, satin, orderly, net, plane, sundress, most, Sasha.
- Full, son, sprinkle, son, rash, cheese, cheese.
- Advice, juice, essay, neighbor, dream, honeycomb, variety, owl, soloist, Sofia, salt, soldier.
- Joint, soup, land, court, sultan, judge, dryness, cloth, cracker, marmot, sum, souvenir, bag, supermerket, Saturday.
- Sit down, sister, gray, seven, second, Seva, village, saddle, Seryozha.
- Symbol, sieve, bruise, lilac, syrup, strength.
The words become more complex (there are other consonants next to the “S” sound): I’ll reduce, I’ll cook, my own, country, stop, jump, go down, follow, rolling pin, senior, boring, savvy, urgent, back, sleep, average, bullfinch, cream, snow, tears, sing, Sveta, descent, whistle, pig, laughter, sour cream, brave, change, trace, saliva, wash off, crumpled, dispute, calm, slope, shooter, how much, sell, syllable, puff pastry, rumor.
Automation C in sentences
To practice pure pronunciation, the child should repeat the sentences. This exercise is considered difficult.
- The soup is carried in a bowl.
- They brought pine from the forest.
- A lumberjack cut down a pine tree.
- An owl sleeps at the very top of the pine tree.
- Sasha’s parents will buy new dishes on Saturday.
- Lucy was painting a plane.
- A branch has dried up on the tree.
- There is a pike perch in the bag.
- Catfish have whiskers.
- Sasha bought scales.
- Aunt Sonya brought new beads.
- Sveta has a beautiful headscarf.
- Our gas went out again. And you?
- Who's carrying the tray?
- Lucy buys a pineapple.
- The sailor raises the sail.
- Nastya loves iris.
- We brought the cat food and called her: “Kitty-kitty.”
- Kostya and Seryozha go into the forest.
- A chair was placed at the table.
- Storks were sitting in the bushes.
- Nastya came backstage wearing a dog mask.
- We will have many guests today.
- Styopa loves to blow the whistle.
- Today we noticed tracks of a moose and a fox in the snow.