Goal: to clarify the pronunciation of the sound “and”, to teach it to intonate, to consolidate the acoustic-articulatory characteristics, to isolate words from the composition, to determine its place in a word. Practice forming possessive adjectives, plural. noun To introduce the symbol of the sound “and”, to develop attention, memory, fine, articulatory, and general associative thinking.
Progress of the lesson
Organizing time.
Game “Name the vowel sound in the word” Poppy, tank, garden, oak, juice, lady, himself, beetle, knock, crayfish, chair, table, catfish, elk, ball...
Main part
1. Articulation gymnastics.
– Smile – Tube – Window – Alternation “Smile” - “Tube” - “Window”
2. Introducing the sound "I"
Ira and Igor were playing, all the toys were scattered. – What sound did you hear most often? “We’ll get to know this sound better today.” The plot picture “Donkey” is exhibited. A relative of the horse is a donkey, wears a long, thin tail, and also has large ears, a decoration on the top of its head. He always sings a song: and-and-and Sing the donkey's song. Let's smile broadly, We'll sing the song easily, The voice sounds playful, “And” it says beautifully. Sponges and teeth do not interfere, the song “I” is not disturbed. You see how long we pulled out this sound, which means this sound is a vowel. The speech therapist introduces the children to photography (Tkachenko’s symbol for the sound “i”). — Why is the photograph of the sound “and” “rectangle”?
3. Game “What does Igor say?” (reading by silent articulation of the sound combinations “au”, “ua”, oui, io...)
4. Work on intonation expressiveness of speech. Game “Quiet and Loud” The sound “I” has a voice and can sing. Make a sound with a gradual weakening of the voice while exhaling smoothly.
5. Development of phonemic hearing.
Game “Be Attentive” - Isolating the sound [and] from a number of vowels: o, a, i, u, o, i, uh, o, and... - Isolating the sound [and] from a number of syllables: their, am, uk, po , ni, fo,.. -Isolation of the sound [i] from the composition of the word: tights, skirt, jacket, jackets, willow, bandage
6.Determining the place of sound in words: whale, willow, roosters
7. Physical exercise “Turkey” A turkey walks around the yard. Like a feather chest. He walks slowly, from side to side, breathing slightly. It shakes its wings with importance and calls the turkey poults to come. And they run single file from their father.
8. Game “One-Many” (pay attention to the position of the sound “I”) Iron, boot, spider, stocking, lock, lump, sock
9.Game “Whose ears” (rabbit, bear, wolf, squirrel)
10.The game “Find a Pair” for the development of associative thinking. (needle, thread, books, sheet, nails, pliers, trousers, jacket, hands, gloves, Christmas trees, pine cones). Make up a sentence and post its diagram with each pair of pictures.
11. Finger gymnastics Show previously learned letters from your fingers.
12. Letter
Lesson summary
Author: Vanifatieva Victoria Viktorovna, teacher-speech therapist, KDOU "Fairy Tale", Pershotravensk, Dnepropetrovsk region. Ukraine
The article is published in the author's edition
Lesson summary for children of senior preschool age "Sound and letter U"
Lesson summary with methodological recommendations.
“Sound and letter U. Visit Umka.
Compiled by a speech therapist
Sadyrina Oksana Leonidovna
1. Justification of the relevance of the development.
Recently, the number of children experiencing learning difficulties has increased significantly, who can be identified as a special group “children with mental retardation (MDD)”. According to statistics, among preschoolers the number of such children is 25%, and among primary schoolchildren - 50%.
As a rule, children with mental retardation are not ready for school in all basic mental parameters:
- knowledge and ideas about the world around us;
- level of development of mental operations, actions and skills;
- cognitive activity;
- regulation of behavior.
Characteristic of children with mental retardation is the absence of gross violations of sound pronunciation and grammatical structure of speech that would interfere with their communication with others, however, in the majority, speech is characterized by sluggish articulation and intonation inexpressiveness. Slurred speech increases with repeated pronunciation of words with complex syllabic structure. This is due to insufficient motor function of the articulatory apparatus and low mobility of the speech organs.
The peculiarity of vocabulary and speech understanding in children with mental retardation is associated with emotional and intellectual deficiency. This is what causes children’s limited, inaccurate and erroneous ideas about the world around them.
It becomes obvious that without special correctional and developmental work, it is difficult for preschoolers with mental retardation to study practically all sections of spelling and grammar of the Russian language.
Thus, taking into account the modern social order, caused by the increase in the number of children with mental retardation, there is a need to develop technologies for comprehensive correctional and developmental support of the educational process.
2. Justification of the novelty of educational and methodological development, determination of the author’s contribution to the work.
In the summary of correctional and developmental activities (CDA), when explaining and consolidating the material being studied, the main emphasis is placed on the use of various gaming techniques
, which arouses keen interest, makes it possible to intensify the cognitive activity of children with mental retardation and promotes faster and more durable memorization of the material being studied.
Game techniques involving fairy-tale characters help children better learn Russian folk tales and works of art by Russian authors, because Classes are preceded by reading relevant stories and fairy tales or watching animated films. This, in turn, provides an example of correct speech, contributes to the cultivation of kindness, responsiveness, a sense of love for the Motherland, inclusion in the general system of moral values of the Russian people and the formation of an active civic position.
3. Theoretical and methodological justification for the development.
This methodological development was compiled on the basis of the Russian Federation Law “On Education”, taking into account the goals and objectives of the main educational program of preschool education, the needs and capabilities of preschool students. It defines correctional tasks, main areas of work, conditions and means.
A summary of correctional and developmental activities, presented in a methodological development, compiled taking into account the methodological recommendations of S.G. Shevchenko (Preparing children with mental retardation for school. - book 1.2. - M.: School Press, 2004, a set of methodological manuals by I. A. Morozova, M. A. Pushkareva on working with children with mental retardation. - M.: Mozaika-Sintez, 2009).
This methodological development proposes correctional and developmental activities for the development of speech (phonemic) perception and preparation for literacy in children 5-7 years old with mental retardation.
The proposed outline of the educational work is based on the basic principles of didactics:
- Development principle.
- The principle of a systems approach.
- The principle of complexity.
- The principle of the activity approach.
- The principle of psychological comfort.
- The principle of the connection of speech with other aspects of mental development.
- The principle of systematicity and concentricity.
- The principle of the orienting function of knowledge.
- Maximum utilization principle.
- The principle of sequential transition.
- An important place is occupied by such didactic principles as: visibility, accessibility, consciousness, individual approach, etc.
The methodological development is intended for teachers-defectologists, teachers of compensatory groups, parents when working with children who have difficulties in mastering educational material in the process of preparing for school, and can also be used by speech therapists in eliminating general speech underdevelopment in children.
3. Goals and objectives.
Goals
methodological development:
- create conditions for increasing the level of mental development of a child with mental retardation (intellectual, emotional, social) in correctional and developmental activities for the development of speech (phonemic) perception in preparation for schooling, leveling their speech and psychophysical development, comprehensive harmonious development;
- preventing possible difficulties in mastering the public school curriculum due to the delayed mental development of older preschoolers, and ensuring equal starting opportunities for pupils when entering school;
- implementation of timely and complete personal development, ensuring emotional well-being through the integration of educational content and the organization of interaction between subjects of the educational process.
In correctional development activities (CD) for the development of speech (phonemic) perception and preparation for learning to read and write, the following correctional tasks
:
- clarification and enrichment of children's vocabulary in connection with the expansion of direct impressions of the world around them;
- development of coherent speech: formation and improvement of purposefulness and coherence of statements, accuracy and variety of words used, grammatical correctness of sentence construction, intelligibility and expressiveness of speech;
- formation in children of an orientation towards the sound side of speech, development of the ability to listen attentively to the sound of a word, recognize and isolate individual sounds and sound complexes from it, distinguish sounds that are similar in sound and pronunciation;
- improving sensory experience in the field of the Russian language: developing the child’s ability, based on his own sensory experience, to identify the essential features of the two main groups of sounds of the Russian language - vowels and consonants;
- the formation of techniques of mental activity necessary for the development of the ability to observe, compare, identify essential features and generalize the phenomena of language.
4. Expected results:
a) in the older group -
- children will learn to distinguish speech sounds by ear, to consistently isolate sounds from words of any syllabic structures, the spelling of which does not differ from the pronunciation;
- learn to denote vowel sounds with letters;
- will gain knowledge about two main groups of sounds - vowels and consonants;
- will learn to distinguish between vowels and consonants, based on the features of their sound and articulation;
- learn to isolate a word from a sentence.
b) in the preparatory group -
- children will learn to conduct a sound analysis of words, distinguish between vowels and consonants, hard and soft consonants;
- learn to copy words from printed text whose spelling does not differ from the pronunciation;
- learn to read syllable-by-syllable small sentences and coherent texts consisting of words with a simple syllable structure;
- learn to listen to fairy tales, poems, stories;
- answer questions based on the text, retell what you heard based on questions or illustrations.
PRACTICAL PART
- ALGORITHM OF WORK BY THE EXAMPLE OF PREPARING A PLAN-SUMMARY OF A Speech Therapy Lesson WITH A SUBGROUP OF OLDER CHILDREN “THE SOUND AND THE LETTER U. VISITING UMKA”
| Algorithm for developing a speech therapy lesson | Analysis of a speech therapy session |
|
|
| 2. Define goals classes taking into account the topics, shortcomings of speech and mental development of the contingent of the speech therapy group, the requirements of classical speech therapy as a science: |
|
| 3. Define type classes for didactic purposes. Classic approach:
| In our case, a speech therapy lesson combines: communication of new knowledge (initial study of the material), formation and consolidation of knowledge and skills (practical lesson), generalization and systematization of knowledge (repeated-generalizing lesson), thus, it is a combined type lesson. |
| 4. The didactic structure of a correctional lesson, like a lesson, includes didactic tasks. |
|
| 5. Didactic methods are selected based on the goals and objectives of the lesson, combined in such a way that the types of activities of children are changed and, thereby, a protective mode of education is implemented. | Our lesson presents all types of didactic methods. According to Lerner I. Ya. these are: 1) Information-receptive. 2) Reproductive. 3) Problematic: a) problematic presentation; b) heuristic; c) research. A change of different types of activities is provided: listening, speaking, thinking, (programmed task), games, physical exercises, etc. The type of activity is mixed (several types of activities of approximately the same duration). |
| 6. A We analyze | Children own
1) determine the presence or absence of sounds indicated by a teacher or speech therapist in a word in someone else’s and one’s own speech; ; 2) divide words into syllables 3) it is difficult for most children to compare objects, phenomena, words, to find similarities; they can find differences, but not always express them in words; 4) have difficulty mastering educational concepts and terms and are not sufficiently capable of memorizing predominantly verbal material; 5) have significant difficulties in developing educational skills (planning upcoming work; determining ways and means of achieving educational goals; monitoring activities; ability to work at a certain pace);
1) not everyone can formulate their thoughts orally; it is especially difficult to answer in a complete sentence using the words of the speech therapist’s question 2) do not always know how to listen and hear the answers of others; 3) in the dialogue they take the position of a follower, because the majority are not active enough and many find it difficult to pose and formulate questions; 4) insufficient development of voluntariness in communication and activity is observed among the entire contingent of the group;
|
| 7. We draw up | Org. moment. Introduction to the topic. Updating the basic knowledge and understanding of preschool children. Formulation of the problem. Learning new things. Consolidation. Bottom line. |
| 8. didactic material in accordance with the requirements of the program, based on the programs and methods used in speech therapy (Lalaeva, Levina, Yastrebova, Shevchenko. | Carrying out differentiated and individual approach, |
| 9. Based on the composition of the group based on the structure of the defect of the majority of students, | Isolating repeated sounds from text. Pronouncing the sound “U” in front of the mirror. Characterize them based on vision, hearing, tactile and kinetic sensations. Designated by the letter "U".. |
| 10. Correctional and educational goals can be focused, first of all, on | The lesson is designed in the form of a game-journey of the fairy-tale hero Umka the bear. Children become not observers, but active helpers of the hero. This form of organization not only implements an activity-based approach, but also contributes to the development of empathy, mutual assistance, and collectivism; develops communication skills in educational and extracurricular situations. In addition, the ability to self-control and regulate one’s behavior during classes and in society is developed. |
| 11. We select and analyze
| Basic educational terms and concepts: sound (speech - non-speech, vowel - consonant. |
| 12. The main task of a speech therapist is We clarify the tasks of individual stages of the lesson. | 1) psychological basis of speech that develops
2)impressive speech (development of perception and understanding of speech) -
3)expressive speech (development of communication skills)
The implementation of correctional and developmental goals involves the inclusion in the lesson of tasks based on several analyzers, special correctional and developmental exercises for higher mental functions: perception, attention, memory, logical thinking, emotional-volitional sphere, etc. |
| 13. We integrate various health-improving activities into the overall plan, using | Gymnastics of the speech apparatus - articulation. Breathing exercises. Physical exercise. |
| 14. We supplement the summary | We use traditional (pronunciation correction, finger gymnastics, manipulation with various objects, breathing exercises, logorhythmics, psychotherapy, etc.) |
| 15. We plan the expected results of correctional work. |
|
| 16. We are thinking about the form of reflection. | Self-esteem correction:
|
| 17. We draw up a proposed dialogue. We plan connecting links and semantic transitions from stage to stage. We think through different formulations of questions in order to eliminate stereotyped thinking and get the desired answer in an expanded form. | Here, the professionalism of the teacher in mastering teaching methods comes first:
|
| 18. On the Internet and in the classroom equipment, we select the necessary | For students with mental retardation and intellectual disabilities, the clarity of a schematic plan is most suitable, for example:
|
| We leave the opportunity to exclude 1 task from the plan if there is not enough time or include an additional task in the lesson if there is too much. |
| The activity takes on a non-standard or playful form. The game situation allows you to assimilate the material as if unnoticed by the child. The game allows you to show initiative and creativity. |
Topic: Sound and letter U. Visiting Umka.
Tasks:
- Teach children to use their voice to highlight the sound “U” in words.
- Reinforce the concept of “vowel sound”. Identification signs of a vowel sound.
- Introduce the letter “U”, learn to print the letter U, recognize it among other letters.
- Develop non-speech mental functions (attention, memory, visual and auditory perception).
- Develop gross and fine motor skills.
- Develop the ability to listen carefully to the teacher and follow instructions correctly.
Equipment: subject pictures, individual cards with images of the letter U, cards with the letter U, a drawing of the Umka bear, a cartoon Umka, snowflakes with images of letters.
| Stages | Activities of a defectologist | Children's activities |
| Stage 1 Goal: organization of children’s activities, development of non-speech mental functions (attention, memory, visual and auditory perception) | The defectologist demonstrates a fragment of the cartoon “Umka” on the interactive board for 1-2 minutes and asks questions: -Guys, tell me what cartoon are these shots from? - Umka invites us to visit, but do you know where polar bears live? Shows a picture of Umka. (See Appendix 3) | Children watch a fragment of a cartoon and answer questions. - Umka. -At the North Pole. |
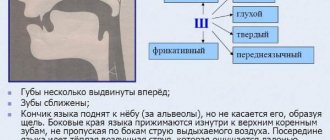
| Stage 2 Goal: familiarization with the sound “U”, development of auditory perception, consolidation of the concept of “vowel sound” | Musical accompaniment sounds (blizzard) -You and I ended up at the North Pole. It is very cold here, a strong wind blows and howls. How can we show a blizzard with our voice? The characteristics of the sound “U” are given, and the articulation (position of the lips, tongue, air passage) is specified. | Listening to music Oooh Observe the correct articulation of the sound U, pronounce it in chorus and individually. |
| Stage 3 Goal: development of correct speech breathing gymnastics “Let’s warm our hands.” | -It’s so cold at the North Pole, let’s warm our hands and blow on them. | Perform appropriate movements with breathing. |
| Stage 4 Goal: highlighting the sound “U” against the background of sounds, developing auditory attention. Stomp-slam game. | The defectologist explains. — It’s very cold at the North Pole, so to avoid freezing we’ll play the game “Stomp and Slam.” If you hear the sound “U”, clap your hands, if not, stomp. (a, y, m, p, y, s, y, v, t, y). | The children are listening. |
| Stage 5 Goal: isolating the sound “U” from words. Game "Catch a Fish". | -Guys, in the North polar bears are fishing (showing a fragment from the cartoon). Umka wants to play with you. You have to use a fishing rod to catch a fish, look. what picture is drawn, and determine whether the sound “U” is in the word or not. | Children listen and watch. They catch fish and determine the presence of the sound U in the names of the pictures. |
| Stage 6 Goal: familiarization with the letter “U”, development of operations of visual analysis and synthesis, visual-motor coordination, tactile sensations. Phys. Minute "Bear". | The defectologist demonstrates the letter “U”. -Convenient letter! What's convenient about it is What can you do with a letter? Hang up your coat! -Guys, let's teach Umka the letter “U”, his name starts with this letter. | The children look carefully. Memorize a poem. Children draw the letter “U” with their fingers on trays with semolina. |
| Stage 7. Goal: to develop gross and fine motor skills. Phys. Minute "Bear". | The speech pathologist reads the text and performs the movements together with the children. Raise your paws bear Bear's paws down Teddy bear, Teddy bear, spin around And then touch the ground And rub your tummy One, two, three - one, two, three! | Children perform exercises in accordance with the words and the model. |
| Stage 8 Goal: recognition of the letter “U” among other letters, development of attentiveness. Game "Find the snowflakes" | The defectologist explains the task. — There is a lot of snow in the north, look how many snowflakes there are. There are letters written on the back of the snowflakes, find snowflakes with the letter “U”. And we will see with Umka who is the most attentive. The defectologist notes the most attentive ones. | Children listen carefully and complete the task. |
| Stage 9 Goal: summarizing the material studied in class. | -Children, it’s time for us to return to kindergarten. Umka has prepared gifts for us, this is a picture with the letter “U” that needs to be colored. And also a picture with Umka | Children receive cards with a picture of the letter Y, which they need to color. Picture with Umka. |