- home
- Directories
- Handbook of Russian for elementary school
- Sounds and letters
- Consonant sounds and letters representing them
- Soft and hard consonants
Consonants can be hard or soft .
Many consonants are paired in softness-hardness , i.e. in different words they can soften or become hard. In transcription, the softness of a consonant is indicated by the [ ' ] symbol.
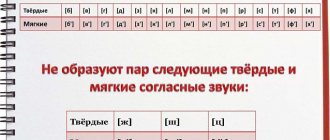
Table of consonant sounds, paired and unpaired by hardness/softness:
| Consonant clusters | Doubles | Unpaired |
| Solid | [b], [c], [d], [d], [h], [k], [l], [m], [n], [p], [p], [s], [t ], [f], [x] | [zh], [w], [ts] |
| Soft | [b'], [c'], [g'], [d'], [z'], [k'], [l'], [m'], [n'], [p'], [p'], [s'], [t'], [f'], [x'] | [th'], [h'], [h'] |
In writing, the hardness of consonant sounds is indicated by the vowels a, o, u, ы, e (which come after the consonant sound) - park [ park], rota [ rota ] , puma [ puma ], kry nka [little jar], s er [sir].
The softness of consonant sounds in writing is indicated by:
- soft sign - shallow [ m'el'], pal that [pal'to], written [ p'is'm'eny']
- vowels e, e, i, yu, i - p e n [p'en'], sv e kla [sv'okla], p i t [p'it'], k l u in [kl'uv], pl i ska [pl'aska].
In addition, consonant sounds paired in hardness/softness can be softened before some soft consonants - z [z'] , s [s'] , n [n'] , t [t'] , l [l'] .
For example: pes n ya [p'es'n'a], es l i[y'es'l'i], tail ik [khvos't'ik] and others.
Also, the consonant [n'] will be soft before the consonant letters ch and shch , while a soft sign is not written between them: donut [pon'ch'ik], racer [gon'sch'ik].
Remember that consonants unpaired in hardness-softness remain only hard or only soft (regardless of whether there is a soft sign after them or what vowel follows them).
Hard unpaired consonants always remain hard.
For example:
[zh] - heat [heat], yellow [yellow']
[sh] - ball [ball], sew [shy'u]
[ts] - heron [heron], circus [circus]
Soft unpaired consonants always remain soft.
For example:
[th'] - yogurt [y'ogurt], my [my']
[h'] - hour [h'as], check [ch'ek]
[sch'] - pike [sch'uka], gap [sch'el']
Share with friends on social networks:
What are soft sounds?
To find out what soft sounds are, let’s compare two words and pay attention to the pronunciation of their initial sounds: “side” and “run”
The first word contains a voiced consonant [b], in the formation of which the lips participate: side [b o k]
The initial consonant sounds quite hard. Compare with the pronunciation of the second word: run [b' e k]
The first voiced consonant is indicated by the same letter “b”, but it sounds slightly different. When pronouncing it, the back of the tongue rushes towards the hard palate, arching like a bridge. Narrow passages for exhaled air are formed on the sides of the tongue, as a result of which the voiced consonant acquires softness, or palatality. The linguistic term "palatality" comes from the Latin word palatum, which literally means "palate".
So, in Russian speech, hard and soft consonants are distinguished.
Compared to hard consonants, all soft sounds during formation are distinguished by the additional participation of the tongue. Soft consonants are noisy sounds, in the formation of which there is additional articulation of the tongue to the palate.
Softness
Only consonant sounds can be soft; the term “soft consonant letters” does not exist in the Russian language, since a letter is just a symbol of the alphabet.
Consonant sounds are called soft because when pronouncing such consonants, the middle back of the tongue is raised towards the hard palate to cause the so-called softness.
To understand how to determine the softness of a consonant sound, you need to monitor the movement of the tongue when pronouncing a particular word.
Softness as an element of transcription has its own designation: '.
In writing, gentleness is expressed in two ways:
- using the vowels i, e, ё, i, yu, which indicate the softness of the previous consonant sounds;
- using a soft sign (b).
A consonant sound is soft not because softness indicators are placed after it; on the contrary, softness indicators are placed after a consonant sound if this consonant sound is soft.
Setting the sound P in stages
Lip exercises
- "Smile".
Smile so that the upper and lower teeth are visible and hold this position for 5-7 seconds. - "Tube".
Stretch your lips with a tube: 1st option - pronounce the sound [U] for a long time without using your voice; 2nd option - pull your lips slightly forward, as if forming a square; teeth are closed. - "The doors are opening." Slowly open your mouth until there is a distance of 10-15 mm between the upper and lower teeth, hold your lips in the “Smile” position.
Tongue exercises
Particular attention should be paid to exercises to control the muscles of the tongue. "Pancake." Place a wide, relaxed tongue on the lower lip. Make sure that the lower lip is not pulled over the teeth, and the upper teeth are also not covered by the upper lip (that is, the “Smile” position is maintained). If the tongue does not take the desired shape, pronounce the syllables “ba-ba-ba” with your tongue sticking out between your lips. Upon achieving success, make the tongue wide without pronouncing these syllables and blow until a groove is formed along the midline of the tongue.
- “Whose teeth are cleaner?”
Open your mouth slightly and use the tip of your tongue to “brush” the inside of your upper teeth, moving your tongue from side to side. - "Kitty."
Bend the wide tip of the tongue up towards the nose. If this movement does not work, then you should first practice licking the upper teeth under the lip from right to left, then licking the upper lip. - "Painter".
Smile, open your mouth and stroke the hard palate with the tip of your tongue, moving your tongue back and forth. - “Swing”
(inside the mouth). Bend the wide tip of the tongue alternately up and down between the teeth, gradually pulling it into the depths of the mouth. All movements should be done slowly, clearly, rhythmically with a mental count of “one-two” (up), “one-two” (down), etc., gradually accelerating the pace in subsequent sessions. - "Horse".
Click the tip of your tongue. Suck the tip of your tongue to the front edge of the roof of your mouth and tear it off, opening your mouth wide. - "Mushroom".
Lips in the “Smile” position, teeth open. Suck the front of your tongue to the hard palate. Holding the tongue in this position, connect and open the teeth until slight pain appears in the area of the hypoglossal ligament. - "Machine gun".
Smile, open your mouth and tap the tip of your tongue behind your upper teeth, repeatedly and clearly pronouncing the sound [D]: “d-d-d.” First pronounce the sound [D] slowly, then gradually speed up the tempo. - "The plane is buzzing."
Lips in the “Smile” position, the upper and lower teeth are visible, open by 10-15 mm. The wide tip of the tongue behind the upper teeth. Pronounce the sounds [Z] or [Zh] (you should get a sound reminiscent of the roar of a motor). Important: The lateral edges of the tongue should be pressed against the molars, the tip of the tongue should be thin and mobile, the lips should not be rounded.
If the child does not succeed in the “The plane is buzzing” exercise for a long time, then you can lift his tongue by the upper teeth with your fingers or a spatula. In this case, the child must pronounce “j-z-z-z” for a long time.
Distinctive features of soft and hard sounds
What sound comes after a consonant:
- If after a consonant there is a vowel a, o, u, e, s, then the consonant is hard.
- If after a consonant there is a vowel and, e, yu, i, then the consonant is soft.
Practice with examples: In the words “mother” and “nora” the consonants are hard, because they are followed by “a” and “o”. In the words “fly” and “nanny” the consonants are soft because they are followed by “e”, “i”, “ya”.
- If another consonant sounds after a consonant, then the first consonant will be hard.
- There are sounds that can only be hard and sounds that can only be soft, no matter what sound is heard or what letter is written after them.
Always hard sounds - zh, sh, ts. Always soft - th, h, shch. A common way to learn these sounds is a simple technique: we write the letters that convey these sounds on a line, and emphasize “th, ch, sch.” The underscore symbolizes the cushion on which the soft sounds sit. The pad is soft, which means the sounds are soft.
Soft sign and hard sign
- If there is a consonant at the end of a word and the letter “b” after it, then the consonant is soft.
This rule is easy to apply if the child sees the written word, but it will not help if the child performs the task by ear.
Movement of the tongue when pronouncing soft and hard sounds
When pronouncing a soft sound, the tongue moves slightly forward, approaching (or touching) the palate with its middle. When pronouncing hard sounds, the tongue does not move forward.
Methods for producing the sound R
- If the child successfully copes with all the exercises, you can begin to directly produce the sound P hard and Pb soft, using mechanical assistance: put a rubber pacifier on a wooden spatula and, placing the tongue in the position for the “The plane is buzzing” exercise, make quick oscillatory movements left and right or back and forth under the tip of the tongue until a steady vibration of the tongue is obtained. Staging the sound [P] using a pacifier is easier and faster in a lying position: the child’s head lies on the teacher’s lap. The mechanical method gives the child the opportunity to feel the vibration of the tongue, muscularly imprint it and subsequently reproduce it without mechanical assistance.
- It is sometimes possible to obtain vibration of the tongue using the following technique: place a thick ball of paper (tied to a long thread that the child holds in his hands) on the tip of the tongue, remove the tongue by the upper teeth and blow it off the tongue with a strong air stream. Important: It is necessary to strictly ensure that the child does not inhale the lump of paper.
- Another technique is based on the rapid repetition of the sound [D] in one exhalation, articulated in a special way: the child is asked to pronounce the sound [D] quickly and repeatedly (“dddddddddddd…”) with a half-open mouth (the tip of the tongue at the upper alveoli). The child should see quick strokes of the tip of the tongue in the mirror. The tempo of these beats gradually increases and the tip of the tongue vibrates at different rates. These rhythmic tongue strokes are then combined with vowels in forward and backward order, for example: ddda addd addda dddy yddd ydddy
While the child is performing these exercises, use a spatula placed under the front edge of the tongue to make frequent oscillatory movements, which causes a rumble characteristic of the sound [P] to be heard.
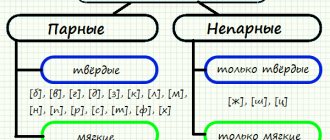
Paired hard and soft consonants
Many voiced and voiceless consonants in the Russian language are distinguished by the sign of hardness/softness and form correlative pairs:
With the help of hard and soft consonants you can distinguish between words:
- rad - row;
- howl - howl;
- son - blue;
- magician - moment.
Several consonant sounds do not have a hard/soft pair. Always hard consonants are the sounds [zh], [sh], [ts]. In any position in a word they sound only firmly:
- fat [f y r]
- silk [s h o l k a v y ']
- citrus [ts y tr rus].
Letters that represent only soft consonants
The letters th, ch, shch always denote soft consonant sounds: [th'], [ch'], [sh'].
The following rule applies here: these soft consonants always remain soft, regardless of the subsequent vowel letter.
Letters that represent soft and hard consonants
The letters b, c, d, d, z, k, l, m, n, p, r, s, t, f, x can denote both hard and soft consonant sounds. This is reflected in the following table:
| Letters | Sounds |
| b | [b], [b'] |
| V | [in], [in'] |
| G | [g], [g'] |
| d | [d], [d'] |
| h | [z], [z'] |
| To | [k], [k'] |
| l | [l], [l'] |
| m | [mm'] |
| n | [n], [n'] |
| P | [p], [p'] |
| R | [р], [р'] |
| With | [s], [s'] |
| T | [t], [t'] |
| f | [f], [f'] |
| X | [x], [x'] |
The consonants presented above are called paired according to softness and hardness.
When comparing the words mom ([mama]) and mint ([m'ata]), one can come to the conclusion that in writing both words use the same letter - m, but the pronunciation of the sounds is different. Only in the second case is the consonant sound soft. This example shows the relationship between a consonant letter and the vowel letter behind it.
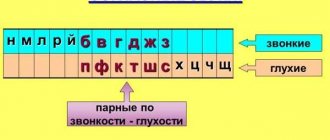
Voiced and unvoiced sounds
Consonant sounds are also classified into voiced and voiceless. The former consist of voice and noise, while the latter consist only of noise.
The voiced category includes: [B], [G], [D], [F], [Z], [V], [Y], [L], [M], [N], [R].
The deaf group includes: [К], [П], [Х], [Ц], [Ч], [С], [Т], [Ф], [Ш], [Ш].
Most consonants can form pairs based on deafness and hardness:
[B]—[P] [V]—[F] [D]—[K] [D]—[T] [G]—[S] [W]—[W]
Voiceless and voiced consonants are easy to remember using two sentences:
- “The Lion and the Toad Have Many Friends” (Voiced)
- “Styopka, do you want a cheek? - Ugh!" (Deaf).
You can memorize them or print them out on a separate card.
How are hard and soft sounds indicated in writing?
In writing, the hardness and softness of consonant sounds are indicated only when writing a transcription. To indicate a soft sound, use the apostrophe "`". Hard sounds are not distinguished by any signs in writing.
Below is an explanatory table that clearly shows that the same sound can be both hard and soft, depending on which vowel follows it.
Table with examples of writing sounds in soft and hard use
| ram | [b] | [b`] | underwear |
| pile | [V] | [in`] | elm |
| hump | [G] | [g`] | weight |
| house | [d] | [d`] | uncle |
| gold | [h] | [z`] | Earth |
| cat | [To] | [k`] | whale |
| skis | [l] | [l`] | lemon |
| garbage | [m] | [m`] | ball |
| Nora | [n] | [n`] | Nyura |
| floors | [P] | [n`] | singing |
| robot | [R] | [r`] | river |
| Sun | [With] | [s`] | seed |
| tone | [T] | [t`] | crown |
| furore | [f] | [f`] | the final |
| hamster | [X] | [x`] | hut |
You can notice that consonant sounds form pairs based on hardness-softness: [v] - [v`]; [k] - [k`], etc. In writing, both hard and soft sounds are indicated by the same letter, but are pronounced differently. With the help of such a table, children can more easily understand the hardness and softness of consonant sounds, while remembering that the sign “b” always makes the consonant soft, and the sign “b” always makes the consonant it follows hard.
What have we learned?
Soft consonant sounds are characterized by the fact that when pronounced, the middle back of the tongue is raised towards the hard palate. This is what allows you to determine the softness of a consonant sound. Soft consonant sounds in writing are indicated by consonant letters; in transcription, the sign ' is used. The softness of consonant sounds is expressed thanks to the vowel letters i, e, ё, i, yu and the soft sign indicating the softness of consonant sounds. In the Russian language there are letters that always indicate a soft consonant sound: й, ч, щ. The following letters can represent soft and hard sounds: b, v, g, d, z, k, l, m, n, p, r, s, t, f, x.
Examples of interesting tasks for developing the skill of distinguishing between soft and hard consonants
A picture or simply a list of thematic words is shown, and the task is given to choose words with soft or hard consonants. For example:
§8. Place of formation of consonants
Consonants differ not only according to the characteristics already known to you:
- deafness-voice,
- hardness-softness,
- method of formation: bow-slit.
The last, fourth sign is important: place of formation . The articulation of some sounds is carried out by the lips, others - by the tongue, its different parts. So, the sounds [p], [p'], [b], [b'], [m], [m'] are labial, [v], [v'], [f], [f' ] – labial-dental, all others – lingual: anterior lingual [t], [t'], [d], [d'], [n], [n'], [s], [s'], [z ], [z'], [w], [zh], [w':], [h'], [ts], [l], [l'], [r], [r'], middle language [ th'] and back-lingual [k], [k'], [g], [g'], [x], [x'].
Examples of tasks for children
Tasks for training the differences between paired consonants can be compiled for each pair according to the following principle (using the example of the D/T pair):
Tasks for distinguishing a pair of consonants G/K
Final test
What determines the quality of a vowel sound?
- From the shape of the oral cavity at the moment of pronouncing the sound
- From the barrier formed by the speech organs at the moment of pronouncing a sound
What is reduction called?
- pronouncing vowels under stress
- pronouncing unstressed vowels
- special pronunciation of consonants
For which sounds does the air stream encounter an obstacle on its path: a bow or a gap?
- In vowels
- In consonants
Can voiceless consonants be pronounced loudly?
- Yes
- No
Are the vocal cords involved in pronouncing voiceless consonants?
- Yes
- No
How many pairs of consonants are formed according to deafness and voicedness?
- 5
- 11
- 20
How many consonants do not have a voiced-voiced pair?
- 5
- 10
- 14
How many pairs do Russian consonants form according to hardness and softness?
- 10
- 15
- 20
How many consonants do not have a hard-soft pair?
- 3
- 6
- 12
How is the softness of consonants conveyed in writing?
- Special icons
- Letter combinations
What is the name of the position of a sound in a stream of speech in which it appears in its basic form, without undergoing positional changes?
- Strong position
- Weak position
What sounds have strong and weak positions?
- In vowels
- In consonants
- For everyone: both vowels and consonants
Right answers:
- From the shape of the oral cavity at the moment of pronouncing the sound
- pronouncing unstressed vowels
- In consonants
- No
- No
- 11
- 14
- 15
- 6
- Letter combinations
- Strong position
- For everyone: both vowels and consonants
Guess
We write signs with transcriptions of words. The child’s task is to name the word and name soft sounds. It is best to make the signs bright and large, then it will be more interesting for children to react to them.
To start the game, select easy words: [m`el]; [soap]; [l`uk]; [WHO]. And at the end you can complicate the task and give the following words: [b`elka]; [ski track]; [kl`on].
While playing, the child visually remembers the designation of soft consonant sounds and gains practical skills in using knowledge when writing.
§1. Sound
Sound is the minimum unit of sounding speech. Each word has a sound shell consisting of sounds. The sound corresponds to the meaning of the word. Different words and word forms have different sound patterns. The sounds themselves are not important, but they serve an important role: they help us distinguish between:
- words: [house] - [tom], [tom] - [there], [m'el] - [m'el']
- forms of the word: [house] – [lady´] – [house´ma].
Note:
words written in square brackets are given in transcription.