The science of speech therapy deals with the detailed study and development of speech.
The term denoting this direction of scientific knowledge is of Greek origin; it was formed by merging two words: “speech” (logos) and “education, teaching” (paideia). Thus, the term itself reveals the essence of speech therapy and its focus. In addition to speech education, this science, being one of the branches of special pedagogy, pays special attention to speech defects, the causes of their occurrence, their mechanisms, symptoms and course. Speech therapy studies pathological deviations of speech development and speech activity in order to find new methods and programs for training people with similar defects to produce correct speech.
The object of study of speech therapy are persons who have been diagnosed with any speech abnormalities (except for physiological deficiencies). Like any other area of scientific study, speech therapy has its own principles, objectives, methods and programs for training individuals with identified speech disorders.
When did the direction originate?
The history of speech therapy does not have an exact date of origin, but goes back several thousand years. We can distinguish four stages in the development of this direction (independent today) of correctional pedagogy. As the industry's development trend demonstrates, it was formed on the basis of knowledge acquired by medicine and pedagogy, and therefore has a direct connection with them.
Scientific knowledge of speech disorders and the discovery of methods for their correction began not so long ago, when medicine became aware of the basic mechanisms of the anatomical and physiological aspects, thanks to which a person is able to carry out speech activity. Around the middle of the 19th century, the first notes appeared on the theory of speech disorders, the author of which was the neuropathologist P. Brock. A little later, another neurologist, K. Wernicke, published his scientific work describing the center of the sensory side of speech capabilities.
We recommend: Stuttering: causes and treatment
Both of these works gave rise to much controversy and debate regarding the mechanisms that support the speech system. It is worth noting that this scientific conflict has become an excellent pretext for collecting new data and knowledge about possible disorders of human speech activity.
In this regard, the results of studies of speech disorders gradually began to appear, which were carried out for experimental purposes not only by neurologists, but also by linguists, psychologists, physiologists, teachers and other specialists.
Thus, speech therapy as a science arose gradually, against the backdrop of the development and improvement of other sciences. And now, being an independent branch of correctional pedagogy, speech therapy is not isolated from other areas. Moreover, it closely interacts with other areas of scientific knowledge of individuals.
In the vastness of Russia, a breakthrough in the development of speech therapy was the event when the state decided to provide assistance to children with speech disorders. In the not-so-distant year 1917, special decrees were issued on the need to include preschool and school institutions (including private ones) in the general education system of the Soviet people.
We recommend: Science defectology
Leading Soviet authorities were involved in the coordination of these documents. Thanks to these decrees, which encouraged the government to take a closer look at the issue of providing assistance to children with speech defects (including abnormal ones), fundamental changes were laid in the field of organizing educational and training processes.
Article on the topic: "Glossary of speech therapy terms to help teachers, educators, parents."
Glossary of speech therapy terms to help teachers, educators, parents
Automation sound
a – the stage of correcting incorrect sound pronunciation, following the stage of setting a new sound, aimed at forming the correct pronunciation of the sound and introducing the set sound into syllables, words, sentences, and independent speech.
Agrammatism
is a violation of the understanding and use of grammatical means of a language.
Agraphia
is a speech disorder expressed in writing impairment, complete loss of writing ability.
Alexia
is a complete inability or loss of the ability to master the reading process.
The articulatory apparatus
is a set of organs that ensure the formation of speech sounds (articulation);
includes the vocal apparatus, muscles of the pharynx, larynx, tongue, soft palate, lips, cheeks, lower jaw, teeth. Gammacism
is a violation of the pronunciation of the sounds G, Gb.
The grammatical structure of speech
is the structure of words and sentences inherent in a given language.
Bilingualism
is equal proficiency in two languages.
Dysarthria
is a violation of the pronunciation side of speech, caused by a violation of the innervation of the speech apparatus.
Dysgraphia
is a specific disorder of written speech that manifests itself in persistent errors.
Dyslalia
is a violation of sound pronunciation with normal hearing and intact innervation of the speech apparatus.
Dyslexia
is a partial disorder of the reading process, manifested in repeated errors of a persistent nature.
Innervation
is the provision of organs and tissues with nerves and, therefore, communication with the central nervous system.
Kappacism
is a lack of pronunciation of the sounds K, Kb.
Lexico - the grammatical structure of speech
- includes vocabulary and grammar.
Nasalization
is the acquisition of a nasal timbre by a sound (mainly a vowel) due to the lowering of the velum and the simultaneous release of an air stream through the mouth and nose.
General speech underdevelopment (GSD)
is a violation of sound pronunciation, phonemic hearing, grammatical structure of speech, insufficient vocabulary, a violation of the syllabic structure of words.
Phonetic-phonemic speech underdevelopment (FFSD)
is a disruption of the process of formation of the pronunciation system of the native language in children with various speech disorders due to defects in the perception and pronunciation of phonemes.
Occlusion
is the relationship between the dentition of the upper and lower jaws during closure.
Prosody
– melodic – intonation side of speech.
Salivation
– excessive salivation.
An active vocabulary
is the presence of words that a given person constantly uses in his speech.
A passive dictionary
is a stock of understandable words.
Spontaneous speech
is involuntary.
Timbre
is the individual coloring of the voice.
Language
is the most important means of communication, a tool for thinking and influencing people on each other.
Basic Concepts
Disorders of speech activity, which speech therapy deals with, are considered to be deviations in the functioning of the muscles of the speech apparatus, disturbances in the pronunciation of sounds or intonation, underdevelopment of speech, pathological development against the background of diseases and other anomalies.
Such defects are studied and determined by specialists in various scientific fields. In the course of studying speech defects, each deviation is considered in accordance with the goals, objectives and methods of each scientific area.
The meaning of speech therapy in this case is the study of the disorder with the aim of preventing it, as well as eliminating it with the help of special programs of correctional education or training. Therefore, speech therapy is considered a branch of special pedagogy. Its structure today is:
- Preschool and school speech therapy.
- Speech therapy for teenage children.
- Speech therapy for adults.
The theoretical foundations of speech therapy make it possible to study the etiology of speech disorders using the evolutionary-dynamic method in combination with the principle of unity of dialectical, biological and social aspects of the development of the speech apparatus.
Based on this, the tasks of speech therapy are determined:
- Study of individual speech characteristics for each form of speech deviation.
- Identification of symptoms, nature of development and degree of deviation of speech activity.
- Determination of development trends in children with speech disorders.
- Identification of the connection between speech disorders and the formation of mental, physical health and personality development.
- Study of the formation of the speech apparatus in children with various developmental defects and the presence of speech deviations.
- Identification of the nature of the occurrence of the disorder, its mechanism of action, accompanying symptoms, as well as structure.
- Development of pedagogical and other methods of knowledge of speech disorders.
- Systematization of acquired practical and theoretical knowledge to create a basis for improving methods for studying speech defects.
- Development of new methods, techniques and principles to prevent and eliminate violations.
- Formulating and raising new, topical issues related to the organization of programs to provide appropriate assistance to people with speech disorders.
The tasks of this scientific direction presented above consider speech disorders from the point of view of:
- Theories - the study of speech disorders in order to be able to develop new methods for prevention, identifying propensities for deviations and overcoming them.
- Practices - the use of preventive measures, methods to identify and eliminate deviations in the speech apparatus.
As you can see, the theoretical side and practical experience of speech therapy are closely related, which allows for a comprehensive scientific approach to solving the problems of diction defects.
Carrying out its direct scientific activities, this branch is based on the basic principles of speech therapy:
1. Systematic principle – considers speech as a unique system with its own complex structure, the components of which are studied separately to obtain an overall picture of the capabilities and structure of the speech apparatus.
2. The principle of complexity – takes into account the patterns and specific features of the development of individuals if they have speech defects.
We recommend: Dyslexia is
3. The principle of development - when carrying out correctional and speech therapy activities, it involves determining the main stages, tasks and identifying complications associated with the immediate environment of the person.
4. The principle of considering speech disorders against the background of the individual’s mental state and its aspects.
5. The principle of the activity approach - for organizing a speech therapy program for raising or training a child with diction disorders, the leading one is his direct activity (games, training, practice).
6. The principle of orthogenetic features.
7. Etiopathogenetic and symptomatic principle.
8. A principle that takes into account the structure of diction defects.
9. The principle of a workaround – considers the possibility of forming a new principle for the functioning of speech “bypassing” the component, which is a violation.
10. General didactic principles.
It is worth noting that the basis of the scientific method is speech therapy principles, general didactic, as well as special (principles of development, systematization of techniques and interconnectedness). They are a practical reinforcement of the theory of R.E. Levina regarding an integrated approach to the implementation of speech therapy activities, which takes into account the characteristics of the individual (in the motor, sensory, volitional and emotional spheres).
Dictionary of speech therapy terms material on speech therapy on the topic
Dictionary of speech therapy terms
A
Automation (of sound) is the stage of correcting incorrect sound pronunciation, which follows after setting a new sound; aimed at developing the correct pronunciation of sounds in coherent speech; consists in the gradual, consistent introduction of a given sound into syllables, words, sentences and into independent speech.
Agnosia is a violation of various types of perception that occurs with certain brain lesions. There are visual, tactile, and auditory agnosias.
Agrammatism is a violation of the understanding and use of grammatical means of a language.
Adaptation is the adaptation of an organism to living conditions.
Acalculia is a violation of counting and counting operations as a result of damage to various areas of the cerebral cortex.
Alalia is the absence or underdevelopment of speech in children with normal hearing and primarily intact intelligence.
Alexia is the impossibility of the reading process.
Amorphous words are grammatically unchangeable root words, “abnormal words” of child speech - words-fragments (in which only parts of the word are preserved), words-onomatopoeia (words-syllables that the child uses to designate objects, actions, situations), contour words ( in which stress and number of syllables are correctly reproduced).
Amnesia is a memory disorder in which it is impossible to reproduce ideas and concepts formed in the past.
Anamnesis is a set of information (about a person’s living conditions, events preceding the disease, etc.) obtained during the examination from the person being examined and (or) persons who know him; used to establish a diagnosis, prognosis of the disease and select corrective measures.
Ankyloglossia is a shortened hyoid ligament.
Anticipation is the ability to foresee the manifestation of the results of an action, “anticipatory reflection”, for example, premature recording of sounds included in the final motor acts.
Apraxia is a violation of voluntary purposeful movements and actions that are not a consequence of paralysis and cuts, but related to disorders of the highest level of organization of motor acts.
Articulation is the activity of the speech organs associated with the pronunciation of speech sounds and their various components that make up syllables and words.
The articulatory apparatus is a set of organs that ensure the formation of speech sounds (articulation), including the vocal apparatus, muscles of the pharynx, larynx, tongue, soft palate, lips, cheeks and lower jaw, teeth, etc.
Ataxia – disorder/lack of coordination of movements.
Atrophy is pathological structural changes in tissues associated with inhibition of metabolism (caused by a disorder of their nutrition).
Asthenia – weakness.
Asphyxia – suffocation of the fetus and newborn – cessation of breathing with continued cardiac activity due to a decrease or loss of excitability of the respiratory center.
An audiogram is a graphic representation of hearing test data using a device (audiometer).
Aphasia is a complete or partial loss of speech caused by local lesions of the brain.
Main forms of aphasia:
- acoustic-gnostic (sensory) – violation of phonemic perception;
- acoustic-mnestic – impairment of auditory-verbal memory;
- semantic – impaired understanding of logical and grammatical structures;
- afferent motor – kinesthetic and articulatory apraxia;
- efferent motor – violation of the kinetic basis of series of speech movements;
- dynamic – violation of the sequential organization of utterances, planning of utterances.
Afferent kinesthetic praxis is the ability to reproduce isolated speech sounds, their articulatory patterns (postures), which are often also called speech kinesthesia or articulomes.
Aphonia – lack of sonority of the voice while maintaining whispered speech; The immediate cause of aphonia is the failure of the vocal folds to close, resulting in air leakage during phonation. Aphonia occurs as a result of organic or functional disorders in the larynx, with a disorder of the nervous regulation of speech activity.
B
Battarism is a speech disorder in which words are pronounced at an excessively fast pace, not clearly, and are not spoken correctly.
Bradylalia is a pathologically slow rate of speech.
Broca's Center is a region of the cerebral cortex located in the posterior third of the inferior frontal gyrus of the left hemisphere (in right-handed people), providing motor organization of speech (responsible for expressive speech).
IN
An utterance is a unit of communication that has semantic integrity.
Verbal - verbal.
Visual communication - eye contact.
Wernicke Center is an area of the cerebral cortex in the posterior part of the superior temporal gyrus of the dominant hemisphere, providing speech understanding (responsible for impressive speech).
G
Gammacism is a lack of pronunciation of the sounds [G], [G].
Hemiplegia is paralysis of the muscles of one half of the body.
Hyperkinesis – automatic violent movements due to involuntary muscle contractions.
Hypoxia is oxygen starvation of the body. Hypoxia in newborns is a fetal pathology that develops during pregnancy (chronic) or childbirth (acute) due to oxygen deficiency. Lack of oxygen supply to the fetus at the beginning of pregnancy can cause delays or disturbances in fetal development, and in later stages it affects the baby’s nervous system, which can significantly affect speech development.
The following factors may put you at risk for developing hypoxia:
- the presence of anemia, STDs, as well as serious diseases of the respiratory or cardiovascular system in the expectant mother;
- disturbances in the blood supply to the fetus and in labor, gestosis, post-term pregnancy;
- pathologies of the fetus and Rh conflict between mother and baby;
- smoking and drinking alcohol by a pregnant woman.
Also, the green color of amniotic fluid indicates oxygen deficiency.
If the doctor suspects hypoxia, he may decide whether a cesarean section is necessary. A newborn with a severe degree of oxygen deprivation is resuscitated, and with a mild degree receives oxygen and medications.
Voice - sounds that arise as a result of vibration of the vocal cords when speaking, singing, laughing, etc.
-voice pitch is a physiological property of the speech voice, controlled by the tension of the vocal cords and the frequency of their vibrations. They are distinguished: high speech voice - developed head sound; low - developed chest sound; medium - mixed sound.
-voice range—the volume of sound, that is, the interval between the highest and lowest sounds of the voice. A voice with a large range of sound has flexibility, mobility, and play of sound.
- voice flight - the duration of the sound of individual phrases, words and sounds. When the sound is rich in intonation, the words are pronounced emotionally, clearly, clearly, and the speaker’s speech reaches the far corners of the audience.
-voice timbre - individual sound coloring, voice quality, characteristic of each person.
- developed voice - the voice is the most fully and comprehensively developed, with great range, strength, sonority, and flexibility.
D
Dysarthria is a violation of the pronunciation aspect of speech caused by insufficient innervation of the speech apparatus.
Dyslalia is a violation of sound pronunciation with normal hearing and intact innervation of the speech apparatus.
Dyslexia is a partial specific disorder of the reading process, caused by the immaturity (impairment) of higher mental functions and manifested in repeated persistent errors.
Dysgraphia is a partial specific disorder of the writing process, caused by the immaturity (impairment) of higher mental functions and manifested in repeated errors of a persistent nature.
Dysphonia - (dis-phone-voice disorder; Greek) voice disorder.
Breathing is conventionally divided into: clavicular, thoracic and abdominal.
- chest - breathing, in which the ribs, rising, increase the volume of the chest in its middle part. At the same time, the voice quickly gets tired.
-clavicular - short, shallow breathing.
-abdominal - diaphragmatic breathing: the diaphragm contracts and increases the volume of the chest.
Z
Speech development delay (SSD) is a lag in speech development from the age norm of speech development at the age of up to 3 years. From 3 years of age and older, the immaturity of all components of speech is classified as GSD (general speech underdevelopment).
Mental retardation is a violation of the normal pace of mental development, as a result of which a child who has reached school age continues to remain in the circle of preschool interests.
Stuttering is a violation of the tempo-rhythmic organization of speech, caused by the convulsive state of the muscles of the speech apparatus.
Onomatopoeia is the conditional reproduction of natural sounds and sounds that accompany certain processes (laughter, whistling, noise, etc.), as well as animal cries.
Defense mechanisms are a set of unconscious techniques with which a person protects himself from mental trauma.
AND
Impressive speech – perception, understanding of speech.
Innervation is the provision of organs and tissues with nerves and, therefore, communication with the central nervous system.
Stroke is an acute cerebrovascular accident (ACVA) caused by a pathological process with the development of persistent symptoms of damage to the central nervous system. Hemorrhagic stroke is caused by hemorrhage in the brain or its membranes, ischemic stroke is caused by the cessation or significant reduction of blood supply to a part of the brain, thrombotic stroke is caused by blockage of a cerebral vessel with a thrombus, embolic stroke is caused by blockage of a cerebral vessel by an embolus.
Intonation - (intono-pronounce loudly; Latin) a set of sound elements of speech (strength, height, timbre, duration of sound). Intonation creates an additional shade of meaning, subtext of speech, and helps to better understand the statement. If the speech is rich in intonations, it is especially clear and beautiful.
- intonation includes: rhythm, tempo, timbre and melody of speech. Melodics - the modulation of the voice for a question, exclamation or statement. Rhythm is a uniform alternation of stressed and unstressed syllables (different in voice strength and duration). Tempo is the speed of speech delivery. (When accelerated, intelligibility decreases; when slowed down, expressiveness decreases). Timbre is the emotional coloring of a phrase, giving speech different shades: surprise, joy, sadness, etc.
TO
Communication - (communico-communicating; Latin) contacts, communication, exchange of information between people.
Pronunciation correction - correction of pronunciation deficiencies.
Kappacism is a lack of pronunciation of the sounds [К], [Кь].
Kinesthetic sensations are sensations of position and movement of organs.
Compensation is a complex, multidimensional process of restructuring mental functions in the event of disruption or loss of any body functions.
Contamination is the erroneous reproduction of words, which consists of combining syllables belonging to different words into one word.
Speech culture is a multi-valued concept that includes: correctness of speech, that is, mastery of the norms of oral and written literary language (rules of pronunciation, stress, word usage, vocabulary, grammar and stylistics), and speech skill, that is, the ability to choose the most accurate from existing options semantically, stylistically and situationally appropriate, expressive, etc. Speech culture presupposes a high general human culture.
L
Lambdacism is the incorrect pronunciation of the sounds [L], [L].
Lexicon - vocabulary.
A logical pause is a pause that divides the speaker’s speech into speech beats in accordance with semantic and grammatical connections between words, characterized by a change in pitch and voice.
Logical stress - highlighting the most important word among other words to give the sentence an exact meaning. Logical stress falls on the word that has an essential meaning, according to the speaker’s intention.
Logicality of speech is the communicative quality of speech. To achieve logical speech, one should strive for semantic consistency of the statement.
Speech therapy is the science of speech disorders, methods of their prevention, identification and elimination by means of special training and education.
Logophobia - (logos-teaching, phobos-fear; Greek) fear of uttering words, speech.
Speech therapy massage is one of the speech therapy techniques that helps normalize the pronunciation aspect of speech and the emotional state of people suffering from speech disorders. Speech therapy massage is part of a comprehensive medical and pedagogical system of rehabilitation for children, adolescents and adults suffering from speech disorders.
Logorrhea is an uncontrolled, incoherent flow of speech, often representing an empty collection of individual words, devoid of logical connection. Observed in sensory aphasia.
Logorhythmics is a system of motor exercises in which various movements are combined with the pronunciation of special speech material. Logorhythmics is a form of active therapy, overcoming speech and related disorders through the development and correction of non-speech and speech mental functions.
Localization of functions - according to the theory of systemic dynamic localization of higher mental functions, the brain is considered as a substrate consisting of departments differentiated by their functions, working as a single whole. Local – local, limited to a certain area, area.
M
Macroglossia – pathological enlargement of the tongue; observed with abnormal development and in the presence of a chronic pathological process in the language. With M., significant pronunciation disturbances are observed.
Microglossia is a developmental anomaly, small size of the tongue.
Voice modulation is a change in the pitch of the voice; with hearing loss, the vocal tract is disrupted, which makes speech monotonous.
Voice mutation is a change in voice that occurs as a result of age-related changes in the vocal apparatus (13-15 years).
Mutism is the cessation of verbal communication with others due to mental trauma.
Speech melody - raising and lowering the tone of the voice.
Facial expressions are a set of facial muscle movements and eye movements of a person, expressing his state or his attitude towards something.
Voice modulation - changing the voice in pitch, strength, timbre and duration.
Motor skills are a set of motor reactions.
Mnemonics are techniques that ensure memorization using artificial associations.
N
Voice disorder is the absence or disorder of phonation due to pathological changes in the voice-forming apparatus.
Speech disorders are deviations in the speaker’s speech from the language norm accepted in a given language environment, manifested in partial (partial) disorders (sound pronunciation, voice, tempo and rhythm, etc.) and caused by disorders of the normal functioning of the psychophysiological mechanisms of speech activity.
Neuropsychology is the science of the brain organization of higher mental functions of a person. N. studies the psychological structure, brain organization of non-speech HMF and speech function. N. studies disorders of speech and other HMF depending on the nature of brain damage (local, diffuse, interzonal connections), as well as the diagnosis of these disorders and methods of correctional and rehabilitation work.
A skill is an automatically performed action that does not require conscious control or special volitional efforts to perform it.
Nonverbal means of communication - gestures, facial expressions, pantomime, expressive movements.
Speech underdevelopment - see General speech underdevelopment.
ABOUT
General speech underdevelopment (GSD) is a variety of complex speech disorders in which children have impaired formation of all components of the speech system related to its sound and semantic side, with normal hearing and intelligence.
Reflected speech is speech repeated after someone.
Feedback is the process of obtaining information about the state of a communication partner in order to improve communication and achieve the desired result.
Communication is a complex, multifaceted process of establishing and developing contacts between people.
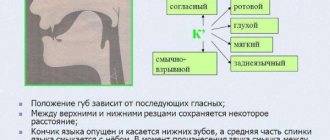
Organs of articulation - lips, tongue, lower jaw, pharynx. Accurate articulation produces clear, clear speech.
P
Finger games are a generally accepted name for activities to develop fine motor skills in children. Finger games develop fine motor skills, and its development stimulates the development of certain areas of the brain, in particular speech centers.
Paraphasia is a violation of speech utterances, manifested in omissions, erroneous replacement or rearrangement of sounds and syllables in words (literal paraphasia, for example, mokolo instead of milk, cheekbone instead of chair) or in the replacement of necessary words with others that are not related to the meaning of the utterance (verbal paraphasia) in oral and written speech.
Pathogenesis is the mechanism of development of a specific disease, pathological process or condition.
Perseverations are cyclical repetition or persistent reproduction, often contrary to the conscious intention of any actions, thoughts or experiences.
Prenatal period – pertaining to the period before birth.
Pantomime is a set of expressive body movements that accompany speech and emotions.
Pause is a stop during speech.
Vocal mobility is the ability of the voice to easily change its pitch and strength. The lack of mobility in the voice makes it monotonous.
Speech mobility is the ability to control the speed of the rhythmic movement of speech, its tempo, freely moving from slow to fast and vice versa. This ability is developed during training.
Paralinguistics - vocal capabilities of the voice.
Prosody is the melodic-intonation side of speech.
R
Speech decay is the loss of existing speech and communication skills due to local brain damage.
Reflex - in physiology - a natural response of the body to a stimulus mediated by the nervous system.
Disinhibition is the cessation of the state of internal inhibition in the cerebral cortex under the influence of extraneous stimuli.
Disinhibition of speech in children – activation of speech development in children with delayed speech development.
Disinhibition of speech in adults – restoration of speech function in speechless patients.
Speech hearing is a person’s ability to perceive and reproduce all phonological means of language when perceiving speech. Components of speech hearing:
- pitch hearing - the ability to hear and perceive the melody of speech;
-rhythmic hearing - the ability to sense and reproduce its internal tempo in speech;
- tonal hearing - the ability to hear and reproduce timbre changes in the voice depending on changes in feelings and relationships;
- physical hearing - the ability to perceive sounding speech in different ranges of volume and height;
- phonemic hearing - the ability to distinguish and reproduce speech sounds.
Speech beat - (syntagma) a word or group of words within a sentence that are united by meaning.
Speech is a system of sound signals, written signs and symbols used by humans to transmit and store information.
-external - speech for others, heard and understood by people around; consists of written and oral speech;
-internal - speech for oneself, devoid of sound design, mental speech.
The rhythm of speech is the sequential alternation of speech elements over the same amount of time.
Rhetoric is the theory and skill of harmonious speech.
Rhinolalia is a violation of voice timbre and sound pronunciation, resulting from excessive or insufficient resonance in the nasal cavity during speech. Such a violation of resonance occurs from the incorrect direction of the voice-exhalatory stream due to either organic defects of the nasopharynx, nasal cavity, soft and hard palate, or disorders of the function of the soft palate. There are open, closed and mixed rhinolalia.
Rhinophony is a change in only the timbre of the voice (nasal tone) with normal sound pronunciation.
Rotacism is a disorder in the pronunciation of the sounds [Р], [Рь].
Sensory – sensitive, feeling, relating to sensations.
WITH
Self-regulation is the process of a person managing his psychological and physiological states and actions.
The strength of the voice depends on the amplitude of vibrations of the vocal cords, which is determined by the amount of air pressure, that is, the pressure of exhaled air during voice formation.
Syntagmatic stress is the main word of speech tact.
Sigmatism is a disorder in the pronunciation of whistling ([С], [Сь], [З], [Зь], [Ц]) and hissing ([Ш], [Х], [Ч], [Ш]) sounds.
A syndrome is a natural combination of signs (symptoms) that have a common pathogenesis and characterize a specific disease state.
Simultaneous – simultaneous.
Somatic is a term used to designate various kinds of phenomena in the body associated with the body, as opposed to the psyche.
Conjugate speech is the joint simultaneous repetition by two or more persons of words or phrases spoken by someone.
Cramps are involuntary muscle contractions that occur during epilepsy, brain injuries, spasmophilia and other diseases. Convulsions are characteristic of a state of excitation of subcortical formations and can be caused reflexively.
Clonic seizures are characterized by rapid alternations between muscle contraction and relaxation. Tonic cramps are characterized by prolonged muscle contraction, which causes a prolonged forced tense position.
Successive – sequential.
T
Tahilalia is a speech disorder, expressed in excessive speed of its tempo (20-30 sounds per second), related in nature to battarism. In contrast to the latter, tachylalia is a deviation from normal speech only in relation to its tempo, with full preservation of phonetic design, as well as vocabulary and grammatical structure.
Tremor – rhythmic oscillatory movements of the limbs, head, tongue, etc. with damage to the nervous system.
Rate of speech - speed of speech, can be measured by the number of words per unit of time.
Communication techniques are ways of pre-setting a person to communicate with people, his behavior in the communication process.
Speech technique is a set of skills and abilities used for optimal speech sound.
U
Stress is distinguished: 1) grammatical (pronunciation with the greatest force of a syllable in a word); 2) phrasal (transmitted by raising or lowering the entire contour of the sentence); 3) syntagmatic (the main word of the syntagma is pronounced with greater intensity).
The frenulum is the sublingual ligament. With a short frenulum, the pronunciation of the sounds [R, L, Sh, Zh, Ch, Shch] is impaired. There is no need for surgical intervention, as there are special exercises for stretching the frenulum.
F
Phonetic-phonemic underdevelopment is a violation of the process of formation of the pronunciation system of the native language in children with various speech disorders due to defects in the perception and pronunciation of phonemes.
Phoneme is the sound of speech. There are 42 phonemes in the Russian language.
Phonemic analysis and synthesis are mental actions to analyze or synthesize the sound structure of a word.
Phonemic hearing is a subtle, systematized hearing that has the ability to carry out operations of discrimination and recognition of phonemes that make up the sound shell of a word.
Phoniatrics is a branch of medicine that studies dental problems and pathologies of the vocal cords and larynx, leading to voice disorders (dysphonia), methods of treatment and prevention of voice disorders, as well as methods of correcting a normal voice in the desired direction. Voice disturbances can also occur as a result of certain psychological disorders. The solution to some problems in phoniatrics is closely related to the problems of speech therapy.
A phoniatrist is a doctor who specializes in problems of the vocal cords and deals with their treatment, as well as the prevention of diseases.
Phonation - voice formation.
X
Hittism is a lack of pronunciation of the sound [X].
C
Cerebral – cerebral, belonging to the brain.
H
Purity of speech - such speech is called pure in which there are no defective sounds; elements alien to the literary language: jargon, dialectisms, vulgarisms, parasitic words.
E
Expressive speech is active oral and written expression.
Extirpation (of the larynx) – removal.
An embolus is a substrate circulating in the blood that is not found under normal conditions and can cause blockage of a blood vessel.
Speech embolus is one of the most common words, part of a word or short phrase before the disease, repeated many times by the patient when trying to speak. It is one of the speech symptoms of motor aphasia.
Etiology is the cause of a disease or pathological condition.
Expression - (expressio-expressiveness; Latin) the power of manifestation of feelings, experiences.
Empathy is sympathy for a person.
Efferent kinetic praxis is the ability to produce a series of speech sounds. Efferent articulatory praxis is fundamentally different from afferent one in that it requires the ability to switch from one articulatory posture to another. These switches are complex in the way they are executed. They involve mastering inserted fragments of articulatory actions - coarticulations, which are “connections” between individual articulatory poses. Without coarticulation, a word cannot be pronounced, even if every sound included in it is available for reproduction.
Echolalia is the involuntary repetition of heard sounds, words or phrases.
I
Language is the most important means of communication, a tool for thinking and influencing people on each other.
What options and techniques does science use?
The methods used by this branch of science make it possible to carry out basic speech therapy practical activities, supported by theoretical knowledge. All methods of speech therapy, as practice has shown, can be divided into groups:
1. Methods for organizing the processes of studying speech mechanisms (comparison, complex study, dynamic research).
2. Empirical (based on acquired experience) methods. In particular, it is observation, experiment and study in psychodynamics. They also include the biographical method, based on the collection, systematization and analysis of data, and praximetric examples of examining speech activity.
3. Methods related to the analysis and computer processing of data obtained through the application of quantitative and qualitative methods.
4. Interpretive methods, which explore how theory can be applied in practice to the phenomena being studied.
Consultation “The Concept of Speech Therapy”
Lyudmila Mineeva
Consultation “The Concept of Speech Therapy”
Terms and concepts of speech therapy
Speech therapy is a science that studies people with speech disorders and develops methods of correctional and pedagogical work with them.
The articulatory apparatus is a set of organs that ensure the formation of speech sounds (articulation)
; includes the vocal apparatus, muscles of the pharynx, tongue, soft palate, lips, cheeks and lower jaw, teeth, etc.
Dyslalia is a violation of sound pronunciation with normal hearing and intact innervation of the speech apparatus.
The speech apparatus is a system of organs involved in the formation of speech sounds; In this system, peripheral and central sections are distinguished. The peripheral part of the speech apparatus includes the organs of voice formation, breathing, articulation, as well as the sensory centers related to them. The central section of the speech apparatus is located in the brain and consists of cortical centers, subcortical nodes, pathways and nuclei of the corresponding nerves.
Dysarthria is a violation of the pronunciation aspect of speech caused by insufficient innervation of the speech apparatus.
Rhinolalia is a violation of voice timbre and sound pronunciation, caused by anatomical and physiological defects of the speech apparatus.
Alalia is the absence or underdevelopment of speech due to organic damage to the speech areas of the cerebral cortex in the prenatal or early period of a child’s development.
Aphasia is a complete or partial loss of speech caused by damage to the cerebral cortex in the absence of disorders of the articulatory apparatus and hearing. They are distinguished: motor aphasia (loss of the ability of voluntary speech without impaired articulation)
;
sensory aphasia (loss of the ability to understand speech)
.
Voice disorder is the absence or disorder of phonation due to pathological changes in the vocal apparatus.
Hysterical mutism is a sudden and complete loss of voice with the impossibility of even whispering speech.
Aphonia is the absence of a sonorous voice in the presence of whispered speech.
The vocal folds do not close completely.
Dysphonia is a partial disorder of the voice manifested in disorders of the main acoustic characteristics: pitch, strength and timbre.
Phonasthenia (weak voice)
– voice disorders expressed in rapid fatigue, interruptions, misfires. Unpleasant subjective sensations. It is an occupational disease.
A pathological mutation is a violation of the acoustic characteristics of the voice.
Violation of resonance appears in the form of hypo (adenoids, polyps, deviated nasal septum)
and hypernasality
(rhinolalia)
.
Voice pitch disorders: monotonous, tremulous, unmodulated, low, falsetto.
Voice timbre disorders: hoarse, rough, guttural-harsh, dull, metallic, diplophonia, “croaking”
, squeaky, polished.
Voice disturbances: aphonia, weak, fading, too loud.
Rate of speech is one of the expressive means of oral speech, which depends on 2 parameters: on the speed of pronouncing successive speech sounds and on the frequency and duration of pauses between words and sentences.
Bradylalia is a pathologically slow rate of speech.
Tahilalia is a pathologically accelerated rate of speech.
Battarism (paraphasia)
- this is the incorrect formation of a phrase as a result of a violation of speech attention and speech rate.
Poltern (stumbling)
– this is pathologically accelerated speech, intermittent tempo of a non-convulsive nature
(stammering, stumbling, unreasonable pauses)
.
Stuttering is a violation of the tempo-rhythmic organization of speech, caused by the convulsive state of the muscles of the speech apparatus.
Phonetic-phonemic underdevelopment of speech is a violation of the processes of formation of the pronunciation system of the native language in children with various speech disorders due to defects in the perception and pronunciation of phonemes.
General speech underdevelopment is a variety of complex speech disorders in which the formation of all components of the speech system, i.e., the sound side (phonetics),
and the semantic side
(vocabulary, grammar)
of speech.
Dysgraphia is a partial specific disorder of the writing process.
Dyslexia is a partial disorder of the reading process, which makes it difficult to master this skill and leads to many errors during reading (omission of letters, syllables , words and substitutions, omission of prepositions , conjunctions, substitution of one word for another, omission of lines).