What is sound? This is the minimum component of human speech. Depicted in letters. In written form, sounds are distinguished from letters by the presence of square brackets [ ] at the first, which are used in phonetic transcription. The letter is o, the sound is [o]. The transcription shows differences in spelling and pronunciation. An apostrophe [ ] indicates soft pronunciation....
The sounds are divided into:
- Vowels. They can be pulled easily. During their creation, the tongue does not take an active part, being fixed in one position. The sound is created due to changes in the position of the tongue, lips, various vibrations of the vocal cords and the force of air supply. Prolongation of vowels is the basis of vocal art (chanting, “singing smoothly”).
- The consonants of the Russian language are pronounced with the participation of the tongue, which, occupying a certain position and shape, creates an obstacle to the movement of air from the lungs. This leads to noise in the oral cavity. At the output they are converted into sound. Also, the free passage of air is hampered by the lips, which close and open during speech.
Consonants are divided into:
- voiceless and voiced. Deafness and sonority of sound depend on the functioning of the speech apparatus,
- hard and soft. The sound is determined by the position of the letter in the word.
Letters representing consonants
Deaf
Quiet, it’s quite difficult to shout them. The vocal cords do not obstruct the movement of air from the lungs, and sound is formed by changing the shape of the lips and the position of the tongue.
Voiceless in Russian: [k], [p], [s], [t], [f], [x], [ts], [sh]. The easiest way to remember is a phrase, and not a set of letters, “Styopka, do you want a cheek? Fi!” containing them all.
An example in which all consonant sounds are unvoiced: rooster, honeycomb, pin.
This is interesting! How phonetic analysis of a word is done: an example of sound analysis
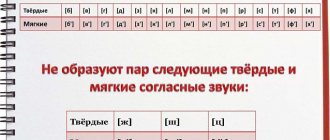
Hardness-softness pairs
In addition to deafness and voicedness, Russian consonants form pairs based on hardness and softness.
This means that some of them are perceived by ear as softer sounding. Then we usually indicate this in writing somehow: for example, we write a soft sign or one of the vowels E, Yo, Yu, Ya.
Oral speech is primary (everyone understands that it appeared before written speech), therefore it is incorrect to say: “The sound [N'] in the word HORSE is soft, because it is followed by b.” On the contrary, we write b because H' is soft.
According to hardness-softness, consonants also form pairs. But even in this case, not everything. In the Russian language there are unpaired soft and unpaired hard consonants.
Unpaired hard consonant sounds are mainly hissing sounds ([Zh], [Sh]) and [C]. They always form at the far palate.
But in the ancestor of our language, Old Church Slavonic, on the contrary, [ZH] and [SH] were always soft and did not have a hard pair. Then [K], [G] and [X] were not soft. Nowadays you can find (once the only possible) pronunciation with a soft [Zh'] [DROZH'ZH'I] or [DOZH'] (rain), but this is no longer necessary.
Unpaired soft ones are [Y'] and again hissing [H'] and [Ш'].
That is, all hissing ones are either always hard or always soft. The letter b after them does not indicate softness, it performs a grammatical function (for example, even without knowing what “baldness” is, anyone will immediately say that this is a feminine word, because in the masculine gender b is not placed after hissing words). Hard unpaired hissing consonant sounds in a word may have b with them, but this does not mean that they should soften. This means that we have a 3rd declension noun, an adverb or a verb.
Unpaired soft consonant sounds in a word make you want to put b after them, which is often not required. Therefore, it makes sense to remember that in combinations CHK, CHN, etc. b after h is not needed.
Voiced
When they are formed, the shape of the tongue is close to the form that produces voiceless sounds, but vibrations are added. Voiced consonant sounds create active vibrations of the ligaments. Vibrations deform the sound wave , and it is not the pure flow of air that enters the oral cavity, but the sound. Subsequently, it is further transformed by the tongue and lips.
Voiced consonants include: b, c, g, d, g, z, j, l, m, n, r.
When they are pronounced, tension is clearly felt in the larynx area. In addition, it is almost impossible to speak them clearly in a whisper.
A word in which all consonants are voiced: Rome, pride, ash, estuary.
Summary table of consonants (voiceless and voiced).
| Sound | [b'] | [b] | [V'] | [V] | [G'] | [G] | [d'] | [d] | [and] | [z'] | [h] | [th] | [l] | [m] | [n] | [R] |
| Ch. | [P'] | [P] | [f'] | [f] | [To'] | [To] | [T'] | [T] | [w] | [With'] | [With] | [X] | [ts] | [h] | [sch] |
Voiced and voiceless, paired and unpaired sounds
Based on their sonority, consonants are divided into voiced and voiceless. Voiced consonants can be sounds created with the participation of the voice: [v], [z], [zh], [b], [d], [y], [m], [d], [l], [r] , [n].
Examples: [bor], [ox], [shower], [call], [heat], [goal], [fishing], [pestilence], [nose], [genus], [swarm].
If a sound is formed without the participation of the voice, it is called deaf: [t], [k], [p], [f], [x], [sch], [f], [sh], [ch], [ts] .
Examples: [kol], [pol], [tom], [sleep], [noise], [sh'uka], [choir], [tsar'], [ch'an].
Paired voiced and voiceless consonants include: [b] - [p], [zh] - [w], [g] - [x], [z] - [s]. [d] - [t], [v] - [f]. Examples: reality - dust, house - volume, year - code, vase - phase, itch - judgment, live - sew.
Sounds that do not form pairs: [h], [n], [ts], [x], [r], [m], [l].
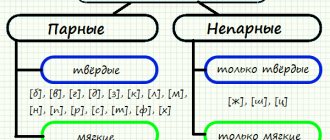
Soft and hard consonants can also have a pair: [p] - [p'], [p] - [p'], [m] - [m'], [v] - [v'], [d] - [ d'], [f] - [f'], [k] - [k'], [z] - [z'], [b] - [b'], [g] - [g'], [ n] - [n'], [s] - [s'], [l] - [l'], [t] - [t'], [x] - [x']. Examples: true story - white, height - branch, city - cheetah, dacha - business, umbrella - zebra, leather - cedar, moon - summer, monster - place, finger - feather, ore - river, soda - sulfur, pillar - steppe, lantern - farm, mansion - hut.
Paired consonants
What does consonant pairing mean? Two letters that are similar in sound and, when pronounced, take similar positions with the tongue, are called paired consonants. The pronunciation of consonants can be divided into one-stage (lips and tongues are involved in their creation) and two-stage - the ligaments are connected first, then the mouth. Those cases when, during pronunciation, mouth movements coincide and create pairs.
Summary table of paired consonants taking into account hardness and softness
| Sound | [b] | [b'] | [V] | [V'] | [G] | [G'] | [d] | [d'] | [h] | [z'] | [and] |
| Ch. | [P] | [P'] | [f] | [f'] | [To] | [To'] | [T] | [T'] | [With] | [With'] | [w] |
In speech, it is common not to pronounce each letter, but to “eat” it. This is not an exception only for Russian speech. This is found in almost all languages of the world and is especially noticeable in English. In Russian, this effect is subject to the rule: paired consonant sounds replace (auditory) each other during speech. For example: love – [l' u b o f'].
But not everyone has their own pair. There are some that are not similar in pronunciation to any others - these are unpaired consonants . The reproduction technique differs from the pronunciation of other sounds and combines them into groups.
Paired consonants
Soft and hard consonants
The phonetics of the Russian language is significantly different from many other languages. It contains hard and soft consonants.
When pronouncing a soft sound, the tongue is pressed harder against the palate than when pronouncing a hard consonant sound, preventing the release of air. This is what distinguishes a hard and soft consonant sound from each other. In order to determine in writing whether a consonant sound is soft or hard, you should look at the letter immediately after the specific consonant.
Consonant sounds are classified as hard in the following cases:
- if the letters a, o, y, e, s follow them - [poppy], [rum], [hum], [juice], [bull];
- after them there is another consonant sound - [vors], [hail], [marriage];
- if the sound is at the end of a word - [darkness], [friend], [table].
The softness of sound is written as an apostrophe: mole - [mol'], chalk - [m'el], wicket - [kal'itka], pir - [p'ir].
It should be noted that the sounds [w'], [y'], [h'] are always soft, and hard consonants are only [w], [ts], [zh].
A consonant sound will become soft if it is followed by “b” and vowels: i, ё, yu, i, e. For example: gen - [g'en], flax - [l'on], disk - [d'ysk] , hatch - [l'uk], elm - [v'el], trill - [tr'el'].
Unpaired consonants
The first group can be pronounced softly. The second has no analogues in pronunciation.
Unpaired consonants are divided into:
- sonors – [th'], [l], [l'], [m], [m'], [n], [n'], [r], [r']. When they are pronounced, a stream of air hits the upper sky, like a dome,
- hissing – [x], [x'], [ts], [h'], [h'].
The Russian alphabet contains letters that are difficult to understand in context. Are the sounds [ch], [th], [ts], [n] voiced or unvoiced? Learn these 4 letters!
Important! [h] - deaf! [th] - sonorous! [ts] is deaf! [n] – sonorous!
Unpaired consonants
Speech sounds
When talking to each other or reading aloud, we pronounce words. Our speech consists of words. Each word is made up of sounds.
Sound is the minimal unit of speech. Speech sounds differ from letters in that sounds are pronounced and letters are written. Letters are used to convey sounds in writing. Sounds create the phonetic shell of a word, which we hear and can reproduce ourselves with the help of our speech organs.
Speech sounds differ from each other in the way they are formed. Some sounds are pronounced in such a way that air passes freely between tense vocal cords and through the oral cavity, which can change its shape. This is how the vowel sounds [a], [o], [u], [e], [i], [s] are formed. They consist only of voice. Other speech sounds, and there are many more of them, are formed differently. During their formation, the exhaled air encounters various obstacles on its way when closing and opening the speech organs and exits through the mouth or nose. In this case, a noise characteristic of each sound arises. This is how consonants are formed:
[c], [p], [k], [s], [t], [b], etc.
Consonant sounds are noisy because they are formed using noise. Most of these speech sounds are paired consonants.
Check the spelling of paired consonants at the root or at the end of the word?
When sounds are pronounced, sometimes dull sounds are heard more often. But despite this, you must write the correct letter. All letters in words cannot change. Even though there is a different sound. To make sure that a word is written correctly, you will need to study certain rules. Thanks to them, it will become clear which sound is used in a word, voiceless or voiced, and the possibility of replacing paired consonant sounds will be excluded.
Paired consonants: rule
Rules for checking the spelling of voiceless and voiced consonants:
- Basically, when writing, the letters do not change; to check the spelling of a particular letter, you need to select a word with the same root in a different form. If there is a vowel after a dubious consonant, then you will decide which letter to write, voiced or unvoiced.
- It is easy to determine which consonant is written in a particular word when it is followed by a sonorant consonant: th, r, m, l, n .
Examples: in order not to make a mistake, in the word sugro b ( p ), you will need to change this word so that there is a vowel at the end: in sugro ba x. The word eye ( s ) , check: eyes , oboz ( s ) - oboz , code d ( t ) - code yes , chat ( d ) - chats .
IMPORTANT: There are some words that cannot be verified. These include - kofta . This word must be remembered and always written in it with the letter - f .
Test on the topic
- /10
Question 1 of 10Choose the correct statement
Start test
Hall of Fame
To get here, take the test.
- Vasilisa Kozlova
8/10
- Aliya Karashaeva
10/10
- Sergey Efremov
8/10
- Olga Gorkova
9/10
- Liliya Golomolzina
10/10
Application of the rule
The spelling of paired consonants needs to be practiced. You need to start by developing the ability to see the spelling pattern being studied. This will be the end of a word or a combination of consonants, in which sounds begin to influence the sound of each other - the subsequent one changes the quality of the pronunciation of the previous one.
| Spelling patterns - paired consonants | |
| at the end of a word | in a consonant cluster |
| bo[n]bro[t]bro[f']gvoz[t']ogoro[t]dro[w] | polo[s]kako[z']bare[z']bagoro[d']bacro[v']stra[sh] |
Next, we practice the skill of selecting test words.
When we know what a paired consonant is, it is not difficult to draw a conclusion about which option to choose:
- bo[p] – beans – bean;
- bro[t] – broda – ford;
- bro [f'] – eyebrows – eyebrow;
- nail[t'] – nails – nail;
- vegetable garden [t] – vegetable gardens – vegetable garden;
- dro[sh] – trembling – trembling;
- stripe [s]ka – stripe – stripe;
- ko[z']ba – mow – mowing;
- re[z']ba – cut – carving;
- goro[d']ba – fence – gorodba;
- kro [v'] – blood – blood;
- str[sh] - guard - guard.
Spelling problems
In words with paired consonants in terms of voicedness and voicelessness, it is quite easy to make a mistake if one sound is heard, but you need to write another. Difficulties can arise when a paired consonant comes before a deaf person or when a word ends with it (tetra[d]ka, bread[b]).
To correctly select a paired consonant when writing a word, controversial sounds must be checked. In difficult cases, the word is changed or a single root word is selected so that the paired consonant appears before the vowel sound (or before the sonorant sound: before th, m, n, r, l).
You can use different ways to select test words:
- Change to plural:
tooth - teeth, train - trains; - Replace with a diminutive:
bed - bed, bread - bread; - Choose a single-root adjective:
carrot - carrot, labor - difficult; - Change according to the principle small - large:
snowdrift - snowdrift, fur coat - fur coat; - Use the word “no” to change:
bicycle - no bicycle, watchman - no watchman.
The sounds are “completely unpaired”
In the Russian language, most consonants are either paired according to both characteristics, or paired according to one characteristic and unpaired according to another. For example , in the word [P'EN'] (stump), the sound [P'] is paired both in deafness-voicing (P' - B'), and in hardness-softness (P' - P), and the sound [N'] paired in hardness-softness (H' - N), but unpaired in deafness-voicedness.
However, there are several sounds that are unpaired in both characteristics. These are the sounds [Y'] (unpaired voiced, unpaired soft), [Ch'] (unpaired soft, unpaired deaf), [Sh'] (unpaired soft, unpaired deaf) and [Ts] (unpaired hard, unpaired deaf). Such sounds are often made in Russian language Olympiads. For example, “Guess the sound by its characteristics: unpaired hard, unpaired dull.” We already see that this is [C].
Paired voiced, voiceless consonants
Thanks to human speech abilities and the help of the tongue, we are able to pronounce various sounds. And the natural hearing aid helps people recognize these sounds. But we will not further study the natural capabilities of the human body. Let's dwell on how consonant sounds are written and sounded and what they are.
Classification of consonants
According to the rules of grammar, there are consonants:
- Voiceless , voiced - their pronunciation varies, thanks to the work of the human speech apparatus.
- Soft , hard - the subsequent letter after the consonant, which comes after it, plays a big role in determining such consonants.
Already from the phrase itself - paired consonants , it is clear that these are letters that have a similar pair in sound. So, voiced and voiceless consonant sounds can be similar in sound.
Some letters vary, as mentioned above, and they have a pair, while others do not. In the deaf-voiced scheme - unpaired are the following: x, ch, c, m, l, th, shch . You need to remember these consonants.
Task: write correctly a voiceless or voiced consonant
IMPORTANT: There are consonant letters in the Russian alphabet; they have their own specific context. Consonant sounds [ts]; [h]; [n]; [th] ; — what can they be classified as? [Ts] is a dull sound; [h] – voiceless consonant; [n] – voiced sound; [th] is a voiced consonant - this should be remembered without fail.
Paired voiced, voiceless consonants:
A number of voiced consonants exist in the Russian language, they include: r, g, v, zh, d, y, z, n, m, l, b . When you pronounce these consonants, you always feel some tension in the larynx. Voiced sounds are difficult to pronounce quietly in a whisper. Examples of words in which all consonants are voiced: ash , pride , gap , Rome , rum , zone . But not all voiced sounds have their own pair of unvoiced sounds.
Types of consonants
Table of paired consonants - voiced, voiceless:
| b | and | h | G | V | d |
| P | w | With | To | f | T |
Thanks to studying this topic at school, students are able to write correctly later. After all, there are rules about writing and checking this or that paired consonant; in particular, let’s look at examples: snow g (x), you can check: what’s missing? Snow , table b (p) - checked as table b y, bread b (p) (check - what is missing? Bread a ).
Russian speech is rich in a whole arsenal of words that are similar in sound, but with different meanings. So, by replacing a voiced consonant with a voiceless one, you can get a completely different word in meaning. Examples: zud – sud , gora – kora , heat – shar .
Exercise to reinforce the topic: paired unvoiced, voiced consonants
There are many visual examples that can help you understand the spelling of voiced and voiceless paired consonants. See some of them:
- Code d(t) – you can check it like this : codes
- One hundred g(x) – test word: one hundred g ami
- Horse d t ) – you can check this way: horse d and
- Boat - heard (t) . Checking the word: boat .
As you can see, checking the spelling of consonant sounds will not be difficult, and thanks to the examples, you can easily teach this topic to your child.