Speech therapy dictionary for parents
Tamara Gurina
Speech therapy dictionary for parents
«Speech therapy dictionary for parents»
Dear parents ! While your child is working with a speech therapist , you may encounter various incomprehensible terms. In order to make your work more productive, I suggest you get acquainted with some terminology.
Automation (sound)
– the stage when correcting incorrect sound pronunciation, following the production of a new sound;
aimed at developing the correct pronunciation of sounds in coherent speech; consists in the gradual, consistent introduction of a given sound into syllables, words , sentences and into independent speech.
Agrammatism is a violation of the understanding and use of grammatical means of language.
Alalia is the absence or underdevelopment of speech in children with normal hearing and primarily intact intelligence.
Amorphous words are grammatically unchangeable root words , “anomalous words ”
children's speech -
words-fragments (in which only parts of the word , words-onomatopoeia ( words-syllables with which the child designates objects, actions, situations, contour words (in which the stress and number of syllables ).
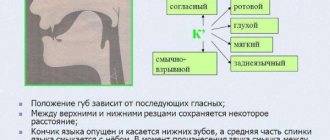
Articulation - the activity of the speech organs, associated with the pronunciation of speech sounds and their various components that make up syllables and words .
The articulatory apparatus is a set of organs that ensure the formation of speech sounds (articulation, includes the vocal apparatus, muscles of the pharynx, larynx, tongue, soft palate, lips, cheeks and lower jaw, teeth, etc.
Dysarthria is a violation of the pronunciation side of speech, caused by insufficient innervation of the speech apparatus.
Dyslalia is a violation of sound pronunciation with normal hearing and intact innervation of the speech apparatus.
Dyslexia is a partial specific disorder of the reading process due to immaturity (impairment)
higher mental functions and manifest themselves in repeated errors of a persistent nature.
Dysgraphia is a partial specific disorder of the writing process caused by immaturity (impairment)
higher mental functions and manifest themselves in repeated errors of a persistent nature.
Delayed speech development (SDD)
– lag in speech development from the age norm of speech development at the age of up to 3 years.
Stuttering is a violation of the tempo-rhythmic organization of speech, caused by the convulsive state of the muscles of the speech apparatus.
Onomatopoeia is a conditional reproduction of natural sounds and sounds that accompany certain processes (laughter, whistling, noise, etc., as well as animal cries.
Impressive speech – perception, understanding of speech.
Innervation is the provision of organs and tissues with nerves and, therefore, communication with the central nervous system.
General speech underdevelopment (GSD)
– various complex speech disorders, in which children have impaired formation of all components of the speech system related to its sound and
semantic side , with normal hearing and intelligence.
Reflected speech is speech repeated after someone.
Finger games are a generally accepted name for activities aimed at developing fine motor skills in children.
Perseverations are cyclical repetition or persistent reproduction, often contrary to the conscious intention of any actions, thoughts or experiences.
Prenatal period – pertaining to the period before birth.
Rhinolalia is a violation of voice timbre and sound pronunciation, resulting from excessive or insufficient resonance in the nasal cavity during speech. Such a violation of resonance occurs from the incorrect direction of the voice-exhalatory stream due to either organic defects of the nasopharynx, nasal cavity, soft and hard palate, or disorders of the function of the soft palate.
of words or phrases spoken by someone .
Cramps are involuntary muscle contractions that occur due to epilepsy, brain injuries, spasmophilia and other diseases.
Expressive speech is active oral and written expression.
"Mnemotechnology"
Preschool childhood is a special period in personality development. During this period, memory is faster than other abilities in terms of development. Children ask a lot of questions, they desperately need new information: the brain requires food.
But along with this, there are many problems in the development of children: poor vocabulary , impaired sound pronunciation and attention, rapid fatigue, loss of interest in activities. Therefore, seeing this situation, we began to look for ways to solve this problem. Considering that nowadays children are overloaded with information, it is necessary that the learning process be interesting, entertaining, and developmental for them.
Taking statements as a basis. K. D. Ushinsky “Teach a child some five words - he will suffer for a long time and in vain, but associate twenty such words with pictures , and he will learn them on the fly.” It is this idea that is inherent in such technology as mnemonics.
Mnemonics is a system of methods and techniques that ensure effective memorization, preservation and reproduction of information and speech development.
Tasks of mnemonics:
• Improve perception, vision, hearing, tactile sensations, smell;
• to develop memory skills, the ability of children to manage their attention, to make it “obedient”
;
• stimulate the child's intellectual development;
• promote memorization of any information.
Like any work, mnemonics is built from simple to complex. It is necessary to start working with the simplest mnemonic squares, sequentially move on to mnemonic tracks, and later to mnemonic tables
• Mnemonic squares
For children of primary preschool age, colored ones are best suited, since sensory standards are formed; children retain individual images in their memory: a Christmas tree - green, a bun - yellow, etc. Later, the images are replaced by a graphic image: a fox - orange geometric shapes (circle, square )
etc. For older children, the diagrams are given in one color.
Algorithm for working with mnemonic squares
1. This is the introduction of symbols.
2. The use of elements of supporting diagrams, symbols in all types of classes, in various types of activities, since the child should not have a “habituation”
, that this symbol is applicable only in one area because the symbol is universal.
3. Introduction of negatives.
4. Children’s independent search for images symbolizing some quality. The task of this stage is to actively search for images and be able to justify your choice.
5. Information is recoded, i.e., converted from abstract symbols to images.
• Mnemonic track
It carries information, but in small quantities, which is very important in the early stages of a child’s education. When working with a mnemonic track, I use application techniques. Symbols characteristic of each season: rain, wind, snow, clouds, warmth, buds, grass, snow melts, birds fly in/fly away, the sun shines little, trees without leaves, etc.
• Mnemonic table
A schema that contains certain information. Each cell of this table can correspond to one word or an entire phrase . In the future, picking up this kind of “cheat sheet”
, the child will be able to reproduce information more successfully.
Mnemonic tables are especially effective when learning poems.
Work algorithm.
Stage 1: Examination of the table and analysis of what is shown on it.
Stage 2: Recoding of information is carried out, i.e. transformation from abstract symbols into images.
3. Sketching mnemonic tables for children (in older groups)
4. Storytelling using mnemonic tables created by children.
The size of mnemonic tables can vary depending on the age of the children and their level of development. It is recommended to use the following table sizes:
• for younger preschoolers - tables for 4 - 9 cells
• for older preschoolers - tables up to 25 cells.
Thus, the use of mnemonic methods:
• facilitates memorization and increases memory capacity, develops speech and thinking activity of children;
• allows the child to systematize his direct experience;
• the child, relying on memory images, establishes cause-and-effect relationships and draws conclusions;
• develops children's creative knowledge
Article:
Dear parents!
As your child works with a speech therapist, you may encounter various unfamiliar terms. In order to make your work more productive, I suggest you get acquainted with some terminology. Automation (sound) – a stage in the correction of incorrect sound pronunciation, following the production of a new sound; aimed at developing the correct pronunciation of sounds in coherent speech; consists in the gradual, consistent introduction of a given sound into syllables, words, sentences and into independent speech.
Agrammatism is a violation of the understanding and use of grammatical means of language.
Alalia is the absence or underdevelopment of speech in children with normal hearing and primarily intact intelligence.
Amorphous words are grammatically unchangeable root words, “abnormal words” of children's speech - words-fragments (in which only parts of the word are preserved, words-onomatopoeia (words-syllables with which the child denotes objects, actions, situations, contour words (in which stress and number of syllables are reproduced correctly).
Articulation is the activity of the speech organs associated with the pronunciation of speech sounds and their various components that make up syllables and words.
The articulatory apparatus is a set of organs that ensure the formation of speech sounds (articulation, includes the vocal apparatus, muscles of the pharynx, larynx, tongue, soft palate, lips, cheeks and lower jaw, teeth, etc.
Dysarthria is a violation of the pronunciation side of speech, caused by insufficient innervation of the speech apparatus.
Dyslalia is a violation of sound pronunciation with normal hearing and intact innervation of the speech apparatus.
Dyslexia is a partial specific disorder of the reading process, caused by the immaturity (impairment) of higher mental functions and manifested in repeated persistent errors.
Dysgraphia is a partial specific disorder of the writing process, caused by the immaturity (impairment) of higher mental functions and manifested in repeated errors of a persistent nature.
Speech development delay (SSD) is a lag in speech development according to the age-related norm of speech development at the age of up to 3 years.
Stuttering is a violation of the tempo-rhythmic organization of speech, caused by a convulsive state of the muscles of the speech apparatus.
Onomatopoeia is a conditional reproduction of natural sounds and sounds that accompany certain processes (laughter, whistling, noise, etc., as well as animal cries.
Impressive speech – perception, understanding of speech.
Innervation is the provision of organs and tissues with nerves and, therefore, communication with the central nervous system.
General speech underdevelopment (GSD) is a variety of complex speech disorders in which children have impaired formation of all components of the speech system related to its sound and semantic side, with normal hearing and intelligence.
Reflected speech is speech repeated after someone.
Finger games are a generally accepted name for activities aimed at developing fine motor skills in children.
Perseverations are cyclical repetition or persistent reproduction, often contrary to the conscious intention of any actions, thoughts or experiences.
Prenatal period – pertaining to the period before birth.
Rhinolalia is a violation of voice timbre and sound pronunciation, resulting from excessive or insufficient resonance in the nasal cavity during speech. Such a violation of resonance occurs from the incorrect direction of the voice-exhalatory stream due to either organic defects of the nasopharynx, nasal cavity, soft and hard palate, or disorders of the function of the soft palate.
Conjugate speech is the joint simultaneous repetition by two or more persons of words or phrases spoken by someone.
Cramps are involuntary muscle contractions that occur due to epilepsy, brain injuries, spasmophilia and other diseases.
Expressive speech is active oral and written expression.
"Mnemotechnology"
Preschool childhood is a special period in personality development. During this period, memory is faster than other abilities in terms of development. Children ask a lot of questions, they desperately need new information: the brain requires food.
But along with this, there are many problems in the development of children: a poor vocabulary, impaired sound pronunciation and attention, rapid fatigue, loss of interest in activities. Therefore, seeing this situation, we began to look for ways to solve this problem. Considering that nowadays children are overloaded with information, it is necessary that the learning process be interesting, entertaining, and developmental for them.
Taking statements as a basis. K. D. Ushinsky “Teach a child some five words unknown to him - he will suffer for a long time and in vain, but connect twenty such words with pictures, and he will learn them on the fly.” It is this idea that is inherent in such technology as mnemonics.
Mnemonics is a system of methods and techniques that ensure effective memorization, preservation and reproduction of information and speech development.
Tasks of mnemonics:
• Improve perception, vision, hearing, tactile sensations, smell;
• to develop memory skills, the ability of children to manage their attention, to make it “obedient”;
• stimulate the child's intellectual development;
• promote memorization of any information.
Like any work, mnemonics is built from simple to complex. It is necessary to start working with the simplest mnemonic squares, sequentially move on to mnemonic tracks, and later to mnemonic tables
• Mnemonic squares
For children of primary preschool age, colored ones are best suited, since sensory standards are formed; children retain individual images in their memory: a Christmas tree - green, a bun - yellow, etc. Later, the images are replaced by a graphic image: a fox - orange geometric shapes (circle, square ) etc. For older children, the diagrams are given in one color.
Algorithm for working with mnemonic squares
1. This is the introduction of symbols.
2. The use of elements of support schemes, symbols in all types of classes, in various types of activities, since the child should not get “accustomed” to the fact that this symbol is applicable only in one area because the symbol is universal.
3. Introduction of negatives.
4. Children’s independent search for images symbolizing some quality. The task of this stage is to actively search for images and be able to justify your choice.
5. Information is recoded, i.e., converted from abstract symbols to images.
• Mnemonic track
It carries information, but in small quantities, which is very important in the early stages of a child’s education. When working with a mnemonic track, I use application techniques. Symbols characteristic of each season: rain, wind, snow, clouds, warmth, buds, grass, snow melts, birds fly in/fly away, the sun shines little, trees without leaves, etc.
• Mnemonic table
A schema that contains certain information. Each cell of this table can correspond to one word or an entire phrase. In the future, having picked up this kind of “cheat sheet”, the child will be able to more successfully reproduce information.
Mnemonic tables are especially effective when learning poems.
Work algorithm.
Stage 1: Examination of the table and analysis of what is shown on it.
Stage 2: Recoding of information is carried out, i.e. transformation from abstract symbols into images.
3. Sketching mnemonic tables for children (in older groups)
4. Storytelling using mnemonic tables created by children.
The size of mnemonic tables can vary depending on the age of the children and their level of development. It is recommended to use the following table sizes:
• for younger preschoolers - tables for 4 - 9 cells
• for older preschoolers - tables up to 25 cells.
Thus, the use of mnemonic methods:
• facilitates memorization and increases memory capacity, develops speech and thinking activity of children;
• allows the child to systematize his direct experience;
• the child, relying on memory images, establishes cause-and-effect relationships and draws conclusions;
• develops children's creative knowledge
List of scientific terms used by a speech therapist teacher in correctional activities
GLOSSARY
speech therapist teacher
Sound Automation
— the stage of correcting incorrect sound pronunciation, which follows after setting a new sound; aimed at developing the correct pronunciation of sounds in coherent speech; consists in the gradual, consistent introduction of a given sound into syllables, words, sentences and into independent speech.
Agnosia
— violation of the processes of recognition of objects and phenomena with
Agrammatism
— violation of the psychophysiological processes that ensure the grammatical orderliness of speech activity; with A. there is omission of prepositions, incorrect agreement of words in gender, number, “telegraphic style”, etc.; A. usually occurs in connection with aphasia or alalia.
Agraphia
- (a-grapho-I don’t write; lat.) speech disorder, expressed in writing impairment, complete loss of the ability to write.
Alexia
- complete inability or loss of ability to master the reading process.
Ambidextrous
- a person whose functions of both hands are equally well developed.
Analysis and synthesis
- opposing and inextricably linked logical techniques; A., by decomposing a complex problem into its component parts, simplifies it and makes it easier for students to understand this phenomenon, and S. makes it possible not only to connect the disparate principles of the subject being studied and understand it as a whole, but also to comprehend the connection of this whole with other objects of human knowledge.
Articulation
- (articulare - clearly pronounce; lat.) the work of the speech organs when pronouncing syllables, words, phrases. Organs of articulation: lips, tongue, lower jaw, pharynx. Accurate articulation produces clear, clear speech.
Articulation gymnastics
- a system of exercises for the speech organs, which are performed daily or several times a day according to the instructions of a speech therapist.
Articulatory apparatus
- a set of organs that ensure the formation of speech sounds (articulation); includes the vocal apparatus, muscles of the pharynx, tongue, soft palate, lips, cheeks and lower jaw, teeth, etc.
Autism
- immersion in the world of personal experiences with weakening or loss of contact with reality, loss of interest in reality; a sign of mental disorder.
Communication barriers
- a psychological phenomenon that arises during communication between interlocutors. We are talking about the emergence of a feeling of hostility, distrust of the speaker, which extends to the information conveyed by him.
Bradylalia
- pathologically slow speech rate.
Attention
- voluntary or involuntary direction and concentration of mental activity.
Will
— a person’s ability to act in the direction of a consciously set goal, while overcoming internal obstacles.
Imagination
- the mental process of forming new images by processing the material of perceptions and ideas obtained in previous experience.
Upbringing
- the process of systematic and purposeful influence on the spiritual and physical development of the individual.
Perception
- the mental process of reflecting reality, forming a subjective image of the objective world; Depending on which of the analyzers is the leading one in a given act of perception, visual, auditory, tactile, gustatory and olfactory perception are distinguished.
Active speech gymnastics
- a system of exercises for the speech organs, which are performed daily or several times a day according to the instructions of a speech therapist.
Passive speech gymnastics
- a form of speech gymnastics, in which the child makes movements only with the help of mechanical influence on the speech organs (pressure from the hand of a speech therapist or an appropriate probe, spatula); after several repetitions an attempt is made, i.e. passive movement is gradually transformed into active.
Voice
- sounds that arise as a result of vibration of the vocal cords when talking, singing, laughing, etc.
— voice pitch is a physiological property of the speech voice, controlled by the tension of the vocal cords and the frequency of their vibrations. They are distinguished: high speech voice - developed head sound; low - developed chest sound; medium - mixed sound.
- vocal range - volume of sound, that is, the interval between the highest and lowest sounds of the voice. A voice with a large range of sound has flexibility, mobility, and play of sound.
- voice flight - the duration of the sound of individual phrases, words and sounds. When the sound is rich in intonation, the words are pronounced emotionally, clearly, clearly, and the speaker’s speech reaches the far corners of the audience.
- voice timbre - individual sound coloring, voice quality - characteristic of each person.
- well-trained voice - the voice is the most fully and comprehensively developed, with great range, strength, sonority, and flexibility.
Grammar
- a branch of linguistics that studies forms of inflection, word combination formulas and types of sentences in abstraction from the specific material (lexical) meaning of words, phrases and sentences.
Grammatical structure
- the structure of words and sentences inherent in a given language.
Bilingualism
- equally perfect command of two languages.
Pronunciation defects
- see Dysarthria, Dyslalia, Rhinolalia.
Diagnostics
- 1) a branch of medicine that studies the content, methods and successive stages of the process of recognizing diseases or special physiological conditions; 2) the process of recognizing the disease and assessing the individual biological and social characteristics of the subject, including a targeted medical examination, interpretation of the results obtained and their generalization in the form of a diagnosis.
Dysarthria
- a violation of the pronunciation side of speech, caused by insufficient innervation of the speech apparatus.
Dysgraphia
- partial disruption of the writing process, in which persistent and repeated errors are observed: distortions and replacements of letters, distortions of the sound-syllable structure of a word, violations of the unity of the spelling of individual words in a sentence, agrammatism in writing.
Dislalia
- violation of sound pronunciation.
Dyslexia
- partial disruption of the reading process, manifested in repeated persistent errors.
Impaired mental function
- temporary lack of development of the psyche as a whole or its individual functions.
Delayed speech development
- a disturbance in the course of speech development, manifested in a discrepancy with normal ontogenesis, a lag in tempo.
Stuttering
- a violation of the tempo-rhythmic organization of speech, caused by the convulsive state of the muscles of the speech apparatus.
Neurosis-like stuttering
- stuttering, similar in appearance to neurotic stuttering, but having a non-psychogenic origin; the term "Z.N." often used as a synonym for the term "organic stuttering".
Neurotic stuttering
- stuttering caused by exposure to traumatic factors; term "Z.n." often used as a synonym for the term “functional stuttering”.
Sound replacements
- a defect in the reproduction of speech sounds, in which, instead of the correct sound, a sound is pronounced that is similar in the method of formation or in the place of articulation, paired in deafness/voice, hardness/softness, depending on whether articulatory or acoustic images of sounds are not formed.
Memorization
- the mental process of imprinting information in memory (distinguish between voluntary and involuntary).
Mirror speech
- pronouncing (reading) words in reverse order, starting with the last and ending with the first sound of the word.
Mirror letter
- 1) writing from right to left with a mirror image of the written text; 2) mirror writing of letters.
Impressive speech
- perception, understanding of speech; I.r. oral is expressed in the auditory perception of oral speech, and I.r. written - in the visual perception of the text (reading).
Intonation
- (intono-pronounce loudly; Latin) a set of sound elements of speech (strength, height, timbre, duration of sound). Intonation creates an additional shade of meaning, subtext of speech, and helps to better understand the statement. If the speech is rich in intonations, it is especially clear and beautiful.
- intonation includes: rhythm, tempo, timbre and melody of speech. Melodics - the modulation of the voice for a question, exclamation or statement. Rhythm is a uniform alternation of stressed and unstressed syllables (different in voice strength and duration). Tempo is the speed of speech delivery. (When accelerated, intelligibility decreases; when slowed down, expressiveness decreases). Timbre is the emotional coloring of a phrase, giving speech different shades: surprise, joy, sadness, etc.
Kappacism
- lack of pronunciation of the sound [K].
Burr
- violation of the pronunciation of the sounds R and L.
Correction
— correction sm. shortcomings; eg, K. vision, K. movements, K. speech.
Tongue-tied
- see Dislalia.
Lambdacism
- incorrect pronunciation of the sound [L]. Common speech impediment.
Vocabulary
- the entire set of words that make up a k.-l. language or dialect.
Lexico-grammatical
- characterized by the unity of lexical and grammatical properties, connecting those and other properties.
Lexico-morphological
- related to the morphology of word formation.
Babbling
- the child’s vocal reactions to positive stimuli; appears in the second month of life in the form of various simple complexes of sounds (humming) and gradually becomes more complex (multiple repetition of syllables); in case of severe speech disorders, it is detected in children late and at a later age.
Logoneurosis
- neurosis, manifested in the form of a speech disorder (neurotic stuttering).
Speech therapist
is a correctional teacher who deals with speech deficiencies in children and adults.
Logophobia
- (logos-teaching, phobos-fear; Greek) fear of pronouncing words, speech
Facial expressions
- a set of movements of the facial muscles, eye movements of a person, expressing his state or his attitude towards something
Morphology
- in linguistics: 1) part of the language system, uniting words as carriers of grammatical meanings, their grammatical classes, the laws of their existence and formation; 2) a section of grammar that studies this part of the language system.
Monologue
- an oral or written statement by one person. A monologue is a significant segment of speech containing interconnected statements. There are three types of monologues: 1) description; 2) narration; 3) reasoning.
Motor skills
- motor activity of the body, its individual organs or parts thereof.
Mutism
- refusal of verbal communication while maintaining the speech apparatus; observed in mental illness, in shy children, etc.
Nasalization
- the acquisition of a nasal timbre by a sound (mainly a vowel) due to the lowering of the velum and the simultaneous release of an air stream through the mouth and nose.
Violation of the visual image of the letter -
mixing letters with a similar visual image, mirror writing.
Violation of the visual image of the word
- violation of the letter composition of a word.
Violation of word structure
- simplification of words, rearrangements, underwriting, merging and splitting of words.
Reading and writing impairment
- a sharp difficulty in mastering the graphic form of speech, most often associated with a general underdevelopment of speech in children with normal hearing and normal mental abilities; most often manifests itself in a general distortion of the sound composition of words and the replacement of letters.
General speech underdevelopment
- various complex speech disorders, in which children have impaired formation of all components of the speech system related to the sound and semantic side.
Ontogenesis
- a set of successive morphological, physiological and biochemical transformations of the body from its inception to the end of life.
Speech organs
- various parts of the human body involved in the formation of speech sounds.
Spelling
- a system of rules that determine the uniformity of methods of transmitting speech in writing.
Pantomime
- a set of expressive body movements that accompany speech and emotions.
Voice mobility
- the ability of the voice to easily change its pitch and strength. The lack of mobility in the voice makes it monotonous.
Speech mobility
- the ability to control the speed of rhythmic movement of speech, its tempo, freely moving from slow to fast and vice versa. This ability is developed during training.
Sound production
- creating, using special techniques, a new connection between auditory (perception of spoken sound), motor-kinesthetic (independent perception of sound) and visual (visual perception of articulation of sound) sensations; production of sounds, breathing, and voice is the first stage in the formation of pronunciation skills in deaf, hard of hearing children, and in children with speech impairments; characterized by the widespread use of intact analyzers (visual, skin, motor, auditory), the use of various methodological techniques, technical devices, as a result of which the child learns one or another pronunciation skill; The stage of pronunciation skills is followed by the stage of their automation, the transformation of skills into strong skills, which is achieved as a result of special exercises and speech practice.
Bite
- the relationship of the dentition of the upper and lower jaws when they are closed.
Proxemics
- a science that studies the norms of organizing communication (in space, in time).
Prosody
- melodic-intonation side of speech.
Speech
- a form of communication mediated by language.
Speech apparatus
- a system of organs involved in the formation of speech sounds. There are peripheral and central sections of R.a.
Speech hearing
- a person’s ability to perceive and reproduce all phonological means of language when perceiving speech. Components of speech hearing:
- pitch hearing - the ability to hear and perceive the melody of speech;
- rhythmic hearing - the ability to sense and reproduce its internal tempo in speech;
- tonal hearing - the ability to hear and reproduce timbral changes in the voice depending on changes in feelings and relationships;
- physical hearing - the ability to perceive spoken speech in different ranges of volume and height;
- phonemic hearing - the ability to distinguish and reproduce speech sounds.
Rhythmics
- a system of physical exercises based on the connection between movement and music.
Resource state
- the optimal internal state of a person. Based on memories of once successfully done work; about pleasant states of confidence and harmony.
Reflection
- a reflection full of doubts and contradictions. The ability to look at yourself from the outside. Analysis of your mental state.
Recipient
- user of information.
Rhythm of speech
- sequential alternation of speech elements over the same amount of time.
Rhetoric
— theory and mastery of harmonious speech.
Rotacism
- a common deficiency in pronouncing the sound [P].
Sigmatism
- deficiencies in the pronunciation of whistling sounds: [S, Z, Ts] and hissing sounds [Zh, Sh, Ch, Shch]
Dictionary passive
- a stock of understandable words.
Dictionary active
- the presence of words that a given person constantly uses in his speech.
Scanned Speech
- speech in syllables, violation of the rhythm of speech.
Mixing sounds
- a lack of speech, expressed in the fact that the child, being able to pronounce certain sounds, mixes them in speech (for example, instead of a hat he says “sapka” and then instead of a sled - “shanki”). N.Z. - a sign of incompleteness of the process of mastering the system of phonemes. Normally, this process ends in a child by the age of 4-5. By this time, all speech sounds are distinguished by children by ear and are pronounced correctly.
Conjugate speech
- the joint repetition by two or more persons of words or phrases spoken or written by someone.
Spontaneous speech
- involuntary.
Clonic seizures
- short-term involuntary contractions and relaxations of muscles quickly following one after another.
Tonic convulsions
- prolonged muscle contractions due to a single impulse.
Tahilalia
- a speech disorder, expressed in excessive speed of its tempo, with full preservation of the remaining components of phonetic design, as well as Lesika and grammatical structure.
Bridle short
- a congenital defect consisting of shortening of the so-called frenulum of the tongue (hyoid ligament). With this defect, tongue movements may be difficult. This usually causes mechanical dyslalia.
Speech phobia
- obsessive fear of speech. Often observed with stuttering.
Phoneme
- speech sound - sound distinguisher. The Russian language has 42 phonemes (6 vowels and 36 consonants).
Phonemic hearing
- the ability to auditory perception of sound speech, phonemes, the ability to distinguish speech sounds in their sequence in words and the ability to distinguish phonemes that are similar in sound. F.s. is important for mastering the sound side of the language. Violation of F.s. in children leads to specific pronunciation deficiencies.
Language
- the most important means of communication, a tool for thinking and influencing people on each other.
Speech therapy games on lexical topics
"ONE IS MANY"
Objectives: formation of plural nouns in the nominative and genitive cases.
For example: no horse, many cows, no pig, many goats, etc.
"BIG SMALL"
Objectives: continue to learn how to form nouns using diminutive and augmentative suffixes.
For example: cat - cat - cat, dog - dog - dog, etc.
"HUGE"
Tasks: formation of nouns with the augmentative suffix -ISCH
For example: cat - cat, cow - cow
"WHO IS BIGGER?"
Tasks: formation of related words
For example: cat - cat - kitten - kitty - cat - kitty - kitty, etc.
“NAME THE MOTHER AND THE BABIES”
Tasks: forming nouns from nouns
For example: crows have crows, owls have owls.
"NAME YOUR FAMILY"
Tasks: forming nouns from nouns
For example: dad is a cat, mom is a cat, children are kittens. This is a cat family.
"A LOT OF"
Objectives: consolidation of nouns in the active dictionary
For example: many cows - a herd, many horses - a herd, many dogs - a pack.
"WHAT IS HE DOING? WHAT ARE THEY DOING?
Tasks: Use singular and plural verbs of the 3rd person present tense.
For example: pecks - they peck, flies - they fly, waves - they wave, etc.
“WHO DOES THIS?”
Objectives: learn to select verbs for a given noun. Select actions for the subject.
For example: she catches mice, purrs, meows, laps - this is a cat.
“WHO IS SCREAMING?”
Tasks: Formation of verbs from onomatopoeia.
For example: a cow moos, a sheep bleats, a goat bleats, etc.
"TELL WHICH"
Objectives: Coordination of adjectives with masculine and feminine nouns, singular and plural, in the nominative case, learning to select adjectives for a given noun
For example: long tail, sharp horns, mustachioed muzzle.
"TELL WHICH"
Objectives: learn to select adjectives for a given noun.
For example: she is horned, big, motley - a cow. He is tall, fast, handsome - a horse, etc.
"WHOSE?"
Tasks: forming possessive adjectives from nouns.
For example: goat fluff, cow's milk, dog's face, etc.
"SAY THE OPPOSITE"
Tasks: compiling complex sentences with the conjunction [a] according to the model. Mastering antonym words.
For example: a horse has a long tail, and a pig…(short), etc. The cat is short, and the horse...(high), etc.
“WHAT PAIL?”
Tasks: Formation of adjectives with a diminutive suffix.
For example: soft, fluffy
“SAY IN ONE WORD, WHAT?”
Tasks: Formation of complex adjectives by merging the stems of two nouns.
For example: a horse has a long mane, it is long-maned; A goat has long hair and is long-haired.
“WHERE, WHERE, WHERE?”
Tasks: use of prepositions ON, IN, IZ, S(SO), UNDER, FOR, etc.
For example: a kitten hid on the floor of the bed, on a shelf, in a box, behind a chair, crawled out from under the bed, from under a chair, out of a box, jumped off the table, etc.
"WHO LIVES WHERE?"
Tasks: Use of prepositional constructions in speech, practical use of the preposition “B” in speech.
For example: a dog lives in a kennel, a cow lives in a barn, a cat lives in a house, etc.
"FUNNY SCORE"
Objectives: learn to coordinate numerals with nouns
For example: a cat has two kittens, a goat has three kids, a sheep has five lambs, etc.
Methods of speech therapy work on the formation of vocabulary in children with general speech underdevelopment
Publications on the topic:
Formation of coherent speech in children of senior preschool age with general underdevelopment of speech Methodological development on the topic: “Formation of coherent speech in children of senior preschool age with general underdevelopment of speech through.
“Educational game as a form of work with preschool children with general speech underdevelopment.” Slide 1 DEVELOPMENTAL GAME - AS A FORM OF WORK WITH PRESCHOOL CHILDREN WITH GENERAL SPEECH UNDERDEVELOPMENT. Slide 2. “You want your child.
Features of the formation of the grammatical structure of speech in children with general speech underdevelopment Introduction: A child’s acquisition of the grammatical structure of speech is a complex, multi-level process that is associated with the work of the cerebral cortex.
Speech therapy work on the formation of the syllabic structure of words in older preschoolers with general speech underdevelopment Among the various tasks of special education in kindergarten, a special place should be given to mastering the sound and syllabic structure.
Event “Use of Lego technologies in speech therapy work with children with general speech underdevelopment” I. Hello, dear teachers. We are pleased to welcome you to this meeting, which we want to devote to: The use of LEGO technology.
Features of dialogical speech of children of senior preschool age with general speech underdevelopment Children with general speech underdevelopment have significant difficulties in communicating between children and with adults. Most children with ODD.
Outline of a lesson on the development of coherent speech in children with general speech underdevelopment Program content: • Correctional and educational tasks: expanding and concretizing ideas about domestic animals. Improvement.
Development of vocabulary in older preschoolers with general speech underdevelopment of level III Speech development is an essential component of the general education of a preschooler; it is closely related to cognitive and mental development.
Development of figurative speech in children of senior preschool age with general underdevelopment of speech in integrated classes Development of figurative speech in children of senior preschool age with general underdevelopment of speech in integrated classes Tukish Tatyana Fedorovna.
Features of the use of theatrical games in speech therapy work with children with general speech underdevelopment Preschool educational institutions and groups for children with speech disorders are the first stage of lifelong education and are included in.